In this client alert, we outline a number of significant UK and international tax developments of recent weeks and months, many of which will continue to take shape as we move forward into 2022.
In the UK, domestic tax policy looks set to play as important a role as ever as the government continues to walk the tightrope of seeking to stimulate economic activity and investment, whilst raising much needed revenue. Forecasters have predicted strong economic growth over 2022, but this is against the backdrop of record pandemic borrowing, a drop in tax revenue figures for 2020/2021, high inflation and expected interest rate rises (of course exacerbating the government’s cost of borrowing). Many will find themselves wondering if the current government will be able to hold out on all aspects of the “triple tax lock” pledge to not raise income tax, National Insurance contributions or VAT until 2024 – of course already side-lined in relation to National Insurance contributions which are due to increase by 1.25% from April 2022.
In the international tax arena, 2022 promises to be a seminal, perhaps “make or break”, year. The OECD’s BEPS 2.0 project is in full motion, at least as regards Pillar II in relation to which model rules were published in a flurry of activity in December 2021. With a scheduled 2023 effective date, some degree of turmoil looks inevitable as numerous stakeholders get to grips with the finer details of local implementation – and that’s before we even begin to understand the interplay with US domestic tax policy and reform. Pillar I proposals on the other hand would appear to be considerably less advanced and so far less certain to succeed, although model rules for domestic implementation are still expected in early 2022.
In any event, we expect to see the UK government continue to stake the UK’s claim to be “open for business”, with significant measures in the asset management and investment funds sector in particular which seek to enable the UK to compete with other jurisdictions and bolster the financial services components of the UK economy – as analysed further below.
We hope that you find this alert useful. Please do not hesitate to contact us with any questions or requests for further information.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist with any questions you may have regarding these developments. For further information, please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work, any member of the Tax Practice Group, or the authors in London:
Sandy Bhogal (+44 (0) 20 7071 4266, sbhogal@gibsondunn.com)
Benjamin Fryer (+44 (0) 20 7071 4232, bfryer@gibsondunn.com)
Bridget English (+44 (0) 20 7071 4228, benglish@gibsondunn.com)
James Chandler (+44 (0) 20 7071 4211, jchandler@gibsondunn.com)
William Inchbald (+44 (0) 20 7071 4264, winchbald@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
For the fourth consecutive year, and complementing the publication of Gibson Dunn’s upcoming tenth annual U.S. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Outlook and Review, we offer this separate International Outlook and Review. As every year, this Outlook and Review provides an overview of past and upcoming developments related to global privacy and cybersecurity laws.
2021 saw an increasing number of data protection bills and laws passed across numerous international jurisdictions. Notably, China, the UAE, Brazil, Russia and Switzerland, among others, passed new laws, amendments or implementing regulations paving the way for a new round of significant data privacy regimes. It is expected that international authorities will make full use of their new powers in order to apply and enforce their respective data protection legislation in the near future.
In the European Union (“EU”), there were a significant number of developments in the evolution of the data protection and cybersecurity landscape:
- In the aftermath of the Schrems II ruling, the EDPB adopted a series of Recommendations and Guidelines in order to clarify the regime and rules applicable to data transfers to the U.S. and other jurisdictions that do not benefit from an adequacy decision, as well as on the territorial scope of the General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”). Furthermore, the European Commission adopted new sets of Standard Contract Clauses (“SCCs”) that must be used as of 27 September 2021 for new contractual arrangements and apply to existing contractual arrangements by 27 December 2022.
- Further to the three-year review of the e-Privacy Regulation Bill by the EU Member States, negotiations between the Council, the European Parliament and the European Commission commenced for its finalisation and adoption, which is due to replace the 20-year-old e-Privacy Directive.
- EU lawmakers have also made progress on the adoption of the revised Network Infrastructure Security Directive (“NIS2 Directive”), which is due to replace the current NIS Directive by expanding its scope and seeking to harmonise further this sector across all levels (including sanctions).
- EU supervisory authorities continued to apply and enforce the GDPR vigorously, imposing record-setting fines and making full use of EU law instruments to achieve a harmonised approach.
We cover these topics and many more in this year’s International Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Outlook and Review.
I. European Union
A. International data transfers
1. Aftermath of the Schrems II Ruling
As we indicated in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, on 16 July 2020, the so-called Schrems II ruling of the Court of Justice of the EU (“CJEU”) struck down the EU-U.S. Privacy Shield, which numerous companies had relied upon to transfer personal data from the EU to the U.S. Despite this, the CJEU also ruled that the SCCs approved by the European Commission, another mechanism used by an even higher number of companies to transfer personal data outside of the EU, remained valid subject to certain caveats.[1]
Further to the Schrems II ruling, organisations transferring personal data to a third country must verify, on a case-by-case basis, if there is anything in the law and practice of the third country which may impinge on the appropriate safeguards of the transfer tools (a “Risk Assessment”). If the law and practice of the third country do impinge the transfer tools safeguards, the organisations are required to implement supplementary measures to ensure an equivalent level of protection.
In this respect, the European Data Protection Board (“EDPB”) issued important new guidance on international transfers of personal data, namely:
- Recommendations 01/2020 on measures that supplement transfer tools to ensure compliance with the EU level of protection of personal data,[2] which provide guidance to help organisations conduct their Risk Assessment and determine which supplementary measures should be implemented;
- Recommendations 02/2020 on the European Essential Guarantees for surveillance measures adopted by the EDPB,[3] which clarify the elements that organisations are required to take into account when assessing the law of a third country dealing with access to data by public authorities for the purpose of surveillance.
In parallel, on 4 June 2021, the European Commission adopted new SCCs to cover data transfers among controllers and processors from the European Economic Area (“EEA”) to third countries not recognised by the European Commission as ensuring an adequate level of protection for personal data.[4] These new set of SCCs replace the old SCCs adopted in 2001 and 2010 under the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC (“e-Privacy Directive”), and take into account the conclusions of the CJEU in Schrems II. Since 27 September 2021, it is no longer possible to execute the old SCCs and, as of 27 December 2022, existing contracts will need to have been replaced or amended to incorporate the new SCCs.
The EDPB also adopted the Guidelines 04/2021 on codes of conduct as tools for transfers[5], the Guidelines 05/2021 on the Interplay between the application of Article 3 and the provisions on international transfers as per Chapter V of the GDPR[6], each for public consultation. The latter Guidelines aim to clarify the territorial scope of the GDPR and the provisions on international transfers, to assist controllers and processors to determine whether a particular data processing activity falls directly under the GDPR, or should be covered by a legal data transfer mechanism to provide adequate safeguards.
In light of these developments, several Member State supervisory authorities issued statements and guidance in relation to matters concerning international data transfers:[7]
- the Austrian Data Protection Authority ruled that the provider of a website using Google Analytics was illegally transferring data to the U.S. considering that Google, as an electronic communication service provider, is subject to U.S. surveillance and that the safeguards provided were insufficient to prevent U.S. intelligence from accessing the data;
- the Italian Garante[8] fined a Milanese university €200,000 in relation to the transfer of personal data to the U.S. on the basis of the SCCs due to the lack of Risk Assessment and insufficient encryption measures;
- the Belgian Conseil d’Etat[9] decided not to suspend a transfer of personal data to the U.S. since it could not exclude that encryption with separate key management can constitute a sufficient supplementary measure in this context;
- in Germany, the Bavarian BayLDA[10] considered a data transfer as being unlawful due to the lack of Risk Assessment;
- the Portuguese CNPD[11] ordered a controller to suspend within 12 hours any international transfers to the U.S. or other third countries without an adequate level of protection; and
- the French Conseil d’Etat[12] decided not to suspend transfers of personal data to the U.S. in view of the safeguards implemented by the controller.
2. Adequacy decisions
On 28 June 2021, the European Commission adopted two adequacy decisions for the United Kingdom,[13] under the GDPR and the Law Enforcement Directive. These decisions will allow personal data to flow freely from the EU to the UK without the need for additional tools or authorisations. The adequacy findings include a ‘sunset clause’, which means that the decisions will automatically expire four years after their entry into force. It is likely that the decisions will only be renewed if the UK continues to ensure an adequate level of data protection of personal data.
On 17 December 2021, the European Commission also adopted the South Korea adequacy decision,[14] making it possible for personal data to be transferred safely from the EU to the Republic of Korea. With this decision, the Commission guarantees that the South Korean legislation on data protection, combined with the additional safeguards implemented in the country, ensure an adequate level of protection for EU data subjects’ personal data.
B. Proposed E-Privacy Regulation and Cookies and Telemarketing Enforcement
As we indicated was likely in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, the e-Privacy Regulation, which was proposed by the European Commission in 2017 to update laws applicable to telecoms, digital and online data processing, was not adopted in 2021.
In 2021, the Council, the European Parliament and the European Commission initiated joint discussions for the adoption of the e-Privacy Regulation. Although the co-legislators failed to find common ground, the situation does not look as dim as in 2020 and 2021. Legislators and industry experts are confident that the final Regulation will be adopted in 2022 or 2023.[15]
Relatedly, European e-privacy laws have continued to be the object of enforcement by EU data protection authorities. As explained further in Section I.E below, in 2021, the Luxemburg, French and Spanish supervisory authorities, among others, imposed significant fines on companies for e-privacy violations (e.g., setting of cookies, the use of online targeted advertising and the use of telemarketing, without consent).
C. Proposed Network Information Security (“NIS2”) Directive Proposal
As explained in past iterations of the International Outlook and Review, the Network and Information Security (“NIS”) Directive, the first piece of EU-wide legislation on cybersecurity, had the specific aim of achieving a high common level of cybersecurity across the Member States.
While the NIS Directive increased the Member States’ cybersecurity capabilities, its implementation proved difficult and resulted in a patchwork of national legislations across the EU. To respond to the growth of digitalisation and cyber-attacks, on 16 December 2020, the European Commission submitted the NIS2 Directive Proposal to replace the NIS Directive. The NIS2 Directive Proposal aims to strengthen the security requirements, address the security of supply chains, streamline reporting obligations and introduce more stringent supervisory measures and stricter enforcement requirements, including harmonised sanctions across the EU. The NIS2 Directive Proposal will also have a broader scope of application, effectively requiring more entities and sectors to take the prescribed measures in relation to cybersecurity.
Further to the Council discussions, the European Parliament adopted its report on 28 October 2021, leading to interinstitutional negotiations with the European Commission.[16] It is expected that the NIS2 Directive will be effectively adopted in 2022 or in 2023.
D. EDPB Guidance
Aside from its guidance on international data transfers, the EDPB issued Guidelines on various topics, including:
- Guidelines 06/2020 on the interplay between the second Payment Services Directive (PSD2) and the GDPR,[17] which notably address lawful grounds for further processing under the PSD2;
- Guidelines 07/2020 on the concepts of controller and processor in the GDPR,[18] which aim to clarify these concepts and the consequences of attributing these roles to entities that collect and process personal data;
- Guidelines 08/2020 on the targeting of social media users,[19] which provide an overview of the main parties and the targeting mechanisms involved in such processing, as well as the related GDPR requirements;
- Guidelines 10/2020 on restrictions under Article 23 GDPR,[20] which address the grounds for restricting data subjects’ rights, including for national security and public defence, and for objectives of general public interest; and
- Guidelines 01/2021 on Examples regarding Data Breach Notification,[21]which aim to assist data controllers in determining how to handle data breaches and what factors to consider during a risk assessment.
The EDPB also issued its Strategy 2021-2023,[22] as well as its Work Program 2021/2022,[23] notably announcing awaited Guidelines on, inter alia, legitimate interest, blockchain and the calculation of administrative fines.
E. Enforcement by Supervisory Authorities
In 2021, the GDPR and the e-Privacy Directive continued to be applied and enforced by EU Member State supervisory authorities. As explained in previous issues of our Outlook and Review, the GDPR put in place a one-stop shop mechanism to enable lead supervisory authorities of one Member State to adopt decisions and impose fines for EU-wide GDPR violations resulting from cross-border data processing activities.
On 15 June 2021, the CJEU generally upheld and confirmed the status of lead supervisory authorities as “sole interlocutors” of controllers and processors that process personal data cross-border within the EU.[24] Other supervisory authorities cannot therefore initiate any action, administrative or in court, that runs in parallel to that of the lead supervisory authority, except in exceptional circumstances foreseen by the GDPR (e.g., in urgency procedures under Article 66).
The GDPR’s jurisdictional rules were also addressed in another matter before the supervisory authority in France. In 2016, the French data protection authority (“CNIL”) had initiated investigations against the EU operations of a U.S. tech company regarding particularly its data sharing activities with the U.S. parent company. Among the alleged grievances being investigated, the CNIL considered that such data sharing was undertaken without appropriate legal basis. However, one of the key procedural issues being disputed was to determine whether the CNIL still had jurisdiction over a case initiated prior to the GDPR, but which continued after the GDPR became applicable in 2018 and after the U.S. tech company set up an EU establishment in charge of its processing activities in the same year. The CNIL eventually held in 2021 that it did not have jurisdiction on this case and did not sanction the U.S. tech company.
On 16 July 2021, the Luxembourg CNPD imposed a record-breaking €746 million fine on an e-commerce and online services corporation and required the company to remedy the instances of non-compliance within six months, with a penalty of €746,000 per day of delay.[25] According to the plaintiff, La Quadrature du Net, the company was processing personal data for targeted advertising purposes without a valid legal basis. The sanction has since been partially suspended by a local administrative court.[26]
On 2 September 2021, the Irish Data Protection Commission (“DPC”) imposed a fine of €225 million on online messaging service provider for allegedly failing to meet its transparency obligations under the GDPR. Given that the company’s data processing activities were cross-border, the DPC’s draft decision was reviewed by other relevant supervisory authorities, as required by the cooperation and consistency mechanism under the GDPR.
On 31 December 2021, the French CNIL imposed a €150 million fine on Google (€90 million for Google LLC and €60 million for Google Ireland Ltd), as well as a €60 million fine on a social network service[27], on the basis of the e-Privacy Directive, for allegedly not enabling users to refuse cookies as easily as to accept them. The CNIL also summoned the companies, in both cases, to bring their practices in compliance with the e-Privacy Directive within three months, with a penalty of €100,000 per day of delay.
On 25 May 2021, the German Competition Authority (“Bundeskartellamt”) opened proceedings under Germany’s 2021 GWB Digitalization Act against Google Germany GmbH, Google Ireland Ltd., Dublin, Ireland, and Alphabet Inc., USA, reviewing Google’s data processing terms and cross-service data processing. Subsequently, on 30 December 2021, it took a decision determining that Google has a paramount significance for competition across markets which is a prerequisite for the further investigation under the new law. Of note, the German Bundeskartellamt is not a supervisory authority under the GDPR, but is an active enforcer in the digital economy – including at the interface to the processing of personal data under the GDPR.
In addition, throughout 2021, several European Supervisory Authorities issued fines around €5-10 million, including for unlawful employee surveillance[28] or marketing calls[29] and lack of valid consent for the processing of personal data.[30]
II. Developments in Other European Jurisdictions: UK, Switzerland, Russia and Turkey
A. UK
In the UK, the Information Commissioner’s Office (“ICO”) has continued to undertake efforts to enforce the UK GDPR and the Data Protection Act 2018. Notably, in 2021, it announced its provisional intent to fine Clearview AI, Inc. £17 million[31] for its processing of biometric data scraped from the internet, and issued a provisional notice to stop further processing and delete the personal data of individuals in the UK. Throughout the year, the ICO also imposed fines of a lower amount to corporations and local businesses for their failure to apply data protection and e-privacy laws.[32]
In addition to its enforcement action, the UK ICO also undertook efforts to complete its regulatory framework post-Brexit. The most important development relates to the publication of draft international data transfer agreement (“IDTA”) and guidance, which were subject to consultation and are intended to replace the EU’s legacy SCCs.[33]
B. Switzerland
As we indicated in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, on 25 September 2020, the Swiss Parliament adopted the revised version of the Federal Act on Data Protection 1992 (“Revised FADP”). In anticipation of its upcoming entry into law in the second half of 2022, on 5 March 2021, the Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner (“FDPIC”) published guidance on how the private sector and federal authorities needed to adapt their processing activities to comply with the new provisions of the Revised FADP. In particular, the guidance covers the right to data portability, codes of conduct, records of processing activities and cross-border transfers and extended requirements around providing information on data processing and transparency under the Revised FADP.[34]
On 23 June 2021, the Swiss Federal Council also released a draft revised Ordinance on the Federal Data Protection Act for public consultation following the adoption of the Revised FADP. In particular, the Council highlighted that the revisions to the Ordinance include minimum data security requirements, the modalities of the duty to inform data subjects, the right of access, data breach notification requirements, and exceptions to the obligation to keep a record of data processing activities for companies with fewer than 250 employees. Furthermore, the draft Ordinance specifies the criteria which the Council must take into account in its assessment of the adequacy of transfers of personal data to third countries, and includes a draft list of 34 countries which are considered to provide an adequate level of protection.[35]
With regard to data transfers, the FDPIC published a guide on 18 June 2021 to allow companies to review the admissibility of data transfers to third countries in accordance with the Federal Act on Data Protection 1992. The guide provides a flowchart detailing the actions required by organisations to ensure data transfers are made in compliance with the Act and, notably, elaborates on the legal requirement that apply to transfers to third countries that do not appear on the FDPIC list of adequate countries.[36]
Furthermore, on 27 August 2021, the FDPIC announced that the new SCCs adopted by the European Commission on 4 June 2021 for data transfers to third countries were also valid under Swiss law. The FDPIC recalled that the Commission’s SCCs may be used by data exporters, provided that the necessary adaptations and amendments be made for use under Swiss data protection law (i.e., replacing references to the EU with references to Switzerland). In addition, in line with the timeline in the EU, the FDPIC confirmed that the European Commission’s old SCCs could still be entered into until 27 September 2021 and existing agreements entered into under the old SCCs may still be used during a transitional period until 31 December 2022.[37]
C. Russia
As we indicated in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, Russia undertook a number of legislative modifications in 2021 to enhance and complete its data protection regime, notably in terms of increasing applicable fines.
In the same vein, Russia adopted a new federal law in 2021 ‘On Amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses’, which increased the amounts of administrative fines prescribed in the Code of Administrative Offenses against the Federal Law On Personal Data. The amendments do not touch upon the highest fines for breaching the data localisation requirement, but do increase the administrative fines for repeated offenses (i.e., offences that occur within one year from the date the previous violation was enforced). Recidivism concerning the localisation requirement may lead to fines between RUB 6,000,000 and 18,000, 000 (approximately USD 80,000 to 240,000) on companies, and responsible managers may face fines between RUB 500,000 and 800,000 (approximately USD 6,600 to 10,500).[38]
In addition, the Russian Federal Service for the Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Communications (“Roskomnadzor”) and the Russian Parliament (“Duma”) have continued to undertake efforts to protect Russian consumers and citizens. First, on 29 March 2021, the Ministry of Digital Development published draft amendments to the Federal Law of 27 July 2006 No. 152-FZ on Personal Data in order to require telecom operators to obtain the consent of subscribers prior to the sale of their personal data for telemarketing purposes.[39]
On 1 July 2021, the Roskomnadzor also announced that it had launched an online service allowing companies to obtain and record consent to the processing of personal data collected directly from the data subject. The Roskomnadzor claims that the template service will enable operators to meet the consent requirements following the entry into force of the amendments to the Federal Law on Personal Data in March 2021. Furthermore, the Roskomnadzor noted that the template may be customised to the specific activities of the operator, and that data subjects may record their preferences as to how their personal data may be processed and further distributed to third parties.
Finally, on 10 November 2021, the Duma registered a bill on ‘Amendments to Article 14.8 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offences’ in order to prohibit companies from forcing consumers to provide personal data in cases where such data is not necessary to complete the transaction and is not provided for by legislation.[40]
D. Turkey
In 2021, the Turkish data protection authority (“KVKK”) proceeded with its significant activity in providing guidance on the application of the Turkish Data Protection Act. Notably, on 20 October 2021, it issued guidance on the right to be forgotten (“RTBF”) in respect of search engines. The guidance follows up on the KVKK Board Decision 2020/481 regarding the requests of individuals to remove names, surnames and the results of searches made through search engines from the index, and it aims to clarify issues relating to the exercise of the RTBF. Among other points, it indicates that the individuals may exercise the RTBF either by making a request to the data controller (search engine) or by complaining to the KVKK.[41]
Finally, throughout 2021, the KVKK continued with its enforcement of the Turkish Data Protection Act. For example, on 21 June 2021, it imposed a fine of TRY 800,000 (approx. €77,390) on an e-commerce site for data security and breach notification failures under the Turkish Data Protection Act. In particular, the KVKK noted that the investigation was triggered by a complaint that access to the information of third-party companies was provided through the customer service panel on the e-commerce site.[42] On 3 September 2021, the KVKK published a summary of review of a decision concerning an online messaging service provider, in which it imposed a fine of TRY 1,950,000 (approx. €195,000) for allegedly failing to take necessary technical and administrative measures to ensure data security pursuant to the Act.[43]
III. Developments in Asia-Pacific
A. Australia
As explained in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, the Australian government is currently undertaking a wholesale review of the Privacy Act 1988 with a view to implementing significant reforms to the country’s privacy regime. In October 2021, the Attorney-General’s Department released a discussion paper considering the items raised in the issues paper published in October 2020 (and referred to in the 2021 International Outlook and Review) and has sought further feedback on the proposed reforms.[44] Submissions on the discussion paper closed on 10 January 2022, and those submissions will now form the basis of a final report to be submitted to government.
The discussion paper proposes wide-ranging reforms which would align Australia’s privacy regime more closely to global equivalents, such as the GDPR, in order to reflect recent developments in the digital economy, including to expand the definition of personal information, impose stricter anonymisation requirements on organisations subject to the laws, increase maximum civil penalties for non-compliance, strengthen the rights of individuals to object to the collection and use of disclosure of their information or require its erasure and to modify the framework for international data transfers.
This review has been conducted concurrently with a public consultation process on the exposure draft of the Privacy Legislation Amendment (Enhancing Online Privacy and Other Measures) Bill 2021 (“Online Privacy Bill”), which was released on 25 October 2021.[45] The Online Privacy Bill proposes to establish a binding privacy code for social media platforms, data brokerage services and large online platforms, expand the enforcement options available to the regulator and significantly broaden the extra-territorial reach of the Privacy Act 1988 to apply to acts performed outside Australia by foreign organisations carrying on business in Australia. Submissions on the Online Privacy Bill closed on 6 December 2021 and those submissions will inform further development of the Online Privacy Bill before its introduction to Parliament in 2022.
In addition to the ongoing review of the Privacy Act 1988 and the Online Privacy Bill, the US and Australian governments signed an agreement on 15 December 2021 to facilitate access to electronic data for investigations authorised by the Clarifying Lawful Overseas Use of Data (CLOUD) Act of 2018.[46] This agreement allows authorities from each country to access certain data directly from providers operating in the others’ jurisdiction to mitigate, detect and investigate serious crimes, including ransomware attacks and terrorism, as well as crimes that sabotage critical infrastructure over the internet. The agreement will undergo parliamentary and congressional review procedures in 2022 and is intended to replace the mutual legal assistance mechanism currently used to access data from such providers, which relevant authorities perceive as too slow and awkward to fulfil its intended purpose.[47]
B. China
1. Passage of the Personal Information Protection Law
On 20 August 2021, the Standing Committee of China’s National People’s Congress passed the Personal Information Protection Law (“PIPL”), which took effect on 1 November 2021.[48] The PIPL applies to “personal information processing entities (‘PIPEs’)”, defined as “an organisation or individual that independently determines the purposes and means for processing of personal information”. The PIPL defines “personal information” broadly as “various types of electronic or otherwise recorded information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person”, excluding anonymised information, and defines “processing” as “the collection, storage, use, refining, transmission, provision, public disclosure or deletion of personal information” (PIPL Article 4).
The PIPL shares many similarities with the EU’s GDPR, including its extraterritorial reach, restrictions on data transfer, compliance obligations and sanctions for non-compliance, amongst others. The PIPL raises some concerns for companies that conduct business in China, even where such companies’ data processing activities take place outside of China, and the consequences for failing to comply could potentially include monetary penalties and companies being placed on a government blacklist.
The PIPL applies to cross-border transmission of personal information and applies extraterritorially. Where PIPEs transmit personal information to entities outside China, they must inform the data subjects of the transfer, obtain their specific consent to the transfer and ensure that the data recipients satisfy standards of personal information protection similar to those in the PIPL. The PIPL applies to organisations operating in China, as well as to foreign organisations and individuals processing personal information outside China in any one of the following circumstances: (1) the organisation collects and processes personal data for the purpose of providing products or services to natural persons in China; (2) the data will be used in analysing and evaluating the behaviour of natural persons in China; or (3) under other unspecified “circumstances stipulated by laws and administrative regulations”. This is an important similarity between the PIPL and GDPR, as the GDPR’s data protection obligations apply to non-EU data controllers and processors that track, analyse and handle data from visitors within the EU. Similarly, under the PIPL, a foreign receiving party must comply with the PIPL’s standard of personal information protection if it handles personal information from natural persons located in China.
The PIPL gives the Chinese government broad authority in processing personal information. State organisations may process personal information to fulfil statutory duties, but may not process the data in a way that exceeds the scope necessary to fulfil these statutory duties. Personal information processed by state organisations must be stored within China.
The PIPL establishes guiding principles on protection of personal information. According to the PIPL, processing of personal information should have a “clear and reasonable purpose” and should be directly related to that purpose. The PIPL requires that the collection of personal information be minimised and not excessive, and that PIPEs ensure the security of personal information. To that end, the PIPL imposes a number of compliance obligations on PIPEs, including requiring PIPEs to establish policies and procedures on personal information protection, implement technological solutions to ensure data security and carry out risk assessments prior to engaging in certain processing activities.
The PIPL adopts a risk-based approach, imposing heightened compliance obligations in specified high-risk scenarios. For instance, PIPEs whose processing volume exceeds a yet-to-be-specified threshold must designate a personal information protection officer responsible for supervising the processing of personal data. PIPEs operating “internet platforms” that have a “very large” number of users must engage an external, independent entity to monitor compliance with personal information protection obligations, and regularly publish “social responsibility reports” on the status of their personal information protection efforts. The law mandates additional protections for “sensitive personal information”, broadly defined as personal information that, once disclosed or used in an illegal manner, could infringe on the personal dignity of natural persons or harm persons or property. “Sensitive personal information” includes biometrics, religious information, special status, medical information, financial account, location information and personal information of minors under the age of 14. When processing “sensitive personal information”, according to the PIPL, PIPEs must only use information necessary to achieve the specified purpose of the collection, adopt strict protective measures and obtain the data subjects’ specific consent.
The PIPL creates legal rights for data subjects. According to the new law, PIPEs may process personal information only after obtaining fully informed consent in a voluntary and explicit statement, although the law does not provide additional details regarding the required format of this consent. The law also sets forth certain situations where obtaining consent is unnecessary, including where necessary to fulfil statutory duties and responsibilities or statutory obligations, or when handling personal information within a reasonable scope to implement news reporting, public opinion supervision and other such activities for the public interest. Where consent is required, PIPEs should obtain a new consent where it changes the purpose or method of personal information processing after the initial collection. The law also requires PIPEs to provide a convenient way for individuals to withdraw their consent, and mandates that PIPEs keep the personal information only for the shortest period of time necessary to achieve the original purpose of the collection. If PIPEs use computer algorithms to engage in “automated decision making” based on individuals’ data, the PIPEs are required to be transparent and fair in the decision making, and are prohibited from using automated decision making to engaging in “unreasonably discriminatory” pricing practices. “Automated decision-making” is defined as the activity of using computer programs to automatically analyse or assess personal behaviours, habits, interests, hobbies, financial, health, credit or other status, and make decisions based thereupon. When individuals’ rights are significantly impacted by PIPEs’ automated decision making, individuals can demand PIPEs to explain the decision making and decline automated decision making.
The PIPL creates penalties for organisations that fail to fulfil their obligations to protect personal information. These penalties include disgorgement of profits and provisional suspension or termination of electronic applications used by PIPEs to conduct the unlawful collection or processing. Companies and individuals may be subject to a fine of not more than 1 million RMB (approximately $154,378.20) where they fail to remediate conduct found to be in violation of the PIPL, with responsible individuals subject to fines of 10,000 to 100,000 RMB (approximately $1,544 to $15,438). Companies and responsible individuals face particularly stringent penalties where the violations are “grave”, a term left undefined in the statute. In these cases, the PIPL allows for fines of up to 50 million RMB (approximately $7,719,027) or 5% of annual revenue, although the PIPL does not specify which parameter serves as the upper limit for the fines. Authorities may also suspend the offending business activities, stop all business activities entirely or cancel all administrative or business licenses. Individuals responsible for “grave” violations may be fined between 100,000 and 1 million RMB (approximately $15,438 to $154,383), and may also be prohibited from holding certain job titles, including Director, Supervisor, high-level Manager or Personal Information Protection Officer, for a period of time. In contrast, fines for severe violations of the GDPR can be up to €20 million (approximately $23,486,300) or up to 4% of the undertaking’s total global turnover of the preceding fiscal year (whichever is higher).
For more details regarding potential issues for companies operating in China and the impact of the PIPL, please see our client alert here.
2. Draft Measures for Data Export Security Evaluations
On 29 October 2021, the Cyberspace Administration of China requested public comments on the draft Measures for Data Export Security Evaluation until 28 November 2021. The draft underscores the need to standardise data exports under the PIPL, Cybersecurity Law and Data Security Law. Under the draft, PIPEs transferring data which meets one of the following requirements outside of China are required to submit a report through the provincial Cyberspace Administration: (1) personal information and important data are generated by operators of critical information infrastructure; (2) outbound data contains important data; (3) personal information processors who have processed personal information of one million people; (4) personal information processors who have processed personal information of more than 100,000 people or sensitive personal information of more than 10,000 people abroad; or (5) other situations required by the Cyberspace Administration.
3. Regulations on the Security Protection of Critical Information Infrastructure
Following the United States’ proposal of the Cyber Incident Notification Act of 2021 and the EU’s adoption of Directive (EU) 2016/1148 on Security of Network and Information Systems in 2016, China introduced rules to protect the country from cyber-attacks on critical information systems. China’s Regulations on the Security Protection of Critical Information Infrastructure (the “Regulations”) took effect on 1 September 2021.[49]
The Regulations are a key feature of China’s Cybersecurity Law, which was implemented on 1 June 2017. The Regulations protect the security of critical information infrastructure (“CII”) and expand on the Cybersecurity Law by imposing additional compliance obligations. Article 31 of the Cybersecurity Law delegates further authority to the State Council to formulate specific security protection measures for CII. By enacting the Regulations, the State Council has broadened the definition of CII, clarified which authorities are responsible for CII protection, outlined the duties of CII operators and third parties in relation to testing / monitoring CII and established penalties for non-compliance.
The Cybersecurity Law defines CII as infrastructure from important industries, including public communication and information services, energy, transportation, water conservancy, finance, public services, e-government and other critical information infrastructure which may endanger national security, national welfare, people’s livelihoods or the public interest if data is disabled, damaged or leaked. The Regulations not only define CII as those industries identified in Article 31 of the Cybersecurity Law, but also national defence and technology industries. This includes:
- Public communications and information services;
- Energy;
- Transportation;
- Water conservancy;
- Finance;
- Public services;
- E-government;
- National defence science, technology and industry; and
- Other important network facilities and information systems that may severely threaten national security, national welfare, people’s livelihood or the public interest if disabled, damaged or leaked.
The Regulations impose obligations on CII operators (“CIIOs”), including, but not limited to: (1) establishing a security management department; (2) conducting background checks on key personnel with the assistance of police and national security agencies; (3) conducting an annual risk audit and assessing security risks; (4) reporting cyber incidents or threats to relevant authorities (including the Cyberspace Administration and the State Council); (5) conducting cybersecurity reviews when the network products and services a CIIO purchases may influence national security; and (6) reporting any corporate activity that may impact cyber security, including mergers or dissolutions (Regulations Articles 15, 19, 21).
The Regulations prohibit any entity or individual from illegally invading, interfering with or destroying CII and carrying out loophole detection or permeability tests on CII (Regulations Article 5). Additionally, no entity or individual may carry out vulnerability monitoring, penetration testing or other such activities on CII that may influence or endanger the security of CII, unless such entity or individual has received approval from the national cyberspace and informatisation department, the State Council public security department or the relevant protection work department or operator (Regulations Article 31). If an entity or individual chooses to carry out such activities on basic telecommunications networks, it must report such activity in advance to the State Council department in charge of telecommunications (Regulations Article 31).
Under the Regulations, companies may face monetary fines of up to RMB 1 million (USD 155,000) for serious violations, and key individuals may face fines up to RMB 100,000 (US 15,000) (Regulations Articles 39, 40, 41, 42 and 43).
The Regulations will impact network operators as more network operators may be deemed CIIOs and more compliance obligations will likely be imposed by competent industry regulators. Network operators in critical industries should remain alert to their industry regulators and ensure their compliance programs align with the Regulations and the Cybersecurity Law. Global clients that operate in China in the identified industries and sectors should be aware of these requirements and alert to the prospect that they may be designed as CIIOs. Further, firms in the business of carrying out vulnerability monitoring or penetration testing on businesses in China operating in the industries outlined above should be conscious of the prospect that their clients could be considered CIIOs, and should ensure that they are seeking assurances from their clients that they are not CIIOs before undertaking this work. Alternatively, these firms should be prepared for the need to seek approval for this work from the national cyberspace and informatisation department, the State Council public security department or the relevant protection work department or operator.
4. Draft Regulations on Algorithmic Recommendation Technology
Chinese authorities announced the Internet Information Service Algorithmic Recommendation Management Provisions, which will come into force on 1 March 2022.[50] These regulations apply to technology such as personalised recommendations, search filters and any algorithms that provide content to users. These regulations cover various services, such as social media platforms and entertainment streaming. The regulations not only apply to the PIPL, but also the Cybersecurity Law, Data Security Law and the Internet Information Services Management Rules for the purpose of promoting national security and public interests.
C. India
As indicated in both the 2020 and 2021 International Outlook and Review, the Personal Data Protection Bill 2019 (“PDP Bill”) was introduced in Indian Parliament on 11 December 2019 and subsequently referred to a Joint Parliamentary Committee (“JPC”) for consideration. On 16 December 2021, after a prolonged review period, the JPC tabled its report and suggested amendments to the PDP Bill, which has not yet been enacted. The resulting report and amendments were primarily informed by the stated need to balance data-driven innovation while catering to national security demands. Some of the key recommendations include:[51]
- Expansion of the scope of the PDP Bill to cover both personal and non-personal data. The JPC suggested that consolidation of the regulatory framework in this manner was necessary in light of the impossibility to distinguish between personal and non-personal data when mass data is collected or transported.
- Preparation and implementation of data localisation policies to ensure that sensitive personal data or other critical data is stored and processed in India, and only transferred outside India with the DPA’s approval (subject to government consultation).
- Establishment of a mechanism for the formal certification of digital and IoT devices to ensure their integrity with respect to data security.
- Assigning responsibility to social media platforms for the content hosted on their platforms and requiring those platforms to set up an office in India.
- Introduction of a fixed timeline of 72 hours for breach reporting.
The JPC recommended that a 24-month transitional period should apply for implementation of the PDP Bill to allow relevant parties to update their policies, infrastructure and processes. The JPC’s report and amendments to the PDP Bill will be reviewed by the Parliament before being enacted. Until the PDP Bill is enacted, the Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules 2011 continue to govern data protection in India.
D. Indonesia
As identified in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, a draft of the Personal Data Protection Act (“PDP Bill”) was submitted to the Indonesian House of Representatives on 24 January 2020.[52] The PDP Bill consolidates the rules related to personal data protection in Indonesia and is anticipated to establish data sovereignty and security as the keystone of Indonesia’s data protection regime.[53]
On 1 September 2020, the Ministry of Communication and Information Technology of Indonesia (“Kominfo”) issued a statement claiming that the PDP Bill would be completed by mid-November 2020.[54] However, as of the date of this review, the Indonesian House of Representatives is still yet to pass the PDP Bill due to ongoing debate over the position, form and independence of the authority slated to oversee its regulation and enforcement.[55] Despite this, the expectation is that the PDP Bill will be enacted in the first quarter of 2022.
E. Hong Kong
The Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (“PDPO”), passed in 1995, is one of Asia’s longest standing data protection laws. The PDPO was amended in 2021 to combat doxxing acts which intrude on personal data privacy.
The Personal Data (Privacy) (Amendment) Bill 2021 (“PDPO Bill”) came into effect on 8 October 2021 after the Hong Kong legislature passed the legislation on 29 September 2021.[56] The PDPO Bill criminalises doxxing acts, including imprisonment for five years and fines up to HK$1 million. In addition, the PDPO Bill empowers the Office of the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data to persecute individuals for doxxing incidents and perform related criminal investigations.
F. Japan
1. APPI Amendments
As explained in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, the Parliament of Japan adopted a bill on 5 June 2020 to amend the currently applicable general data protection law, the Act on the Protection of Personal Information (“APPI”). The APPI will take force on 1 April 2022, while transitional measures for companies that share data with third parties took effect on 1 October 2021.
2. Review of EU-Japan Mutual Adequacy Agreement
On 26 October 2021, the Personal Information Protection Commission of Japan, the European Commission and other relevant authorities conducted the first review of the EU-Japan mutual adequacy arrangement effective in 2019. The Commissions will publish separate reports to conclude the review process.[57]
G. Mongolia
In 2021, the Standing Committees on Innovation and e-Policy and Legal Affairs in Mongolia opened discussions on a Draft Law on the Protection of Personal Information, which details data subject rights, requirements and responsibilities for data processors and controllers, and requirements for overseas data transfers.
H. New Zealand
The New Zealand Privacy Act 2020 (“NZ Privacy Act”) came into force on 1 December 2020, repealing and replacing an existing 1993 act. In implementing the new act, the New Zealand government sought to modernise the privacy regime in New Zealand and reflect global trends in international privacy standards and the digital economy. While the NZ Privacy Act remains less onerous than international equivalents, such as the GDPR, it nonetheless introduces significant reforms to the privacy regime in the country, such as mandatory data breach reporting, broader investigative and enforcement powers for the regulator and new criminal offences and penalties, including fines of up to NZ$10,000. Pursuant to the changes, the NZ Privacy Act applies extraterritorially to overseas organisations carrying on business in New Zealand and which hold information about New Zealand individuals.[58]
Despite these recent reforms, the Office of the Privacy Commissioner of New Zealand recommended in 2021 that “further changes are desirable” in response to fast-changing technologies. The proposed changes include the introduction of a right of personal information portability and a right to be forgotten, protection against the risk of re-identification from de-identified information, limitation of harm caused by automated decision making algorithms, increased civil penalties for non-compliance and expanded powers of the regulator to require compliance reporting by organisations subject to the NZ Privacy Act.[59]
I. Philippines
On 4 February 2021, the National Privacy Commission of the Philippines (“NPC”) announced the approval of a substitute bill to amend the Data Privacy Act of 2012 (“PDPA”). The proposed bill seeks to implement wide-ranging reforms to the Philippines privacy regime, including to redefine “sensitive personal information” to include biometric and genetic data, clarify the extra-territorial application of the PDPA (including in circumstances where an organisation offers goods or services, or monitors the behaviour of individuals within the Philippines or where it has a link with the country), render performance of a contract as a lawful basis for processing of personal information, allow controllers outside of the Philippines to authorise processors within the Philippines to notify the Commissioner of a data breach, widen the enforcement powers of the regulator and modify the criminal penalties for non-compliance.[60]
J. Singapore
As explained in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, data protection in Singapore is currently governed by the Personal Data Protection Act 2012 (“Singapore PDPA”).
The initial phase of the Personal Data Protection (Amendment) Act 2020 (No. 40 of 2020) (“Singapore PDPA Amendments”) took effect on 1 February 2021. On 1 February 2021, the Singapore PDPA Amendments’ requirement for mandatory notification to the Personal Data Protection Commission (“PDPC”) for data breaches came into force. This requires organisations to notify the PDPC no later than three calendar days after the organisation determines that a data breach is notifiable if either of the following occurs: (1) a data breach that results in or is likely to result in significant harm to the data subject or (2) a data breach of a significant scale (i.e. which involves more than 500 affected data subjects). The PDPC also made follow-up amendments on 1 October 2021 to clarify these situations.[61]
On 25 November 2021, the PDPC announced its collaboration with the Singapore Police Force and Cyber Security Agency of Singapore to develop a handbook on the Singapore PDPA, Cybersecurity Act 2018 (No. 9 of 2018) and Computer Misuse Act (Cap. 50A).[62]
On 9 December 2021, Singapore and the United Kingdom published a Digital Economy Agreement (“DEA”). The DEA aims to facilitate cross-border data flows while upholding data protection standards. Furthermore, both countries have committed that neither will introduce unjustified data localisation requirements, giving businesses in the United Kingdom a guarantee that they will not have to pay for data storage and processing in Singapore. The DEA will require both countries to maintain their data protection frameworks.[63]
K. South Korea
As explained in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, data protection in South Korea is currently governed by the Personal Information Protection Act (“PIPA”).
As noted above, on 17 December 2021, the PIPC and the European Commissioner for Justice formally announced an adequacy agreement between South Korea and the European Union for transfers of personal data. This adequacy agreement promotes the transfer of personal data between South Korea and the European Union without additional mechanisms or authorisations for data transfers.[64]
L. Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka’s official gazette published the Regulation of Processing of Personal Data (2021) on 25 November 2021 to be considered by the Parliament of Sri Lanka.[65]
M. Thailand
As noted in both the 2020 and 2021 International Outlook and Review, the Personal Data Protection Act 2019 (“Thailand PDPA”), which is the first consolidated data protection law in Thailand, was originally expected to come into full effect on 27 May 2020. However, in May 2020, and then again in May 2021, the government of Thailand approved a Royal Decree to postpone the application of the Thailand PDPA until 31 May 2021 and, subsequently, 31 May 2022, citing the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and the requirement for further legislative work as the primary reasons for doing so.[66]
Reference must be made to the fact that the Thailand PDPA is largely modelled upon the GDPR, containing many similar provisions, although they differ in areas such as anonymisation. Moreover, the Thailand PDPA provides for the creation of a 16-member Personal Data Protection Committee (“PDPC”), which is yet to be fully established. As such, the MDES is currently acting as the supervisory authority for any data protection–related issues within Thailand. Once created, the PDPC is expected to adopt notices and regulations to clarify and guide data controllers and other stakeholders on how to prepare for and remain compliant with the requirements under the Thailand PDPA once it is passed.
N. Vietnam
As explained in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, the data protection framework in Vietnam is fragmented, and relevant provisions can be found in numerous laws. In February 2020, however, a draft personal data protection decree (“Draft PDPD”) was released, which sets out principles of data protection, including purpose limitation, data security, data subject rights and the regulation of cross-border data transfers. Moreover, the Draft PDPD contains provisions on obtaining consent of data subjects, the technical measures needed to protect personal data, the creation of a data protection authority and the introduction of penalties for non-compliance, ranging between VDN 50 million to VDN 100 million.
From February to April 2021, the Ministry of Public Security sought public comments on the Draft PDPD with a view to the final decree coming into effect on 1 December 2021. As of the date of this publication, the Draft PDPD remains unissued, with little clarity over the timing of the parliamentary process required for it to come into effect.
IV. Developments in Africa
A. Botswana
On 15 October 2021, the Data Protection Act entered into effect, more than three years after it was passed by the National Assembly on 12 July 2018. The Act’s transition period is 12 months from the date of commencement and will automatically end on 15 October 2022, meaning that data controllers, including companies and organisations, must take compliance measures until that date. The Act requires data controllers and processors to respect in their processing: the lawfulness and fairness of processing, imposes limitations with respect to the purpose of processing, personal data retention and minimisation, in addition to other protections concerning the relevance and adequacy, integrity and confidentiality of personal data collected by entities. Further, the Act provides for data subject rights, including the right to be informed, the right to access, the right to be given reasons if the access is denied, the right to object and revoke consent and the right to raise a challenge for purposes of deletion and amendment, in addition to setting out restrictions of matters such as direct marketing, sensitive data and data transfers. The Act creates the Information and Data Protection Commission, which will be responsible to protect the personal rights of individuals with regard to their personal data, and to ensure the effective application and enforcement of the Act. Unlike the GDPR, the Act also provides for significant potential prison terms ranging from three to 12 years for certain violations.[67]
B. Kenya
In 2021, the Ministry of ICT, Innovation and Youth Affairs launched a public consultation on three draft data protection regulations, which remained open until 11 May 2021:
- The Data Protection (General) Regulations 2021, which set out the procedures for enforcement of the rights of the data subjects and outline the duties and obligations of the data controllers and data processors.
- The Data Protection (Registration of Data Controllers and Data Processors) Regulations 2021, which define the procedure that will be adopted by the Office of the Data Commissioner in registering data controllers and data processors.
- The Data Protection (Compliance and Enforcement) Regulations, 2021, which outline the compliance and enforcement provisions for Data Commissioner, Data Controllers and Data Processors.
In January 2021, the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner published a guidance note on access to personal data during the Coronavirus pandemic. According to the guidance, the access and processing of personal data of individuals in response to the pandemic is subject to the Data Protection Act No. 24 of 2019. The key principles emphasised by the guidance include the processing of personal data in an accountable manner, the maintenance of the integrity and confidentiality of data and the responsibility for the implementation of a protection and safeguarding personal data mechanism.[68]
C. Nigeria
The National Information Technology Development Agency (“NITDA”) announced in a press release on 12 November 2021 its collaboration with the Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (“FCCPC”) in order to combat data privacy abuse by money lending operators.[69] The partnership is anticipated to provide a more robust and concerted regulatory approach while ensuring that Nigerians get necessary reprieve from the illegal use of their personal data for money lending operations, including through joint investigations, enforcement and possible prosecution for non-compliance.[70]
In this regard, NITDA announced, on 17 August 2021, that it had fined Soko Loans Lending Company Limited NGN 10 million (approx. €20,700) for various violations of the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation, 2019 (“NDPR”), marking the first fine issued under the NDPR. NITDA outlined that the fine followed an investigation into a series of complaints against Soko Loans for unauthorised disclosures, failure to protect customers’ personal data and defamation of character, as well as failure to carry out the necessary due diligence required by the NDPR. Soko Loans grants its customers uncollateralised loans and requires them to download its mobile application on their phone and activate a direct debit in the company’s favour. The app gains access to the borrowing customer’s phone contacts. Following the complainant customers’ failures to meet loan repayment obligations, the company unilaterally sent privacy invading messages to their contacts (who were neither were parties to the loan transaction nor consented to the processing of their data). In addition, NITDA found that Soko Loans embedded trackers that share data with third parties inside its mobile application without providing users information about it or using the appropriate lawful basis. NITDA therefore found that Soko Loan and its entities violated multiple provisions of the NDPR.
In addition to a financial penalty, NITDA compelled Soko Loans to suspend the issuance of privacy-invading messages to any Nigerian until the company and its entities show full compliance with the NDPR, paid for the conduct of a Data Protection Impact Assessment by a NITDA appointed DPCO, and were placed on mandatory Information Technology and Data Protection supervision for nine months.[71]
D. Rwanda
Law No. 058/2021 of 13 October 2021 Relating to the Protection of Personal Data and Privacy (the “Law”) came into effect upon its publication in the Rwanda Official Gazette on 15 October 2021. The Law establishes provisions relating to the processing of personal data, including the rights of the data subject such as the right to object to the processing of personal data, to personal data portability, to the erasure of personal data and to rectification of incorrect personal information.
The Law also provides for the duties and powers of the supervisory authority relating to the protection of personal data and privacy, stipulates the obligations and registration requirements of data controllers and processors, and includes provisions regarding the sharing, transfer and retention of personal data. Moreover, the Law provides for the consequences and sanctions of non-compliance, including fines ranging from RWF 2,000,000 (approx. €1,500) to RWF 5,000,000 (approx. €4,243) or, in the case of a corporate body or legal entity, 1% of their global turnover in the preceding financial year.
The Law provides for a two-year transitional period before its application to data controllers or data processors who are already in operation.[72] The National Cyber Security Authority (“NCSA”) has been designated as the supervisory authority in charge of enforcement of the Law.[73]
On 10 December 2021, the NCSA issued a notice on the Personal Data Law detailing that the Personal Data Law requires all those who wish to process personal data to register with the NCSA as a data controller or data processor.[74]
On 14 December 2021, the NCSA also published a notice clarifying that consent of the data subject is a key foundation to the lawful collection and processing of personal data and may be made in oral, written or electronic format.[75]
E. South Africa
The enforcement powers of the supervisory authority of South Africa (the “Information Regulator”) under the Protection of Personal Information Act, 2013 (“POPIA”) came into effect on 1 July 2021, following the conclusion of a 12-month transitional grace period.[76]
In 2021, the Information Regulator issued a set of notices and rules for guidance on different sections of POPIA. Notably:
- Guidance note on the processing of special personal information under sections 26 and 27(1) of POPIA to guide responsible parties who are required to obtain authorisation from the Information Regulator to process special personal information, as provided for in section 27(2) of POPIA. The guidance provides for the manner of submission of an application for authorisation and outlines specific exemptions in which the prohibition on processing of personal information does not apply.[77]
- Guidance note on Exemptions from the Conditions for Lawful Processing of Personal Information under sections 37 and 38 of POPIA. In particular, the guidance outlines that these exemptions include that the processing is either in the public interest or involves a clear benefit to the data subject.[78]
- Rules on the manner in which a complaint must be submitted and handled by the Information Regulator which will come into operation on a future date that the Information Regulator determines.[79]
On the enforcement front, the Information Regulator has initiated its action by targeting both local and international businesses. For example, in a media statement published on 13 May 2021, the Information Regulator announced that it was preparing a litigation opinion contending the need for an online messaging service provider to adopt its EU privacy policy in South Africa and other developing countries with frameworks similar to the GDPR. However, the service provider has so far declined to make any revisions to its South African privacy policy.[80]
Finally, on 1 June 2021, the President assented to the Cybercrimes Act 19, 2020, which intends to criminalise the disclosure of harmful data messages, regulate relevant government authorities’ powers to investigate cybercrimes, provide for the establishment of a designated Point of Contact and impose obligations to report cybercrimes. The President has not yet proclaimed the commencement date of this new legislation.[81]
F. Other African Jurisdictions
Other developments in 2021 in data protection and cybersecurity regulation in Africa include:
- Togo: On 29 June 2021, the National Assembly adopted a Bill authorising the ratification of the Convention on Cyber Security and Personal Data Protection. According to the National Assembly, this convention will strengthen the country’s legal framework for electronic transactions, the protection of personal data and the fight against cybercrime.[82]
- Uganda: The Data Protection and Privacy Regulations, 2021 of the Republic of Uganda (“the Regulations”) came into force on 12 March 2021. The Regulations establish provisions for the collection and processing of personal data and the rights of data subjects in regard to their personal data, in addition to establishing an independent Personal Data Protection Office (“PDPO”) in the National Information Technology Authority of Uganda (“NITA-U”), which shall be responsible for personal data protection and privacy and for the implementation of the Data Protection and Privacy Act, 2019, including the imposition of administrative, civil or criminal sanctions for non-compliance. [83]
On 2 November 2021, the PDPO issued a press release announcing that it required data collectors, processors and controllers to register on its website before the end of the grace period of 31 December 2021 and that it will begin enforcement measures for those that do not in January 2022.[84]
- Zambia: On 23 March 2021, the Parliament of Zambia enacted the Data Protection Act No. 3 of 2021, which stipulates a system for the use and protection of personal data by regulating the collection, use, transmission, storage and processing of personal data. The Act also establishes the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner and outlines the duties of data controllers and data processors, the rights of data subjects and the conditions for cross-border transfer of personal data. The Minister will appoint the date of the commencement of the Act by statutory instrument.[85]
- Zimbabwe: The Data Protection Act [Chapter 11:12] was enacted on 3 December 2021. The Act provides for the establishment of the Cyber Security and Monitoring Center and the designation of the Postal and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority of Zimbabwe (“POTRAZ”) as the data protection authority. The Act addresses the processing of personal data collected and processed by companies, cross-border transfers of personal data, and general provisions, including the appeals process, offences and penalties. The Act does not establish a date of application or a transitional period prior to its application.[86]
V. Developments in the Middle East
A. Israel
On 6 January 2022, the Government of Israel published a Bill[87] amending and updating Israel’s Protection of Privacy Law, 5741-1981 (“PPL”).[88] The Deputy Prime Minister and the Minister of Justice announced that the Bill aims to protect citizens and adapt the PPL’s provisions and enforcement to the current digital era. The most noteworthy amendments, summarised by Israel’s Privacy Protection Authority (“PPA”), include the expansion of PPA’s substantive investigation and enforcement powers, including the imposition of administrative sanctions in an amount up to 3.2 million NIS ($1 million), the adaptation of definitions in the law to technological and social developments, and the reduction of bureaucratic burdens through a significant reduction in the obligation to register databases.[89] The Bill would be effective six months after its approval by the parliament.
Before the introduction of the Bill, a ransomware attack on sensitive data of more than 290,000 Israeli medical patients and members of an LGBTQ+ website was reported. An Iranian-based hacking group targeted host program CyberServe and, on 2 November 2021, released the data, demanding a ransom of $1 million that the company refused. Israel’s National Cyber Directorate had previously warned CyberServe on multiple occasions that its systems were not secure.[90] The ransomware attack was followed by a press release of the U.S. Department of the Treasury on 14 November 2021, announcing that it established a partnership with Israel to combat ransomware.[91]
On the enforcement side, on 23 May 2021, the PPA announced that, following a serious information security incident that resulted in the disclosure of sensitive personal information from the databases of the Hod Hasharon Municipality, it had determined that the Hod Hasharon Municipality had violated the Privacy Protection Law and regulations under it. The PPA’s investigation concluded that sensitive personal information, including documents, email correspondence and complaints from residents (including names and ID numbers and information about employees using municipal systems) contained in the municipality’s database, was accessible to unauthorised persons, and that the municipality did not take appropriate measures to assure that access to the database was carried out by authorised users. Additionally, according to the PPA’s findings, the municipality had not conducted an assessment to identify security risks in its systems at the required time and did not correct the findings of a previous assessment, as required by the Protection of Privacy (Data Security) Regulations, 5777 – 2017. In light of this, the PPA gave the municipality instructions to correct the deficiencies discovered and fined it NIS 10,000 (approx. €2,530) for failing to register databases required to be registered under the provisions of the PPL.[92]
In his efforts to support the global fight against COVID-19, Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced an agreement between the Israeli Ministry of Health (“MoH”) and Pfizer for an expedited supply of COVID-19 vaccines to Israel, under which Israel agreed to share with Pfizer “statistical data that would help develop strategies for defeating the coronavirus”. In order to address privacy and transparency concerns, the MoH published a partially redacted version of its Real-World Epidemiological Evidence Collaboration Agreement with Pfizer. The agreement provides that the MoH will share “aggregate de-identified data” and jointly analyse such data with Pfizer. In particular, the MoH is required to provide “data transfers” that include, “at a minimum”, weekly counts of confirmed COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, severe or critical cases, ventilator use, deaths, symptomatic cases, vaccines given “by age and other demographic subgroups” and COVID-19 cases by age groups “and other demographic factors”. The MoH undertook to provide such data “solely in a form rendered anonymised by the MoH in accordance with Regulatory Requirements” so that the data could not reasonably be used to re-identify the identity of an individual.[93]
B. United Arab Emirates
In late 2021, the UAE issued its first federal data protection law (Federal Decree Law No. 45/2021 on the Protection of Personal Data) (the “Data Protection Law”), alongside a law establishing the new UAE Data Office with the mandate to ensure the full protection of personal data, monitor the application of the Data Protection Law and issue necessary guidelines and instructions for its implementation (Federal Decree Law No. 44/2021 on Establishing the UAE Data Office).
According to the announcement of the Cabinet of UAE,[94] the Data Protection Law relevantly:
- has extraterritorial effect and applies to the processing of personal data (a) inside the country or (b) outside the country about data subjects within the country;
- prohibits the processing of personal data without the consent of its owner (subject to prescribed exceptions);
- defines the controls for the processing of personal data and the general obligations of companies that have personal data to secure personal data and maintain its confidentiality;
- defines the rights and cases in which the owner has the right to request correction of inaccurate personal data, restrict or stop the processing of personal data; and
- sets out the requirements for the cross-border transfer and sharing of personal data for processing purposes.
The Data Protection Law became effective on 2 January 2022. Executive regulations are due to be issued within six months of the date of issuance of the Data Protection Law (i.e. by 20 March 2022). UAE companies will then have six months from the issuance of those executive regulations to comply with the Data Protection Law (although that period may be extended by the Cabinet).[95]
On 14 February 2021, following public consultation conducted in 2020, the Abu Dhabi Global Market (“ADGM”) announced that it had enacted the Data Protection Regulations 2021, which replaced the Data Protection Regulations 2015. In its announcement, ADGM endorsed the EU’s GDPR for its robust data protection provisions and outlined that the new Regulations intend to be proportionate and business friendly, without undermining the key ambition of achieving a high standard of protection for personal data. Acknowledging that the adoption of the new Regulations will result in additional responsibilities for data controllers and data processors, ADGM proposed a transitional grace period of 12 months for current establishments and six months for new establishments, starting from 14 February 2021.[96] The Office of Data Protection (“ODP”) has been established to monitor the compliance with the new Regulations.[97] The ODP has also published several guidance notes and templates to support ADGM entities and authorities in compliance with the Regulations.[98]
C. Other Middle East Jurisdictions
Other developments in 2021 in data protection and cybersecurity regulation in the Middle East include:
- Jordan: On 29 December 2021, the Council of Ministers approved a draft law on the protection of personal data.[99] The draft law intends to protect personal data in light of the ease of its collection, retention and processing, and to prevent attacks on the rights of citizens. The law also aims to establish a safe and stable online environment and define the obligations of persons responsible for personal data. A personal data protection board will be established to enforce the draft law. The draft law became publicly available in January 2022[100] and its commencement will follow upon approval by the parliament and the king.
- Pakistan: On 25 August 2021, the Ministry of Information Technology (“MOITT”) published a revised draft for consultation on the Personal Data Protection Bill 2021. The revised draft provides for the establishment of the National Commission for Personal Data Protection. The draft includes also provisions for the cross-border transfer of personal data, the right to data portability and the right not to be subject to a decision based solely on automated processing. Unlike the previous draft Personal Data Protection Bill 2020, which was presented to the Cabinet of Pakistan for approval in April 2020, the revised draft requires data controllers to notify the supervisory authority and the data subject in the event of a data breach without undue delay and, where reasonably possible, not beyond 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach.[101]
- Qatar: On 16 August 2021, the Qatar Financial Centre (“QFC”) Authority launched a public Consultation Paper proposing changes to the QFC Data Protection Regulations and Rules.[102] The proposed changes aim to make the scope of the QFC Data Protection Regulations consistent with the provisions of international data protection laws and reflect the needs for expanded digitalisation in a global business environment. The amendments, inter alia, propose additional rights for data subjects and increased responsibilities for data controllers and data processors. On 31 January 2021, the Compliance and Data Protection Department at the Ministry of Transport and Communications released guidelines on the Personal Data Privacy Protection Law No. 13 of 2016 to inform individuals, regulated entities and stakeholders on their respective responsibilities, rights and practices as per the amended law.[103]
- Saudi Arabia: The National Centre for Documents and Archives Royal Court published, on 24 September 2021, the new Personal Data Protection Law (“PDPL”), marking the introduction of Saudi Arabia’s first data protection law. The PDPL includes provisions for data controllers, the rights of data subjects and sanctions for non-compliance. The PDPL will come into force 180 days after the date of its publication in the Official Gazette.[104] In the field of cybersecurity, the Regulatory Framework for Cyber Security for Service Providers in the Communications, Information Technology and Postal Sector came into force on 29 May 2021. That framework intends to raise the level of cybersecurity maturity of service providers by requiring them to improve their cybersecurity risk management in accordance with international best practices and frameworks.[105]
VI. Developments in Latin America and the Caribbean
A. Brazil
As we indicated in the 2021 International Outlook and Review, the biggest data protection development in Brazil in 2020 was the entry into force of Law No. 13.709 of 14 August 2018 and the General Personal Data Protection Law (as amended by Law No. 13.853 of 8 July 2019) (“LGPD”), on 18 September 2020.
During 2021, the Brazilian data protection authority (“ANPD”) adopted and published a series of guidance and FAQs regarding the LGPD. In particular:
- Guidance for Personal Data Processing Agents and Data Protection Officers, which aims to resolve common issues, set out non-binding guidelines for data processing agents and explain who may exercise the role of a data controller, operator and/or data protection officer. For each of those roles, the Guidance also specifies their respective liability regime, legal definition and example cases, in addition to FAQs regarding the same.[106]
- FAQs related to the commencement of the application of sanctions and fines under the LGPD.[107]
- Regulation CD/ANPD No. 1, on the Inspection Process and the Sanctioning Administrative Process’, which aims to establish procedures with respect to the conduct of inspections and rules with respect to the administrative processes carried out by the ANPD. Moreover, the Regulation covers topics such as inspection, monitoring, guidance, injunctive measures and provides for an administrative fining procedure.[108]
- FAQs on data subjects’ rights to petition controllers to enforce their data subject rights under the LGPD, which provide guidance on, among other things, procedures to be observed by data controllers, as well as the right of data subjects to complain about possible irregularities regarding the processing of their personal data.[109]
Finally, while the ANPD assumed its enforcement and fining powers, other Brazilian authorities have applied and enforced rules that concerned the protection of personal data in their territories. For example, on 14 June 2021, the Brazilian Federal Department of Consumer Protection of the National Consumer Secretariat (“SENACON”) announced that it had fined Banco Cetelem S.A. with BRL 4,000,000 (approx. €653,200) for financial fraud that included the contracting of payroll loans with the improper use of personal data of elderly consumers.[110] In addition, on 13 July 2021, the Protection and Consumer Defence Foundation of the State of Mato Grosso (“Procon-MT”) fined the pharmacies Droga Raia S.A and Drogasil S.A BRL 572,680.71 (approx. €94,210) for the irregular receipt of authorisation from customers for the processing and use of their data.[111]
B. Developments in Other Latin American and Caribbean Jurisdictions
There have also been significant developments in the adoption and enforcement of cybersecurity and data privacy laws in other Central and South American jurisdictions in 2021. We have set out highlights in key countries below:
- Argentina: On 16 April 2021, the Central Bank of Argentina (“BCRA”) published guidelines on cybersecurity incident response and recovery. The BCRA noted that the guidelines are aimed at financial institutions, payment service providers that offer payment accounts and financial market infrastructures. However, the BCRA highlighted that, due to their general nature, the guidelines can also be adopted by any institution in the financial sector, as well as by information technology and communication service providers, among others.[112]
- Chile: On 5 November 2021, the Information Security Incident Response Team (“CSIRT”) released cybersecurity guidelines for small and medium-sized enterprises (“SMEs”). In particular, the guidelines aim at supporting SMEs in the digitalisation process in a secure manner, helping them manage risks of data breaches, loss of business continuity, phishing, ransomware and other cyber threats.[113]
- Costa Rica: On 12 February 2021, the Bill No. 22.388 was published to Reform the Law on the Protection of Persons Regarding the Processing of their Personal Data No. 8968 of 2011. In particular, the bill aims to reform the current data protection law in Costa Rica by, among other things, improving the legal definitions for certain technical concepts (e.g., biometric data, genetic data and pseudonymisation), developing the principles governing the processing of personal data (such as transparency and data minimisation), improving data subject rights; strengthening the Costa Rican data protection authority, and strengthening the sanctions regime.
- Ecuador: On 21 May 2021, the Organic Law on the Protection of Personal Data was published, triggering a two-year grace period for companies and other entities that process personal data to adapt their operations to the new law.[114]
- Panama: On 28 May 2021, the National Authority of Transparency and Access to Information (“ANTAI”) announced that the President of the Republic of Panama approved the Executive Decree No. 285 of 28 May 2021 that regulates the Law No. 81 on Personal Data Protection. The Executive Decree obliges all companies to put in place protocols or procedures to process data in compliance with the new law. Furthermore, the Executive Decree includes general provisions, information gathering requirements, the functions of the new role of data protection officer and the criteria for applying sanctions.[115]
- Paraguay: On 30 April 2021, the Chamber of Deputies announced the official presentation of the bill on the Protection of Personal Data of the Republic of Paraguay. The bill provides for the regulation of, among other things, data subject rights, security standards and obligations, data protection officer activities, and issues related to the creation of and procedures applicable to a supervisory authority.[116]
- Uruguay: On 16 September 2021, the Uruguayan data protection authority (“URCDP”) announced the adoption of Resolution No. 23/021 of 8 June 2021, which implements important changes in the international data transfer regime in Uruguay. In particular, the resolution excludes the U.S. from the list of territories considered appropriate, in addition to suggesting the use of other mechanisms to transfer personal data abroad (e.g., contractual clauses, consent of the interested parties and other elements justifying transfers). Moreover, to assist data controllers and processors, the URCDP published Resolution No. 41/021 of 8 September 2021, which includes a guide for the drafting of contractual clauses to transfer personal data.[117]
VII. Conclusion
As can be seen, 2021 was an eventful year in the field of data protection and privacy worldwide. In addition to the recently adopted laws and regulations on data privacy adopted by China, UAE, Brazil and Mexico, international lawmakers put a special focus on the regulatory treatment of key issues such as data localisation and transfers (e.g., in the EU, Russia and India).
2022 promises to be an equally active year from a legal and enforcement perspective, as regulators worldwide commence to make use of new legal tools and apply their respective national laws. We will continue to monitor the events in this space, and cover them in our monthly updates and in the Outlook and Review of 2023.
_______________________________
[1] See http://curia.europa.eu/juris/document/document.jsf;jsessionid=2BDC80771D0FB7EA8B6F60B9A3C4F572?text=&docid=228677&pageIndex=0&doclang=EN&mode=lst&dir=&occ=first&part=1&cid=20032710.
[2] See
https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2021-06/edpb_recommendations_202001vo.2.0_supplementarymeasurestransferstools_en.pdf.
[3] See https://edpb.europa.eu/sites/default/files/files/file1/edpb_recommendations_202002_europeanessentialguaranteessurveillance_en.pdf.
[4] See https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/law-topic/data-protection/international-dimension-data-protection/standard-contractual-clauses-scc_en.
[5] See https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2021-07/edpb_guidelinescodesconducttransfers_publicconsultation_en.pdf.
[6] See https://edpb.europa.eu/our-work-tools/documents/public-consultations/2021/guidelines-052021-interplay-between-application_en.
[7] See, e.g., the French CNIL published guidance on the implementation of the SCCs, two Q&As on the content and the consequences of the Schrems II ruling, as well as a methodology to help controllers identify and process data transfers outside of the EU. German authorities released revised recommendations and updated guidance on international data transfers. The UK ICO launched a public consultation on its draft international data transfer agreement that would replace the current SCCs to take into account the Schrems II ruling.
[8] See https://www.garanteprivacy.it/web/guest/home/docweb/-/docweb-display/docweb/9703988.
[9] See http://www.raadvst-consetat.be/Arresten/251000/300/251378.pdf#xml=http://www.raadvst-consetat.be/apps/dtsearch/getpdf.asp?DocId=42765&Index=c%3a%5csoftware%5cdtsearch%5cindex%5carrets%5fnl%5c&HitCount=10&hits=28+29+2c+6b+de+17a+1de+505+150c+1884+&11111202021318.
[10] See https://edpb.europa.eu/news/national-news/2021/bavarian-dpa-baylda-calls-german-company-cease-use-mailchimp-tool_en.
[11] See https://edpb.europa.eu/news/national-news/2021/census-2021-portuguese-dpa-cnpd-suspended-data-flows-usa_en.
[12] See https://www.conseil-etat.fr/fr/arianeweb/CE/decision/2021-03-12/450163.
[13] See https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_21_3183.
[14] See https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/1_1_180366_dec_ade_kor_new_en.pdf.
[15] Relatedly, some Member States have continued to update their e-privacy legislation under the e-Privacy Directive. For example, in Germany, the Data Protection and Privacy in Telecommunications and Telemedia Act was enacted effective 1 December 2021, and contains comprehensive data protection regulations in the e-privacy field.
[16] See https://www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document/EPRS_BRI(2021)689333.
[17] See https://edpb.europa.eu/sites/default/files/files/file1/edpb_guidelines_202006_psd2_afterpublicconsultation_en.pdf.
[18] See https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2021-07/eppb_guidelines_202007_controllerprocessor_final_en.pdf.
[19] See https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2021-04/edpb_guidelines_082020_on_the_targeting_of_social_media_users_en.pdf.
[20] See https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2021-10/edpb_guidelines202010_on_art23_adopted_after_consultation_en.pdf.
[21] See https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2022-01/edpb_guidelines_012021_pdbnotification_adopted_en.pdf.
[22] See https://edpb.europa.eu/sites/default/files/files/file1/edpb_strategy2021-2023_en.pdf.
[23] See https://edpb.europa.eu/system/files/2021-03/edpb_workprogramme_2021-2022_en.pdf.
[24] See https://curia.europa.eu/juris/document/document.jsf?text=&docid=242821&pageIndex=0&doclang=EN&mode=req&dir=&occ=first&part=1&cid=558920.
[25] See https://d18rn0p25nwr6d.cloudfront.net/CIK-0001018724/cbae1abf-eddb-4451-9186-6753b02cc4eb.pdf.
[26] See https://justice.public.lu/fr/actualites/2021/12/communique-presid-trib-adm-ordonnance-amazon-cnpd.html.
[27] See https://www.cnil.fr/en/cookies-cnil-fines-google-total-150-million-euros-and-facebook-60-million-euros-non-compliance.
[28] See, e.g. Lower-Saxony Supervisory Authority https://lfd.niedersachsen.de/startseite/infothek/presseinformationen/lfd-niedersachsen-verhangt-bussgeld-uber-10-4-millionen-euro-gegen-notebooksbilliger-de-196019.html.
[29] See, e.g. Spanish AEPD https://www.aepd.es/es/documento/ps-00059-2020.pdf and Italian Garante https://www.garanteprivacy.it/web/guest/home/docweb/-/docweb-display/docweb/9570980.
[30] See, e.g. Norwegian Datatilsynet https://www.datatilsynet.no/en/regulations-and-tools/regulations/avgjorelser-fra-datatilsynet/2021/gebyr-til-grindr/ and Spanish AEPD https://edpb.europa.eu/news/national-news/2021/spanish-data-protection-authority-aepd-imposes-fine-6000000-eur-caixabank_en.
[31] See https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/news-and-events/news-and-blogs/2021/11/ico-issues-provisional-view-to-fine-clearview-ai-inc-over-17-million/.
[32] See https://ico.org.uk/action-weve-taken/enforcement/.
[33] See https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/news-and-events/news-and-blogs/2021/08/ico-consults-on-data-transferred-outside-of-the-uk/.
[34] See https://www.edoeb.admin.ch/dam/edoeb/en/dokumente/2021/revdsg.pdf.download.pdf/revDSG_EN.pdf.
[35] See https://www.bj.admin.ch/dam/bj/fr/data/staat/gesetzgebung/datenschutzstaerkung/vdsg/vorentw.pdf.
[36] See https://www.edoeb.admin.ch/dam/edoeb/en/dokumente/2021/Anleitung für die Prüfung von Datenübermittlungen mit Auslandbezug EN.pdf.download.pdf/Anleitung für die Prüfung von Datenübermittlungen mit Auslandbezug EN.pdf.
[37]&nbnbsp; See https://www.edoeb.admin.ch/edoeb/en/home/latest-news/aktuell_news.html#-1259254222.
[38] See https://iapp.org/news/a/level-up-russia-enhances-the-protection-of-personal-data/#:~:text=Russia%20amends%20data%20protection%20law%20to%20increase%20personal%20data%20subjects’%20rights,-schedule%20May%2013&text=Beginning%20March%2027%2C%202021%2C%20Russia,period%20for%20data%2Drelated%20breaches.
[39] See https://rg.ru/2021/03/29/sotovym-operatoram-zapretiat-tajno-prodavat-dannye-klientov.html.
[40] See https://sozd.duma.gov.ru/bill/1184517-7#bh_note.
[41] See https://kvkk.gov.tr/SharedFolderServer/CMSFiles/11b6fd99-d42a-45b1-a009-21f2d36ded21.pdf.
[42] See https://kvkk.gov.tr/Icerik/6981/2021-427.
[43] https://www.kvkk.gov.tr/Icerik/7045/WHATSAPP-UYGULAMASI-HAKKINDA-YURUTULEN-RESEN-INCELEMEYE-ILISKIN-KAMUOYU-DUYURUSU.
[44] See https://consultations.ag.gov.au/rights-and-protections/privacy-act-review-discussion-paper/.
[45] See https://consultations.ag.gov.au/rights-and-protections/online-privacy-bill-exposure-draft/.
[46] See https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/united-states-and-australia-enter-cloud-act-agreement-facilitate-investigations-serious-crime.
[47] See https://www.itnews.com.au/news/australia-and-us-sign-cloud-act-deal-for-cross-border-data-access-574128.
[48] An unofficial English translation of the newly enacted PIPL is available at <https://digichina.stanford.edu/news/translation-personal-information-protection-law-peoples-republic-china-effective-nov-1-2021> and the Mandarin version of the PIPL is available at <http://www.npc.gov.cn/npc/c30834/202108/a8c4e3672c74491a80b53a172bb753fe.shtml>.
[49] An unofficial translation of the Regulations is available <https://digichina.stanford.edu/news/translation-critical-information-infrastructure-security-protection-regulations-effective-sept>.
[50] An unofficial English translation of the Internet Information Service Algorithmic Recommendation Management Provisions is available at <https://digichina.stanford.edu/work/translation-internet-information-service-algorithmic-recommendation-management-provisions-effective-march-1-2022/>.
[51] See https://www.dsci.in/sites/default/files/Summary-%20and-Primer-on-Joint-Parliamentary-Committee-Report-and-Data-Protection-Bill-2021.pdf.
[52] Press release (in Indonesian) available athttps://www.kominfo.go.id/content/detail/24039/siaran-pers-no-15hmkominfo012020-tentang-presiden-serahkan-naskah-ruu-pdp-ke-dpr-ri/0/siaran_pers; the PDP Bill (in Indonesian) is available athttps://web.kominfo.go.id/sites/default/files/users/4752/Rancangan%20UU%20PDP%20Final%20%28Setneg%20061219%29.pdf.
[53] Press release (in Indonesian) available athttps://www.kominfo.go.id/content/detail/24041/menkominfo-indonesia-akan-menjadi-negara-ke-5-di-asean-pemilik-uu-pdp/0/berita_satker.
[54] Press release (in Indonesian) available athttps://www.kominfo.go.id/content/detail/29084/siaran-pers-no-104hmkominfo092020-tentang-pemerintah-apresiasi-pandangan-fraksi-terhadap-ruu-pdp/0/siaran_pers.
[55] See https://kr-asia.com/indonesia-needs-a-data-protection-authority-but-cant-decide-how-to-create-one.
[56] The PDPO Bill is available at <https://www.gld.gov.hk/egazette/pdf/20212540/es12021254032.pdf>.
[57] For more information on the first review of the EU-Japan mutual adequacy arrangement, please click <https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/just/items/724795/en>.
[58] See https://www.natlawreview.com/article/less-two-weeks-to-go-new-zealand-privacy-act-commences-1-december-2020.
[59] See https://www.privacy.org.nz/publications/reports-to-parliament-and-government/2020-briefing-to-the-incoming-minister-of-justice/.
[60] See https://www.privacy.gov.ph/2021/06/a-stronger-data-privacy-law-sought-in-proposed-amendments/.
[61] The PDPC’s updated advisory guidelines are available at https://www.pdpc.gov.sg/Guidelines-and-Consultation/2020/03/Advisory-Guidelines-on-Key-Concepts-in-the-Personal-Data-Protection-Act and <https://www.pdpc.gov.sg/Guidelines-and-Consultation/2020/02/Advisory-Guidelines-on-the-Personal-Data-Protection-Act-for-Selected-Topics>.
[62] The handbook on the Singapore PDPA, Cybersecurity Act 2018 (No. 9 of 2018), and Computer Misuse Act (Cap. 50A) is available at <https://www.csa.gov.sg/News/Publications/overview-of-legislations>.
[63] More information on the Digital Economy Agreement between Singapore and the United Kingdom is available at <https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/uk-singapore-digital-economy-agreement-agreement-in-principle-explainer/uk-singapore-digital-economy-agreement-agreement-in-principle-explainer>.
[64] The adequacy decision between South Korea and the European Union is available at <https://ec.europa.eu/info/files/decision-adequate-protection-personal-data-republic-korea-annexes_en>.
[65] The Regulation of Processing of Personal Data (2021) is available at <http://documents.gov.lk/files/bill/2021/11/152-2021_E.pdf>.
[66] See https://www.bangkokpost.com/business/2110719/controversial-law-on-personal-data-againt-postponed-for-another-year.
[67] See Act No. 32 of 2018 Data Protection Act (12 July 2018), available athttps://www.bocra.org.bw/sites/default/files/documents/32%20Act%2010-08-2018-Data%20Protection.pdf and Data Protection Act (Commencement Date) Order, 2021 (15 October 2021).
[68] See Republic of Kenya, Office of the Data Protection Commissioner, “Guidance Note on access to personal date during Covid-19 pandemic” (January 2021), available at https://ict.go.ke/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Draft-Data-Request-Review-Framework-Jan-2021.pdf.
[69] The FCCPC is empowered to administer and enforce provisions of every Nigerian law with respect to competition and protection of consumers under Section 17(a) of the Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
[70] See “NITDA Collaborates With The Federal Competition And Consumer Commission (FCCPC) To Tackle Data Abuse By Money Lending Operations”, Press Release (12 November 2021), available athttps://nitda.gov.ng/nitda-collaborates-with-the-federal-competition-and-consumer-commission-fccpc-to-tackle-data-abuse-by-money-lending-operations/.
[71] See “NITDA Sanctions SokoLoan For Privacy Invasion”, Press Release (17 August 2021), available athttps://nitda.gov.ng/nitda-sanctions-soko-loan-for-privacy-invasion/.
[72] See Law No. 058/2021 Law relating to the protection of personal data and privacy (15 October 2021), available at https://www.minijust.gov.rw/fileadmin/user_upload/Minijust/Publications/Official_Gazette/_2021_Official_Gazettes/October/OG_Special_of_15.10.2021_Amakuru_bwite.pdf.
[73] See “Rwanda passes new Law protecting personal data”, Press Release (21 October 2021), available at https://www.minict.gov.rw/fileadmin/user_upload/minict_user_upload/Documents/Press_Release/211021_PRESS_RELEASE_Rwanda_s_New_Data_Protection_Law_ENGLISH.pdf.
[74] See National Cyber Security Authority, “The Significance of Rwanda’s Personal Data Protection and Privacy Law” (10 December 2021), available at https://cyber.gov.rw/updates/article/the-significance-of-rwandas-personal-data-protection-and-privacy-law-1/.
[75] See National Cyber Security Authority, “Consent, Ownership and Lawful Data Processing” (14 December 2021), available at https://cyber.gov.rw/updates/article/consent-ownership-and-lawful-data-processing-1/.
[76] See Section 110 of POPIA.
[77] See Information Regulator (South Africa), “Guidance Note on Processing of Special Personal Information” (June 2021), available at https://www.justice.gov.za/inforeg/docs/InfoRegSA-GuidanceNote-Processing-SpecialPersonalInformation-20210628.pdf.
[78] See Information Regulator (South Africa), “Guidance Note On Exemptions From The Conditions For Lawful Processing Of Personal Information In Terms Of Section 37 And 38 Of The Protection Of Personal Information Act 4 Of 2013, 2021” (June 2021), available at https://www.justice.gov.za/inforeg/docs/InfoRegSA-GuidanceNote-PPI-LawfulProcessing-202106.pdf.
[79] See Information Regulator (South Africa), “Rules of procedure relating to the manner in which a complaint must be submitted and handled by the Regulator, 2021” (October 2021), available at https://www.justice.gov.za/inforeg/legal/20211012-InfoReg-RulesOfProcedure-HandlingPOPIAcomplaints.pdf.
[80] See “Information Regulator to take further action regarding the WhatsApp privacy policy”, Media Statement (13 May 2021), available at https://www.justice.gov.za/inforeg/docs/ms/ms-20210513-WhatsAppPrivacyPolicy.pdf.
[81] See Act No. 19 of 2020 Cybercrimes Act, 2020 (1 June 2021), available at https://www.gov.za/sites/default/files/gcis_document/202106/44651gon324.pdf.
[82] See “Togo : l’Assemblée nationale ratifie la convention de Malabo et actualise le fonctionnement de la CNDH” (in French) (14 July 2021), available at https://togomedia24.com/2021/07/01/togo-lassemblee-nationale-ratifie/.
[83] See Statutory Instrument No. 21 of 2021 The Data Protection and Privacy Regulations, 2021 (12 March 2021).
[84] See “Requirement to register with Personal Data Protection Office”, Press Release (2 November 2021), available at https://www.linkedin.com/posts/personal-data-protection-office-pdpo_press-release-on-requirement-to-register-activity-6863366852064628736-wJc_.
[85] See Act No. 3 of 2021 The Data Protection Act, 2021 (24 March 2021).
[86] See Data Protection Act [Chapter 11:22].
[87] Bill (in Hebrew), available at https://documentcloud.adobe.com/link/review?uri=urn:aaid:scds:US:1510391d-592a-3272-bd12-d559164b70e2#pageNum=1.
[88] An unofficial translation of the Protection of Privacy Law, 5741 – 1981 is available at https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/legalinfo/legislation/en/ProtectionofPrivacyLaw57411981unofficialtranslatio.pdf.
[89] Press Release (in Hebrew), available at https://www.gov.il/he/departments/news/amendments_privacy_protection_act.
[90] See “Iranian Hacking Group Leaks Patient and LGBTQ Info” (4 November 2021), available at https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/iranian-hacking-group-leaks/.
[91] See “U.S. Department of the Treasury Announces Partnership with Israel to Combat Ransomware”, Press Release (14 November 2021), available at https://home.treasury.gov/news/press-releases/jy0479.
[92] Announcement (in Hebrew), available at https://www.gov.il/he/departments/news/privacy_hod_hasharon_city.
[93] See “Israel to Share Vaccination Data With Pfizer as Part of Secret Deal” (10 January 2021), available at https://www.haaretz.com/israel-news/.premium-israel-to-share-covid-vaccine-data-with-pfizer-but-agreement-remains-secret-1.9438504, and a partially redacted version of the Real-World Epidemiological Evidence Collaboration Agreement, available at https://govextra.gov.il/media/30806/11221-moh-pfizer-collaboration-agreement-redacted.pdf.
[94] See “UAE adopts largest legislative reform in its history”, Media Release, available at https://uaecabinet.ae/en/details/news/uae-adopts-largest-legislative-reform-in-its-history.
[95] The Data Protection Laws of UAE are available at https://u.ae/en/about-the-uae/digital-uae/data/data-protection-laws.
[96] See “ADGM enacts its new Data Protection Regulations 2021”, Media Release (14 February 2021), available at https://www.adgm.com/media/announcements/adgm-enacts-its-new-data-protection-regulations-2021.
[97] See the dedicated website of the Office of Data Protection, available at https://www.adgm.com/operating-in-adgm/office-of-data-protection/overview.
[98] The Data Protection Guidance 2021, templates and assessments are available at https://www.adgm.com/operating-in-adgm/office-of-data-protection/guidance.
[99] Prime Minister’s announcement (in Arabic), available at http://www.pm.gov.jo/content/1640846700/%D9%85%D8%AC%D9%84%D8%B3-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%88%D8%B2%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D9%8A%D9%82%D8%B1%D9%91-%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%B9-%D9%82%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%88%D9%86-%D8%AD%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A8%D9%8A%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B4%D8%AE%D8%B5%D9%8A%D9%91%D9%8E%D8%A9.html, and Ministry’s announcement (in Arabic), available at https://modee.gov.jo/Ar/NewsDetails/%D9%82%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%88%D9%86_%D8%AD%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%8A%D8%A9_%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A8%D9%8A%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%A7%D8%AA_%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B4%D8%AE%D8%B5%D9%8A%D9%91%D9%8E%D8%A9_%D9%84%D8%B3%D9%86%D8%A9_2021%D9%85.
[100] The text of the draft law (in Arabic) is available at http://www.lob.jo/?v=1.14&url=ar/DraftDetails?DraftID:10254,AddComment:0,PageIndex:1&DraftTitle:%D9%82%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%88%D9%86-%D8%AD%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A8%D9%8A%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B4%D8%AE%D8%B5%D9%8A%D8%A9-/–%D8%AA%D9%85-%D8%AA%D9%85%D8%AF%D9%8A%D8%AF-%D9%85%D8%AF%D8%A9-%D9%86%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%87-%D8%B9%D9%84%D9%89-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D9%88%D9%82%D8%B9-%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%A8%D8%B9-%D8%A7%D9%8A%D8%A7%D9%85-%D8%B9%D9%85%D9%84-%D8%A7%D8%B6%D8%A7%D9%81%D9%8A%D8%A9.
[101] The Consultation Draft of the Personal Data Protection Bill 2021 (25 August 2021) is available at https://moitt.gov.pk/SiteImage/Misc/files/25821%20DPA%20Bill%20Consultation%20Draft_docx.pdf.
[102] See the announcement of the Qatar Financial Centre (QFC) Authority “Consultation on proposed changes to QFC Data Protections Regulations & Rules”, available at https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:6833700338965512192/, and the Consultation Paper “QFCA CP No. 1 of 2021 Proposed Changes to QFC Data Protection Regulations and Rules”, available at https://qfcra-en.thomsonreuters.com/rulebook/qfca-cp-no-1-2021-proposed-changes-qfc-data-protection-regulations-and-rules.
[103] See “MOTC Releases Guidelines on Personal Data Privacy Protection Law”, Media Release (31 January 2021), available at https://www.motc.gov.qa/en/news-events/news/motc-releases-guidelines-personal-data-privacy-protection-law.
[104] See Personal Data Protection Law, implemented by Royal Decree M/19 of 17 September 2021 approving Resolution No. 98 (in Arabic) (14 September 2021), available at https://ncar.gov.sa/Documents/Details?Id=waEbJasbk9cJVNdJ%2B31GUA%3D%3D.
[105] See “The Communications Commission announces the entry into force of the Regulatory Framework for Cyber Security for Service Providers in the Communications, Information Technology and Postal Sector”, Press Release (29 May 2021), available at https://www.citc.gov.sa/ar/mediacenter/pressreleases/Pages/20210529.aspx, and the Commission’s portal on cybersecurity regulations, available at https://www.citc.gov.sa/ar/RulesandSystems/CyberSecurity/Pages/default.aspx.
[106] See https://www.gov.br/anpd/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/2021-05-27-guia-agentes-de-tratamento_final.pdf.
[107] See https://www.gov.br/anpd/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/sancoes-administrativas-o-que-muda-apos-1o-de-agosto-de-2021.
[108] See https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-cd/anpd-n-1-de-28-de-outubro-de-2021-355817513.
[109] See https://www.gov.br/anpd/pt-br/canais_atendimento/cidadao-titular-de-dados/peticao-de-titular-contra-controlador-de-dados/reclamacao.
[110] See https://www.gov.br/mj/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/secretaria-nacional-do-consumidor-multa-banco-por-utilizar-dados-sem-consentimento-de-consumidores-idosos.
[111] See http://www.procon.mt.gov.br/-/17501890-procon-estadual-multa-rede-de-farmacias-por-infracao-a-lei-de-protecao-de-dados-pessoais.
[112] See http://www.bcra.gov.ar/Noticias/Ciberincidentes-lineamientos-para-respuesta-y-recuperacion.asp.
[113] See https://www.ciberseguridad.gob.cl/media/2021/11/Ciberguía-para-pymes.pdf.
[114] See https://www.dinardap.gob.ec/dos-anos-tienen-las-entidades-publicas-y-empresas-privadas-para-adaptar-sus-procesos-a-la-ley-de-proteccion-de-datos-personales/.
[115] See https://www.antai.gob.pa/reglamentan-ley-81-de-proteccion-de-datos-personales/.
[116] See http://silpy.congreso.gov.py/expediente/123459.
[117] See https://www.gub.uy/unidad-reguladora-control-datos-personales/institucional/normativa/resolucion-n-23021 and https://www.gub.uy/unidad-reguladora-control-datos-personales/institucional/normativa/resolucion-n-41021.
The following Gibson Dunn lawyers assisted in the preparation of this article: Alejandro Guerrero in Brussels; Ahmed Baladi, Vera Lukic, Clémence Pugnet, and Lena Bionducci in Paris; Connell O’Neil, Nicholas Hay, and Jocelyn Shih in Hong Kong; Kai Gesing in Munich; and Alex Southwell, Ryan Bergsieker, and Cassandra Gaedt-Sheckter in the United States.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding these developments. Please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work, the authors, or any member of the firm’s Privacy, Cybersecurity and Consumer Protection practice group:
Europe
Ahmed Baladi – Co-Chair, PCDI Practice, Paris (+33 (0)1 56 43 13 00, abaladi@gibsondunn.com)
James A. Cox – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4250, jacox@gibsondunn.com)
Patrick Doris – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4276, pdoris@gibsondunn.com)
Kai Gesing – Munich (+49 89 189 33 180, kgesing@gibsondunn.com)
Bernard Grinspan – Paris (+33 (0)1 56 43 13 00, bgrinspan@gibsondunn.com)
Penny Madden – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4226, pmadden@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Walther – Munich (+49 89 189 33-180, mwalther@gibsondunn.com)
Alejandro Guerrero – Brussels (+32 2 554 7218, aguerrero@gibsondunn.com)
Vera Lukic – Paris (+33 (0)1 56 43 13 00, vlukic@gibsondunn.com)
Sarah Wazen – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4203, swazen@gibsondunn.com)
Asia
Kelly Austin – Hong Kong (+852 2214 3788, kaustin@gibsondunn.com)
Connell O’Neill – Hong Kong (+852 2214 3812, coneill@gibsondunn.com)
Jai S. Pathak – Singapore (+65 6507 3683, jpathak@gibsondunn.com)
United States
Alexander H. Southwell – Co-Chair, PCDI Practice, New York (+1 212-351-3981, asouthwell@gibsondunn.com)
Debra Wong Yang – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7472, dwongyang@gibsondunn.com)
Matthew Benjamin – New York (+1 212-351-4079, mbenjamin@gibsondunn.com)
Ryan T. Bergsieker – Denver (+1 303-298-5774, rbergsieker@gibsondunn.com)
Cassandra L. Gaedt-Sheckter – Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5203, cgaedt-sheckter@gibsondunn.com)
Howard S. Hogan – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3640, hhogan@gibsondunn.com)
Kristin A. Linsley – San Francisco (+1 415-393-8395, klinsley@gibsondunn.com)
H. Mark Lyon – Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5307, mlyon@gibsondunn.com)
Karl G. Nelson – Dallas (+1 214-698-3203, knelson@gibsondunn.com)
Ashley Rogers – Dallas (+1 214-698-3316, arogers@gibsondunn.com)
Deborah L. Stein – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7164, dstein@gibsondunn.com)
Eric D. Vandevelde – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7186, evandevelde@gibsondunn.com)
Benjamin B. Wagner – Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5395, bwagner@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Li-Ming Wong – San Francisco/Palo Alto (+1 415-393-8333/+1 650-849-5393, mwong@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
With the backdrop of the continuing COVID-19 pandemic and high M&A volume, 2021 presented new issues for dealmakers. Hear from seasoned practitioners on how deals are getting done and the issues being confronted. This discussion covers various M&A-related topics, including the following:
• Key deal issues to navigate in light of increased antitrust regulatory scrutiny;
• Limitations on liability for fraud;
• Clauses to include in deal documents to avoid pitfalls; and
• Current state of play for SPAC transactions, and forecasts for the future.
PANELISTS:
Quinton C. Farrar is a corporate partner in the New York office of Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher. Mr. Farrar advises public and privately held companies, including private equity sponsors and their portfolio companies, investors, financial advisors, boards of directors and individuals in connection with a wide variety of complex corporate matters, including mergers and acquisitions, asset sales, leveraged buyouts, spin-offs, joint ventures and minority investments and divestitures. He also has substantial experience advising clients on corporate governance issues as well as in advising issuers and underwriters in connection with public and private issuances of debt and equity securities.
Abtin Jalali is a partner in the San Francisco office of Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher. He is a member of Gibson Dunn’s Private Equity and Mergers and Acquisitions Practice Groups. Mr. Jalali has extensive experience representing private equity firms and their portfolio companies in all aspects of their businesses, with a focus on mergers and acquisitions, divestitures, growth equity investments, minority investments and general corporate matters. Mr. Jalali’s representative private equity clients include Serent Capital, True Wind Capital, TPG Capital, FTV Capital, Gryphon Investors and Tower Arch Capital.
Robert B. Little is a partner in Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher’s Dallas office. He is a Global Co-Chair of the Mergers and Acquisitions Practice Group. Mr. Little has consistently been named among the nation’s top M&A lawyers every year since 2013 by Chambers USA. Admired by clients as “very efficient, always knowledgeable in the subjects with immediate recommendations for action” and “an excellent corporate attorney well suited for negotiating tough deals” (Chambers, 2021), his practice focuses on corporate transactions, including mergers and acquisitions, securities offerings, joint ventures, investments in public and private entities, and commercial transactions. Mr. Little has represented clients in a variety of industries, including energy, retail, technology, infrastructure, transportation, manufacturing, and financial services.
Kristen P. Poole is a corporate partner in the New York office of Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher, where her practice focuses on mergers and acquisitions and private equity. Ms. Poole represents both public and private companies, as well as financial sponsors, in connection with mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, minority investments, restructurings and other complex corporate transactions. She also advises clients with respect to general corporate governance matters and shareholder activism matters.
MCLE CREDIT INFORMATION:
This program has been approved for credit in accordance with the requirements of the New York State Continuing Legal Education Board for a maximum of 1.0 credit hour, of which 1.0 credit hour may be applied toward the areas of professional practice requirement. This course is approved for transitional/non-transitional credit.
Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP certifies that this activity has been approved for MCLE credit by the State Bar of California in the amount of 1.0 hour.
Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP is authorized by the Solicitors Regulation Authority to provide in-house CPD training. This program is approved for CPD credit in the amount of 1.0 hour. Regulated by the Solicitors Regulation Authority (Number 324652).
Application for approval is pending with the Colorado, Illinois, Texas, Virginia and Washington State Bars.
Most participants should anticipate receiving their certificates of attendance via e-mail in approximately 4-6 weeks following the webcast.
Members of the Virginia Bar should anticipate receiving the applicable certification forms in approximately 6-8 weeks.
On January 27, 2022, the Supreme Court of California issued a decision that changes the burden for employers that are defending against current or former employees’ whistleblower retaliation claims. In Lawson v. PPG Architectural Finishes, Inc., No. S266001,___ Cal.5th ___, the Court answered a question that the Ninth Circuit had certified in an effort to dispel “widespread confusion” over the evidentiary standard for retaliation claims bought under California Labor Code section 1102.5. Some courts had concluded the traditional burden-shifting framework set out in McDonnell Douglas Corp. v. Green (1972) 411 U.S. 792, should apply, with plaintiffs having to prove that they were retaliated against for a pretextual reason. Others had decided that the more employee-friendly California Labor Code section 1102.6 should apply, with employers having to prove by clear and convincing evidence that the plaintiffs would have suffered the challenged consequence (such as losing their jobs) even if they had not identified any wrongdoing. The California Supreme Court sided with the latter group, holding that section 1102.6’s framework applies both on summary judgment and at trial.
In Lawson, the plaintiff sued his former employer under section 1102.5 for firing him after he complained of allegedly fraudulent practices. The district court granted the employer’s motion for summary judgment on the ground that the plaintiff failed to demonstrate that the employer’s stated reasons for termination, including poor performance, were pretextual.
The issue on appeal was the appropriate framework for Lawson’s claim. The district court applied McDonnell Douglas’s three-part burden-shifting framework: (1) the employee establishes a prima facie case of retaliation; (2) the burden of production shifts to the employer to articulate a legitimate reason for its decision; and (3) the burden shifts back to the employee to show that that the employer’s reason is pretextual. Lawson argued the district court instead should have followed section 1102.6’s two-part framework, which mirrors the analysis required for retaliation claims brought under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and related federal statutes: (1) the employee demonstrates (by a preponderance of the evidence) that retaliation was a “contributing factor” in the adverse employment action, and (2) the burden shifts to the employer to prove (by clear and convincing evidence) that the adverse action would have occurred even if the employee had not engaged in protected conduct. The Ninth Circuit certified the question to the California Supreme Court because, it observed, the “state’s appellate courts do not follow a consistent practice.”
In a unanimous decision written by Justice Leondra Kruger, the Court held that section 1102.6 governs section 1102.5 retaliation claims. The Court anchored its conclusion in the statutory text: The statute “[b]y its terms” specifies “the applicable substantive standards and burdens of proof.” The statute’s legislative history, by contrast, “yields no clear answers on the McDonnell Douglas question.” The Court also observed that the McDonnell Douglas framework is not “well suited” to employee-whistleblower claims because while McDonnell Douglas presumes an employer’s reason for adverse action “is either discriminatory or legitimate,” a section 1102.5 plaintiff can prove unlawful retaliation “even when other, legitimate factors also contributed to the adverse action.” Finally, the Court rejected the employer’s argument that the McDonnell Douglas framework should apply at least during the summary judgment stage, explaining that “the parties’ burdens of proof at summary judgment generally depend on their burdens of proof at trial.”
The Court’s decision changes the burden that employers must satisfy in attempting to prove that they took adverse employment actions for legitimate, nonretaliatory reasons. Under McDonnell Douglas, an employer has to show only a legitimate, nonretaliatory reason for its decision, at which point the burden shifts to the employee to prove that reason is pretextual. But under section 1102.6, an employer must instead prove, by “clear and convincing” evidence, that it would have taken the same action against the employee “even had the plaintiff not engaged in protected activity.” Section 1102.6 thus makes it easier for employees alleging retaliation to prove their case and avoid summary judgment. Yet the Court’s decision did not change plaintiffs’ burden to establish, by a preponderance of the evidence, that their protected activity “was a contributing factor in a contested employment action.” The Court also made clear that under the section 1102.6 framework, employers will “be able to raise a same-decision defense on summary judgment,” allowing courts to dismiss “meritless” retaliation claims before trial.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have about these matters or regarding developments at the California Supreme Court or in state or federal appellate courts in California. Please feel free to contact any member of the Appellate and Constitutional Law or Labor and Employment practice groups, or the following appellate lawyers in California:
Theodore J. Boutrous, Jr. – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7000, tboutrous@gibsondunn.com)
Julian W. Poon – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7758, jpoon@gibsondunn.com)
Theane Evangelis – Co-Chair, Litigation Group, Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7726, tevangelis@gibsondunn.com)
Bradley J. Hamburger – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7658, bhamburger@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Holecek – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7018, mholecek@gibsondunn.com)
Daniel R. Adler – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7634, dadler@gibsondunn.com)
Ryan Azad – San Francisco (+1 415-393-8276, razad@gibsondunn.com)
Matt Aidan Getz – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7754, mgetz@gibsondunn.com)
Matthew Ball – Denver (+1 303-298-5731, mnball@gibsondunn.com)
Please also feel free to contact the following Labor and Employment practice leaders and members:
Harris M. Mufson – Co-Head, Whistleblower Team of Labor & Employment Group, New York (+1 212-351-3805, hmufson@gibsondunn.com)
Jason C. Schwartz – Co-Chair, Labor & Employment Group, Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8242, jschwartz@gibsondunn.com)
Katherine V.A. Smith – Co-Chair, Labor & Employment Group, Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7107, ksmith@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
We are pleased to present Gibson Dunn’s ninth “Federal Circuit Year In Review,” providing a statistical overview and substantive summaries of the 76 precedential patent opinions issued by the Federal Circuit between August 1, 2020 and July 31, 2021. This term included significant panel decisions in patent law jurisprudence with regard to standing (ABS Global, Inc. v. Cytonome/ST, LLC, 984 F.3d 1017 (Fed. Cir. 2021) and Gen. Elec. Co. v. Raytheon Techs. Corp., 983 F.3d 1334 (Fed. Cir. 2020)); subject matter eligibility (cxLoyalty, Inc. v. Maritz Holdings Inc., 986 F.3d 1367 (Fed. Cir. 2021) and Illumina, Inc. v. Ariosa Diagnostics, Inc., 967 F.3d 1319 (Fed. Cir. 2020)); venue (In re Samsung Elecs. Co., 2 F.4th 1371 (Fed. Cir. 2021) and Valeant Pharms. N. Am. LLC v. Mylan Pharms. Inc., 978 F.3d 1374 (Fed. Cir. 2020)); IPR procedures (Facebook, Inc. v. Windy City Innovations, LLC, 973 F.3d 1321 (Fed. Cir. 2020)); and public accessibility of prior art (M & K Holdings, Inc. v. Samsung Elecs. Co., 985 F.3d 1376 (Fed. Cir. 2021) and VidStream LLC v. Twitter, Inc., 981 F.3d 1060 (Fed. Cir. 2020)). Each of these decisions, as well as all other precedential decisions issued by the Federal Circuit in the 2020‒2021 term, is summarized in the Federal Circuit Year In Review.
Use the Federal Circuit Year In Review to find out:
- The easy-to-use Table of Contents is organized by substantive issue, so that the reader can easily identify all of the relevant cases bearing on the issue of choice.
- Which issues may have a better chance (or risk) on appeal based on the Federal Circuit’s history of affirming or reversing on those issues in the past.
- The average length of time from issuance of a final decision in the district court and docketing at the Federal Circuit to issuance of a Federal Circuit opinion on appeal.
- What the success rate has been at the Federal Circuit if you are a patentee or the opponent based on the issue being appealed.
- The Federal Circuit’s history of affirming or reversing cases from a specific district court.
- How likely a particular panel may be to render a unanimous opinion or a fractured decision with a majority, concurrence, or dissent.
- The Federal Circuit’s affirmance/reversal rate in cases from the district court, ITC, and the PTO.
The Year In Review provides statistical analyses of how the Federal Circuit has been deciding precedential patent cases, such as affirmance and reversal rates (overall, by issue, and by District Court), average time from lower tribunal decision to key milestones (oral argument, decision), win rate for patentee versus opponent (overall, by issue, and by District Court), decision rate by Judge (number of unanimous, majority, plurality, concurring, or dissenting opinions), and other helpful metrics. The Year In Review is an ideal resource for participants in intellectual property litigation seeking an objective report on the Court’s decisions.
Gibson Dunn is nationally recognized for its premier practices in both Intellectual Property and Appellate litigation. Our lawyers work seamlessly together on all aspects of patent litigation, including appeals to the Federal Circuit from both district courts and the agencies.
Please click here to view the FEDERAL CIRCUIT YEAR IN REVIEW
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding developments at the Federal Circuit. Please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work or the authors of this alert:
Mark A. Perry – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3667, mperry@gibsondunn.com)
Nathan R. Curtis – Dallas (+1 214-698-3423, ncurtis@gibsondunn.com)
Florina Yezril – New York (+1 212-351-2689, fyezril@gibsondunn.com)
Please also feel free to contact any of the following practice group co-chairs or any member of the firm’s Appellate and Constitutional Law or Intellectual Property practice groups:
Appellate and Constitutional Law Group:
Allyson N. Ho – Dallas (+1 214-698-3233, aho@gibsondunn.com)
Mark A. Perry – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3667, mperry@gibsondunn.com)
Intellectual Property Group:
Kate Dominguez – New York (+1 212-351-2338, kdominguez@gibsondunn.com)
Y. Ernest Hsin – San Francisco (+1 415-393-8224, ehsin@gibsondunn.com)
Josh Krevitt – New York (+1 212-351-4000, jkrevitt@gibsondunn.com)
Jane M. Love, Ph.D. – New York (+1 212-351-3922, jlove@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
In February and March 2021, we published updates on global legislative developments in relation to mandatory human rights due diligence and supply chain reporting (see here and here).
At that time, it was expected that the European Commission (“EC”) would publish draft legislation at the pan-European level in the form of a Sustainable Corporate Governance proposal (“SCG”) in Summer 2021. The anticipated draft directive was hailed as a potential game-changer: directing how companies should manage matters in their own operations and value chains as regards human rights, climate change and the environment, and related governance.
By comparison, fewer material developments have arisen in the United States, with the most notable change to the law in this field in recent years being the California Transparency in Supply Chains Act 2010. But the landscape may be changing, both with the recently passed federal Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act and a new proposed law pending in New York State (the draft “Fashion Sustainability and Social Accountability Act”) that may impose significant reporting requirements on the fashion industry.
Pan-European Developments – EC draft legislation significantly delayed
As it stands, the EC draft directive has not yet been handed down and updates on its status have not been forthcoming from the EC. However, it is reported that the delay is a result of a (second) rejection by the EC’s internal Regulatory Scrutiny Board (an independent body charged with quality control and impact assessment of legislation). The latest indications by the EC are that the draft directive is now expected in February 2022.
Unsurprisingly, this delay has been met with widespread condemnation and concern from civil society. For example, on 8 December 2021, in an open letter signed by 47 civil society and trade union organizations to EC President Ursula von der Leyen (see here), complaints were made about delays to a “crucial new law that can help millions of people to demand justice against human rights violations…” and expressing “dee[p] concer[n]” about the “complete lack of transparency on the reasons for this new delay”. The letter called on the President to “publicly reiterate [the] commitment … to making supply chains of companies active on the EU market sustainable through ambitious, binding human rights and environmental due diligence legislation”.
US Developments – Groundbreaking draft legislation proposed
Meanwhile, in the US, human rights due diligence legislation has advanced with two meaningful developments.
On the federal level, on 23 December 2021, President Biden signed the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (the “UFLPA”) into law. The UFLPA creates a rebuttable presumption that all goods manufactured – even partially – in China’s Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region are the product of forced labor and therefore not entitled to entry at US ports. The UFLPA also builds on prior legislation, such as the Uyghur Human Rights Policy Act of 2020, by expanding that Act’s authorization of sanctions to cover foreign individuals responsible for human rights abuses related to forced labor in the Xinjiang region. We explore the UFLPA in detail in our client alert, here.
On the state level, earlier this month, two New York State Senators introduced historic legislation to set broad sustainability mandates for the fashion industry – an industry which is (according to some estimates) responsible for approximately 4-8.6% of global greenhouse gas emissions. The Fashion Sustainability and Social Accountability Act (the “FSSAA”), sponsored by Senator Alessandra Biaggi and assembly member Dr. Anna Kelles, is a proposal that, if enacted, would require fashion retailers and manufacturers doing business in New York State with annual global gross revenues that exceed $100 million to publish extensive disclosures on their websites about their “environmental and social due diligence policies, processes and outcomes, including significant real or potential adverse environmental and social impacts” (see here). The FSSAA would therefore place obligations on many household fashion names and brands based around the world.
The disclosures under the draft FSSAA include, among other things: (i) supply chain mapping of at least 50% of suppliers by volume across all tiers of production; (ii) a “sustainability report” identifying each business’s risks, as informed by United Nations and International Labor Organization principles; (iii) independently verified greenhouse gas reporting; and (iv) quantitative measures, such as publishing the median wages of workers of suppliers compared with the local minimum wage. The FSSAA requires that all disclosures be made on the retail or manufacturer’s website within a year of the legislation’s enactment into law.
In terms of enforcement, the FSSAA, if passed, would require New York’s Attorney General (“AG”) to publish an annual report regarding companies’ compliance with the law. And, if enacted, failure to meet the legislation’s requirements would result in the AG having the power to fine sellers and manufacturers up to 2% of annual revenues of $450 million or more. Such money will then be deposited into a community benefit fund, which will be used for environmental projects that directly and verifiably benefit environmental justice communities.
While legislation can take years, advocates are hoping that the bill is passed by Spring 2022 and certainly no later than the end of the 2022 New York State legislative session in June. The legislation has four cosponsors and is currently pending before the New York House Consumer Affairs and Protection and Senate Consumer Protection Committees and, if it advances out of committee, it will be voted on by the full legislative body.
Conclusion
These initiatives in the US are a further indication of the general direction of evolving due diligence expectations. If enacted, the FSSAA would not only make waves in the fashion world, but could also foreshadow legislation requiring ESG disclosures for other industries in the US.
With this in mind, together with the anticipated EC legislation and individual country developments, companies should continue to reflect on their knowledge of their own supply chains, human rights and environmental risks within their business, and internal due diligence processes/compliance methodologies. The expectations of companies in terms of their substantive management of environmental and human rights risks, as well as their reporting obligations, looks set only to increase.
This alert has been prepared by Susy Bullock, Stephanie Collins, and Ryan Butcher* in London; and Roscoe Jones, Jr., Howard S. Hogan, Perlette Michèle Jura, and Jessica C. Benvenisty in the United States.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding these developments. Please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work, any member of the firm’s Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) practice, or the following authors in London and the US:
Susy Bullock – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4283, sbullock@gibsondunn.com)
Stephanie Collins – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4216, SCollins@gibsondunn.com)
Roscoe Jones, Jr. – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3530, rjones@gibsondunn.com)
Howard S. Hogan – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3640, hhogan@gibsondunn.com)
Perlette M. Jura – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7121, pjura@gibsondunn.com)
Jessica C. Benvenisty – New York (+1 212-351-2415, jbenvenisty@gibsondunn.com)
Please also feel free to contact the following ESG practice leaders:
Susy Bullock – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4283, sbullock@gibsondunn.com)
Elizabeth Ising – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8287, eising@gibsondunn.com)
Perlette M. Jura – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7121, pjura@gibsondunn.com)
Ronald Kirk – Dallas (+1 214-698-3295, rkirk@gibsondunn.com)
Michael K. Murphy – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8238, mmurphy@gibsondunn.com)
Selina S. Sagayam – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4263, ssagayam@gibsondunn.com)
* Ryan Butcher is a trainee solicitor working in the firm’s London office who is not yet admitted to practice law.
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
On the heels of a record-setting 2020, the year 2021 saw a more modest pace of Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”) enforcement, particularly as it relates to corporate actions. The inevitable slowdown from any changeover in presidential administrations, combined with the lingering impacts of the global pandemic, undoubtedly contributed to this phenomenon. But with the Biden Administration doubling down on the strategic importance of global anti-corruption enforcement, and with continuing robust FCPA-related enforcement against individuals, we fully anticipate a return to substantial corporate FCPA enforcement in the years to come.
This client update provides an overview of the FCPA and other domestic and international anti-corruption enforcement, litigation, and policy developments from 2021, as well as the trends we see from this activity. Gibson Dunn has the privilege of helping our clients navigate anti-corruption-related challenges every day, and we are honored to have been ranked again this year Number 1 in the Global Investigations Review “GIR 30” ranking of the world’s top investigations practices—Gibson Dunn’s fourth consecutive year and sixth in the last seven years to have been so honored. For more analysis on anti-corruption enforcement and related developments over the past year, we invite you to join us for our upcoming complimentary webcast presentations:
- “FCPA 2021 Year-End Update” on February 1, 2022 (to register, Click Here)
- “Corporate Compliance and U.S. Sentencing Guidelines” on March 30, 2022 (to register, Click Here)
FCPA OVERVIEW
The FCPA’s anti-bribery provisions make it illegal to corruptly offer or provide money or anything else of value to officials of foreign governments, foreign political parties, or public international organizations with the intent to obtain or retain business. These provisions apply to “issuers,” “domestic concerns,” and those acting on behalf of issuers and domestic concerns, as well as to “any person” who acts while in the territory of the United States. The term “issuer” covers any business entity that is registered under 15 U.S.C. § 78l or that is required to file reports under 15 U.S.C. § 78o(d). In this context, foreign issuers whose American Depositary Receipts (“ADRs”) or American Depositary Shares (“ADSs”) are listed on a U.S. exchange are “issuers” for purposes of the FCPA. The term “domestic concern” is even broader and includes any U.S. citizen, national, or resident, as well as any business entity that is organized under the laws of a U.S. state or that has its principal place of business in the United States.
In addition to the anti-bribery provisions, the FCPA also has “accounting provisions” that apply to issuers and those acting on their behalf. First, there is the books-and-records provision, which requires issuers to make and keep accurate books, records, and accounts that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the issuer’s transactions and disposition of assets. Second, the FCPA’s internal controls provision requires that issuers devise and maintain reasonable internal accounting controls aimed at preventing and detecting FCPA violations. Prosecutors and regulators frequently invoke these latter two sections when they cannot establish the elements for an anti-bribery prosecution or as a mechanism for compromise in settlement negotiations. Because there is no requirement that a false record or deficient control be linked to an improper payment, even a payment that does not constitute a violation of the anti-bribery provisions can lead to prosecution under the accounting provisions if inaccurately recorded or attributable to an internal controls deficiency.
International corruption also may implicate other U.S. criminal laws. Increasingly, prosecutors from the FCPA Unit of the Department of Justice (“DOJ”) have been charging non-FCPA crimes such as money laundering, mail and wire fraud, Travel Act violations, tax violations, and even false statements, in addition to or instead of FCPA charges. Without question, the most prevalent amongst these “FCPA-related” charges is money laundering—a generic term used as shorthand for statutory provisions that generally criminalize conducting or attempting to conduct a transaction involving proceeds of “specified unlawful activity” or transferring funds to or from the United States, in either case to promote the carrying on of specified unlawful activity, to conceal or disguise the nature, location, source, ownership or control of the proceeds, or to avoid a transaction reporting requirement. “Specified unlawful activity” includes over 200 enumerated U.S. crimes and certain foreign crimes, including the FCPA, fraud, and corruption offenses under the laws of foreign nations. Although this has not always been the case, in recent years, DOJ has frequently deployed the money laundering statutes to charge “foreign officials” who are not themselves subject to the FCPA. It is now commonplace for DOJ to charge the alleged provider of a corrupt payment under the FCPA and the alleged recipient with money laundering violations.
FCPA AND FCPA-RELATED ENFORCEMENT STATISTICS
The below table and graph detail the number of FCPA enforcement actions initiated by DOJ and the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), the statute’s dual enforcers, during the past 10 years.
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||||||
|
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
|
11 |
12 |
19 |
8 |
17 |
9 |
10 |
10 |
21 |
32 |
29 |
10 |
22 |
17 |
35 |
19 |
21 |
11 |
11 |
4 |
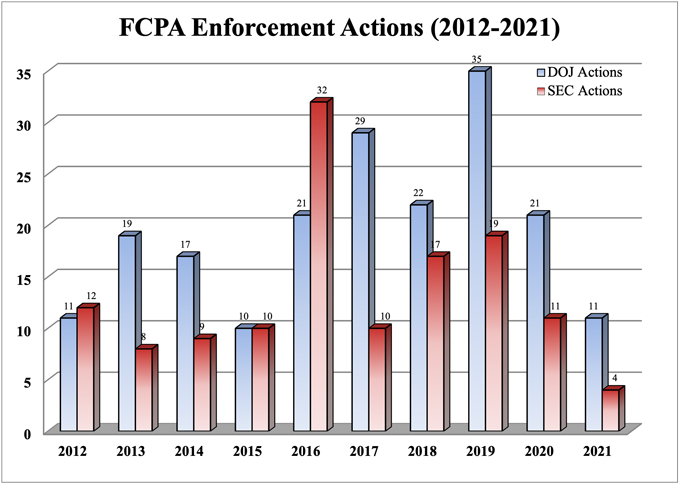
But as our readers know, the number of FCPA enforcement actions represents only a piece of the robust pipeline of international anti-corruption enforcement efforts by DOJ. Indeed, the increasing proportion of “FCPA-related” charges in the overall enforcement docket of FCPA prosecutors is a trend we have been remarking upon for years. In total, DOJ brought 17 such FCPA-related actions in 2021, bringing the overall anti-corruption figures for the past year to 28 cases filed or unsealed by DOJ. The past 10 years of FCPA plus FCPA-related enforcement activity is illustrated in the following table and graph.
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||||||
|
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
DOJ |
SEC |
|
12 |
12 |
21 |
8 |
23 |
9 |
12 |
10 |
27 |
32 |
36 |
10 |
48 |
17 |
54 |
19 |
40 |
11 |
28 |
4 |
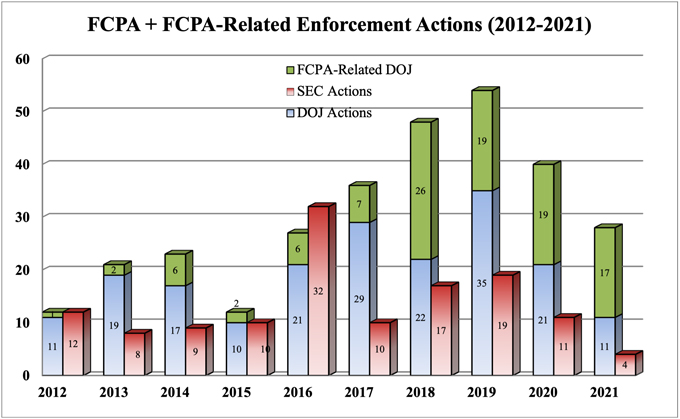
2021 FCPA-RELATED ENFORCEMENT TRENDS
In each of our year-end FCPA updates, we seek not merely to report on the year’s FCPA enforcement actions, but also to distill the thematic trends we see stemming from these individual events. For 2021, we have identified three key enforcement trends that we believe stand out from the rest:
- Sharp downturn in corporate FCPA enforcement actions and financial penalties;
- DOJ continues substantial FCPA and FCPA-related enforcement against individuals; and
- Biden Administration policies foreshadow a return to robust corporate anti-corruption enforcement in the coming years.
Sharp Downturn in Corporate FCPA Enforcement Actions and Financial Penalties
The modern era of FCPA enforcement (often described as beginning with the blockbuster Siemens resolution in 2008) may certainly be characterized by its penchant for setting enforcement records in one year, and then breaking them the next. But this overall trend has not always been linear, and indeed, frequently, there is a drop-off in cases in the years that presidential administrations change. So, it is accurate to say that corporate FCPA enforcement—after reaching new heights of penalties imposed in 2019 ($2.66 billion in corporate penalties on 21 enforcement actions) and 2020 ($2.79 billion in corporate penalties on 16 enforcement actions)—fell off the proverbial cliff in 2021 ($259.5 million on 6 enforcement actions). But we would not go nearly so far as to foretell the demise of corporate anti-corruption enforcement in the years to come. Indeed, based on what we are seeing at DOJ and the SEC, we counsel against such predictions.
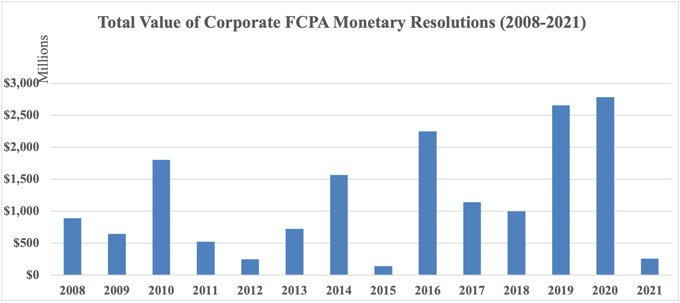
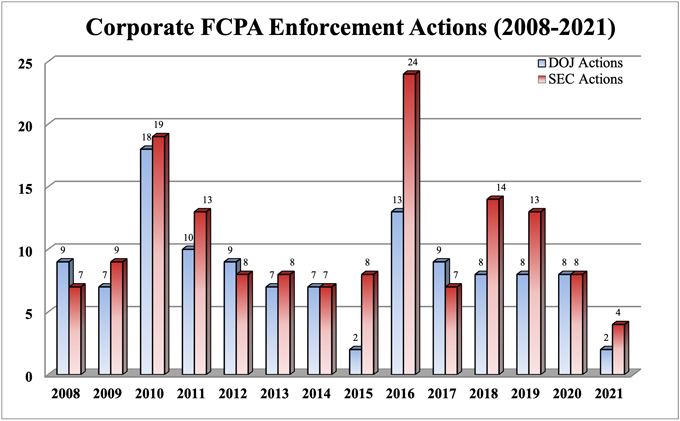
The first corporate FCPA enforcement action of 2021 was with German financial institution and U.S.-issuer Deutsche Bank AG, which on January 8 reached a coordinated FCPA resolution with DOJ and the SEC to resolve allegations of internal control deficiencies and inaccurate record-keeping associated with the use of third-party business development consultants between 2009 and 2016. The DOJ allegations focused on consultants in Abu Dhabi and Saudi Arabia, each of which was allegedly known by Deutsche Bank employees to be relatives or close associates of government officials who would pass portions of their consulting payments on to the officials in exchange for business awarded to the bank. The SEC resolution additionally identified purportedly questionable consulting relationships in China and Italy.
To resolve the criminal charges, Deutsche Bank entered into a three-year deferred prosecution agreement with DOJ alleging conspiracy to violate each of the FCPA’s books-and-records and internal controls provisions, as well as a separate wire fraud conspiracy charge associated with an unrelated commodities trading scheme that was charged together with the FCPA matter. For the FCPA misconduct, the bank paid a criminal penalty of $79.6 million, which represented a 25% discount from the middle of the U.S. Sentencing Guidelines range—this was the maximum discount for cooperation (in a non-voluntary disclosure case), but the discount was taken from the middle rather than the bottom of the range because of a prior criminal antitrust resolution in 2016. To resolve the SEC charge, Deutsche Bank consented to the entry of an administrative cease-and-desist order charging FCPA accounting violations and agreed to pay $43.3 million in disgorgement and prejudgment interest. Gibson Dunn represented Deutsche Bank in these matters.
On June 25, 2021, global engineering firm Amec Foster Wheeler Ltd. (“AFW”), which during the relevant period was principally based in the UK but traded on a U.S. exchange, reached a $177 million coordinated resolution with anti-corruption authorities in Brazil, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The U.S. charging documents allege that between 2011 and 2014, an AFW subsidiary used several agents—including one that failed AFW’s due diligence process based on compliance concerns, but nonetheless continued working “unofficially” on the project—to make more than $1 million in improper payments to win a contract with state-owned oil company Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. (“Petrobras”).
On the U.S. front, to resolve the SEC’s investigation, AFW consented to the entry of an administrative cease-and-desist order charging FCPA bribery and accounting violations and ordering $22.76 million in disgorgement and prejudgment interest. To resolve a criminal FCPA bribery conspiracy charge, a UK subsidiary of AFW entered into a three-year deferred prosecution agreement with DOJ and agreed to a criminal penalty of $18.375 million. Both the SEC and DOJ applied offsetting credits for payments to authorities in Brazil and the UK in connection with the coordinated resolution, bringing the total due to the SEC to $10.13 million and $7.66 million to the United States. The Petrobras-related allegations were only a part of a larger anti-corruption resolution reached by the UK AFW subsidiary and the SFO, which as described in our UK section below imposed the USD-equivalent of $142.7 million in penalties and disgorgement for alleged improper payments in India, Malaysia, Nigeria, and Saudi Arabia, as well as Brazil, as part of its own, separate three-year deferred prosecution agreement. The U.S. resolutions, which were coordinated by Gibson Dunn, acknowledged AFW’s cooperation and remediation by applying the maximum available 25% discount from the bottom of the U.S. Sentencing Guidelines range and not requiring an independent compliance monitor.
The third corporate FCPA enforcement action of 2021, and the only one that was resolved solely with civil SEC charges, was with WPP Plc, the world’s largest advertising group and an ADS issuer. On September 24, 2021, the SEC announced that WPP consented to the entry of a cease-and-desist order charging FCPA bribery and accounting violations, and agreed to pay $10.1 million in disgorgement, $1.1 million in prejudgment interest, and an $8 million civil penalty, without admitting or denying the SEC’s allegations.
According to the SEC’s charging document, prior to 2018, WPP deployed a global growth strategy by which it entered markets through acquisitions of smaller advertising agencies, frequently with an “earn-out provision” that deferred a portion of the purchase price pending the accomplishment of future financial goals, which in many cases the acquired agency’s founder stayed on to achieve. These newly acquired agencies and their founders were the focus of this enforcement action, with the SEC alleging improper payments in Brazil, China, India, and Peru. A DOJ investigation reportedly is ongoing, and it is not clear whether additional charges are forthcoming.
Closing out the year in corporate FCPA enforcement, on October 19, 2021 Swiss financial institution and ADR issuer Credit Suisse Group AG agreed to an FCPA resolution with the SEC and a related non-FCPA, wire fraud resolution with DOJ. The DOJ and SEC allegations concern the same Mozambique loan bribery and kickback scheme that we first reported in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, wherein we described FCPA and FCPA-related charges against three Credit Suisse bankers, two former Mozambican government officials and a business consultant, as well as two Lebanese former executives of a UAE shipbuilding company. The allegations are that between 2013 and 2016, the defendants structured three syndicated loan and securities offerings worth $2 billion involving Mozambican state-owned entities, from which at least $200 million was allegedly misappropriated for bribes and kickbacks to the scheme participants.
To resolve the SEC’s charges, Credit Suisse consented to an administrative cease-and-desist proceeding alleging violations of the FCPA’s accounting provisions, as well as fraud-based securities violations, and agreed to pay combined disgorgement and prejudgment interest of $34 million plus a $65 million civil penalty. To resolve the criminal investigation, Credit Suisse entered into a three-year deferred prosecution agreement with DOJ concerning, and a UK subsidiary pleaded to, wire fraud charges, and agreed to pay a cumulative criminal fine of $247.5 million, plus $10.34 million in criminal forfeiture. After applying a variety of offsets, Credit Suisse ultimately agreed to pay $99 million to the SEC, $175 million to DOJ, and $200 million to the UK Financial Conduct Authority (“FCA”) in a related resolution. The bank also agreed to forgive $200 million in debt owed by the Government of Mozambique, which the prosecutors and regulators considered, together with Credit Suisse’s remediation and cooperation efforts, in setting the $475 million combined resolution amount.
DOJ Continues Substantial FCPA and FCPA-Related Enforcement Against Individuals
DOJ filed or unsealed FCPA or FCPA-related charges against 25 individual defendants in 2021, which may be grouped as follows.
Ecuadorian Police Pension Fund Defendants
On March 2, 2021, DOJ announced the arrest of Ecuadorian citizens John Luzuriaga Aguinaga and Jorge Cherrez Miño for their alleged roles in a long-running bribery scheme involving the Instituto de Seguridad Social de la Policia Nacional (“ISSPOL”), Ecuador’s public police pension fund. DOJ alleges that from 2014 to 2020, Cherrez, an investment advisor with operations in Florida and Panama, paid more than $2.6 million in bribes to ISSPOL officials, including now-former ISSPOL Risk Director Luzuriaga, in exchange for the right to manage ISSPOL funds. Two-and-a-half months later, on May 19, 2021, Ecuadorian investment company manager Luis Alvarez Villamar pleaded guilty to money laundering conspiracy for his role in accepting funds from Cherrez in connection with the ISSPOL corruption scheme. Luzuriaga is currently scheduled for trial on money laundering charges in the Southern District of Florida in February 2022, and Cherrez is considered a fugitive on his pending FCPA bribery and money laundering charges.
Additional PDVSA (Citgo) Charges
For years, we have been covering a multi-faceted corruption investigation by DOJ with the common nucleus being Venezuelan state-owned oil company Petróleos de Venezuela S.A. (“PDVSA”). One of the investigation strands has involved a pay-to-play corruption scheme at Citgo Petroleum Corporation, PDVSA’s U.S. subsidiary, as covered most recently in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update. On March 12, 2021, DOJ unsealed money laundering conspiracy charges initially filed two years earlier against another defendant, former Citgo buyer Laymar Giosse Pena-Torrealba. According to the charging documents, Pena-Torrealba accepted bribes from Juan Manuel Gonzalez (who himself pleaded guilty in May 2019) in exchange for helping Gonzalez’s companies to secure contracts with Citgo. Pena-Torrealba pleaded guilty to one count of money laundering conspiracy and was sentenced in November 2021 to three years of probation.
Additional PetroEcuador Charges
We also have been reporting for several years now on a multi-agency investigation into alleged corruption at Ecuador’s state-owned oil company, Empresa Publica de Hidrocarburos del Ecuador (“PetroEcuador”). This has included coordinated charges brought by DOJ and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”) against energy trading firm Vitol, Inc., as well as several of its traders, as covered in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update. On April 6, 2021, DOJ unsealed an August 2020 criminal complaint against Canadian citizen Raymond Kohut, a now-former employee of a different Swiss energy trading firm. According to the charges, two Asian state-owned entities contracted to provide loans to PetroEcuador backed by periodic oil deliveries, and Kohut’s employer negotiated with the Asian entities to market and sell those oil products. Starting in 2012, Kohut and his co-conspirators allegedly made more than $22 million in corrupt payments to PetroEcuador officials to award contracts to the Asian entities under favorable terms so that Kohut’s company could then enter related, advantageous trading agreements with the Asian entities. Kohut and his co-conspirators allegedly met to discuss the conspiracy in Florida, and some of the payments flowed through New York correspondent bank accounts. Kohut pleaded guilty to a single count of money laundering on April 6, 2021, and awaits sentencing.
Additional Odebrecht-Related Charges
The blockbuster multinational anti-corruption resolution with Odebrecht S.A. in 2016, first covered in our 2016 Year-End FCPA Update, continues to be a recurring source of FCPA and FCPA-related charges against individual defendants. On May 20, 2021, DOJ unsealed money laundering charges against Austrian citizens and bank executives Peter Weinzierl and Alexander Waldstein. The indictment alleges that Weinzierl and Waldstein moved more than $170 million through a series of fraudulent transactions and sham agreements from Odebrecht’s New York bank accounts, through Weinzierl’s and Waldstein’s Austrian bank, into accounts at an Antiguan bank allegedly used by Odebrecht as a slush fund used to pay bribes to Brazilian, Mexican, and Panamanian officials. Weinzierl was arrested on May 25, 2021 in the United Kingdom, where he is currently undergoing extradition proceedings. Waldstein remains at large.
Chadian Oil Rights Defendants
On May 24, 2021, DOJ announced the indictment of two diplomats from Chad—Mahamoud Adam Bechir and Youssouf Hamid Takane—Bechir’s wife Nouracham Bechir Niam, and the founder of a Canadian energy company, Naeem Riaz Tyab, all on FCPA or FCPA-related charges stemming from an alleged bribery scheme relating to the award of oil rights in the Republic of Chad. According to the indictment, while serving in Washington, D.C. as Chad’s Ambassador to the United States and Canada and Deputy Chief of Mission, respectively, Bechir and Takane collectively solicited and accepted $2 million in bribes, plus corporate shares, in exchange for awarding Tyab’s company oil rights worth tens of millions of dollars. Bechir’s wife Niam was allegedly brought into the scheme when Tyab received legal advice not to enter a consulting contract with a company owned by Bechir, and so instead, entered into substantially the same consulting contract with a company owned by Niam, in addition to awarding Niam substantial shares in Tyab’s company. Tyab and Niam were both charged with conspiracy to violate the FCPA, and all four defendants were charged with conspiracy to commit money laundering.
The indictment was initially handed down in February 2019, shortly before Tyab was arrested in New York City. According to court documents, Tyab immediately began cooperating and pleaded guilty in April 2019. But the case remained sealed as DOJ sought to obtain custody of the other three defendants. More than two years later, in May 2021, DOJ acknowledged that its efforts to arrest the other defendants were unlikely to be successful in the near term and moved to unseal the indictment. Further illustrating the long tail of these corruption cases, Tyab’s company—Griffiths Energy International Inc.—pleaded guilty to violations of Canada’s Corruption of Foreign Public Officials Act in 2013 as covered in our 2013 Year-End FCPA Update. Bechir, Takane, and Niam all remain at large, and Tyab is currently scheduled to be sentenced in February 2022.
Bolivian Military Equipment Defendants
Also in May 2021, DOJ announced charges against five individuals in an alleged pay-to-play bribery scheme involving the sale of tactical defense equipment to the Bolivian Ministry of Defense. DOJ alleges that Bryan Berkman, the owner of Bravo Tactical Solutions LLC, his father Luis Berkman, and his business associate Philip Lichtenfeld, all conspired to make over $600,000 in corrupt payments to former Bolivian Minister of Government Arturo Carlos Murillo Prijic and his former Chief of Staff Sergio Rodrigo Mendez Mendizabal in exchange for a $5.6 million contract to supply tear gas and other non-lethal riot equipment to the Ministry of Defense. Four of the five defendants have pleaded guilty—Bryan Berkman and Lichtenfeld to FCPA conspiracy charges and Luis Berkman and Mendez to money laundering conspiracy charges. Murillo is currently set for a May 2022 trial date on a superseding eight-count money laundering indictment.
Nigeria Oil Contract Defendant
On July 26, 2021, DOJ filed a criminal information charging Anthony Stimler, a former West Africa-based oil trader for a Swiss commodity trading and mining firm, with one count each of conspiracy to violate the FCPA’s anti-bribery provisions and money laundering conspiracy. According to the charging document, between 2007 and 2018, Stimler participated in a scheme to bribe employees of the state-owned Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation to obtain contracts for more lucrative grades of oil on better delivery schedules for the commodity trading firm. Stimler has pleaded guilty and is cooperating with DOJ on the ongoing investigation of Stimler’s former employer.
CASA Corruption Defendant
On August 4, 2021, DOJ announced the arrest of Florida businessman Naman Wakil on charges that between 2010 and 2017 he allegedly bribed officials of both PDVSA and Venezuelan state-owned food company Corporación de Abastecimiento y Servicios Agrícola (“CASA”) to secure approximately $250 million in contracts for his companies. Wakil faces substantive and conspiracy FCPA and money laundering charges. He has pleaded not guilty and is currently set for a November 2022 trial date.
Ericsson Djibouti Defendant
On September 8, 2021, DOJ announced the unsealing of a June 2020 FCPA and money laundering conspiracy indictment of former Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson Horn of Africa Account Manager Afework Bereket. According to the indictment, between 2010 and 2014, Bereket participated in a scheme to pay approximately $2.1 million to two high-ranking officials in Djibouti’s executive branch and one employee of a Djibouti state-owned telecommunications company to secure a €20.3 million contract with the state-owned entity. The indictment further alleges that Bereket concealed the bribes by entering a sham consulting contract with a company owned by the spouse of one of the officials, and concealing that ownership interest from others at Ericsson. As first reported in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, in 2019, Ericsson entered into an FCPA resolution with DOJ and the SEC that included the Djibouti scheme. Bereket remains at large.
CLAP Corruption Defendants
On October 21, 2021, DOJ announced a money laundering indictment returned against five defendants stemming from alleged corruption involving Comité Local de Abastecimiento y Producción (“CLAP”), a Venezuelan state-owned and state-controlled food and medicine distribution program. The indictment alleges a scheme involving a staggering $1.6 billion in food and medicine contracts obtained by Colombian businessmen Alvaro Pulido Vargas, Emmanuel Enrique Rubio Gonzalez, and Carlos Rolando Lizcano Manrique, and Venezuelan businesswoman Ana Guillermo Luis obtained through corrupt payments to the then-governor of Venezuelan State Táchira, Jose Gregorio Vielma-Mora. All five defendants are considered fugitives. Pulido—who additionally faces money laundering charges stemming from a separate pay-to-play scheme described in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update—along with Rubio and Vielma-Mora also were sanctioned by the Office of Foreign Assets Control in 2019 for alleged CLAP-related corruption.
Egyptian Coal Sale Defendant
On November 3, 2021, DOJ charged Frederick Cushmore Jr., the now-former Head of International Sales for a Pennsylvania-based coal mining company, with one count of conspiracy to violate the FCPA’s anti-bribery provisions. According to the criminal information, between 2016 and 2020, Cushmore and others at his company engaged an Egyptian sales agent to secure $143 million in coal contracts with an Egyptian state-owned company, knowing that the agent would provide a portion of his $4.8 million in commissions to officials at the state-owned entity. The information further alleges that Cushmore and others used encrypted messaging applications and commercial email accounts in an effort to avoid detection of their corruption scheme. Cushmore is currently scheduled to be sentenced in the Western District of Pennsylvania in March 2022, but the limited information available publicly suggests additional charges may be forthcoming, which would likely impact that sentencing date.
Biden Administration Policies Foreshadow Return to Robust Corporate Anti-Corruption Enforcement in the Coming Years
As noted above, there may be a slowdown in government enforcement actions that takes place with any change in presidential administrations. Although most prosecutors and enforcement lawyers at DOJ and the SEC are career attorneys who holdover across administrations, the senior political leadership often changes, and that can cause a delay in necessary approvals or willingness to move more significant cases forward until new leadership is in place. This is particularly true for high-profile enforcement activities such as corporate FCPA actions. If there was any lingering doubt, further tempering overreliance on last year’s comparatively low corporate FCPA enforcement rate, the Biden Administration took several notable steps in 2021 that lead us to anticipate a return to robust corporate enforcement in the years to come.
Biden Administration Announces U.S. Strategy on Countering Corruption
On June 3, 2021, the White House published a National Security Study Memorandum that identifies “countering corruption as a core United States national security interest.” The memorandum emphasizes the significant costs of corruption, estimated at between two and five percent of global GDP, as well as its associated impacts on less tangible (but equally important) societal goods, such as rule of law, inequality, trust in government, and national security. The memorandum directed the National Security Advisor and Assistants to the President for Economic Policy and Domestic Policy to conduct a review across numerous government agencies to devise a comprehensive anti-corruption strategy report and recommendations within 200 days.
On December 6, 2021, the Biden Administration released its first-ever “United States Strategy on Countering Corruption.” This 38-page Strategy Memorandum is structured around five “pillars”: (1) “modernizing, coordinating, and resourcing U.S. Government efforts to fight corruption”;
(2) “curbing illicit finance”; (3) “holding corrupt actors accountable”; (4) “preserving and strengthening the multilateral anti-corruption architecture”; and (5) “improving diplomatic engagement and leveraging foreign assistance to advance policy goals.” The Strategy Memorandum further emphasizes that the Biden Administration will pursue “aggressive enforcement action” in support of its anti-corruption objectives through enforcement of the FCPA and other statutes by U.S. enforcers in coordination with foreign law enforcement partners. It also suggests that the Biden Administration will seek additional tools to broaden the reach of its anti-corruption enforcement powers, including through enhanced legislation to target the “demand side” of bribery. The Strategy Memorandum further recognizes the need for increased coordination and synergy between the U.S.’s anti-corruption and anti-money laundering efforts and to address “deficiencies in the U.S. anti-money laundering regime” through the extension of regulatory compliance and reporting requirements to non-financial institution “gatekeepers,” such as lawyers, accountants, and trust and company service providers.
For additional details regarding the Strategy Memorandum, please consult our recent Client Alert, “U.S. Strategy on Countering Corruption Signals Focus on Enforcement.” And for further details on the Biden Administration’s overall approach to anti-corruption enforcement, please consult our Client Alert “Big Changes Afoot for FCPA and Anti-Bribery Enforcement?“
Deputy Attorney General Announces Changes to DOJ Criminal Enforcement Policies
In a sign of an increasingly tough approach to corporate enforcement generally, on October 28, 2021, Deputy Attorney General Lisa O. Monaco announced that DOJ is modifying certain corporate criminal enforcement policies. Specifically, these policy changes: (1) restore prior guidance concerning the need for corporations to provide non-privileged information about all individuals involved in misconduct (not just those substantially involved) in order to receive cooperation credit; (2) require prosecutors to consider a corporation’s full criminal, civil, and regulatory record in making charging decisions (not just conduct related to the misconduct at issue in the present case); and (3) make clear that there is no general presumption against monitorships and prosecutors are free to require the imposition of a corporate monitor whenever they determine it appropriate. Further, Monaco highlighted DOJ’s increasing scrutiny of companies that have received pretrial diversion (such as deferred or non-prosecution agreements) in the past, including to determine whether they continue their criminal conduct during the period of those agreements. Close in time to Monaco’s speech, several companies announced that DOJ is investigating breach allegations, including in the FCPA context an announcement by Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson that DOJ determined the company breached its obligations under its deferred prosecution agreement covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update.
Although these policy changes concern general corporate criminal enforcement, they touch closely upon corporate FCPA matters. For further details on Deputy Attorney General Monaco’s speech, please see our recent Client Alert, “Deputy Attorney General Announces Important Changes to DOJ’s Corporate Criminal Enforcement Policies.”
2021 FCPA-RELATED ENFORCEMENT LITIGATION
Following the filing of FCPA or FCPA-related charges, criminal and civil enforcement proceedings can often take years to wind through the courts. A selection of prior-year matters that saw material enforcement litigation developments during 2021 follows.
Two Alleged Fugitives Challenge Their Indictments from Abroad
A recurring theme in FCPA investigations is indictments returned and sometimes unsealed while the defendant is abroad. A frequently litigated issue that arises in these circumstances is whether the defendant is able to challenge the charges—frequently on jurisdictional grounds—from abroad without submitting themselves physically to the Court’s jurisdiction. Courts have reached differing conclusions on whether these challenges are barred by the so-called “fugitive disentitlement” doctrine, including two district court decisions from different circuit courts of appeal going in opposite directions in 2021.
On March 18, 2021, the Honorable Robert N. Scola, Jr. of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Florida denied a motion to enter a special appearance and challenge the indictment filed by Alex Nain Saab Moran, a joint Colombian and Venezuelan national charged with money laundering offenses in connection with a $350 million construction-related bribery scheme in Venezuela as covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update. In January 2021, 18 months after the indictment was returned, Saab moved to vacate his fugitive status with leave to challenge his indictment on the grounds that he is a Venezuelan diplomat entitled to absolute immunity under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, as well as that the indictment does not state an offense given Saab’s lack of connection to the United States. Saab’s motion followed his arrest in the Republic of Cape Verde, where he was detained as his plane stopped for refueling en route from Venezuela to Iran based on an INTERPOL “red notice” request filed by the United States.
Saab argued that the fugitive disentitlement doctrine should not apply because he was not in the United States when the indictment was returned—indeed he asserted he had not been to the United States in nearly three decades, long before the alleged criminal activity—and therefore he could not be correctly described as a fugitive who fled the charges. But Judge Scola disagreed, holding that a defendant who is aware of an indictment and does not appear in court to answer the charges is a fugitive regardless of whether they affirmatively fled the United States to avoid the charges—this concept is known in the Eleventh Circuit as “constructive flight.” The Court denied the motion for a special appearance and declined to consider the substantive motion to dismiss.
Saab has appealed the district court’s ruling, and DOJ has moved to dismiss the appeal. Meanwhile, the Republic of Cabo Verde granted the extradition request and transferred Saab to the United States, where he is now being detained pending trial. To fulfill a condition of the extradition, DOJ dismissed seven of the eight counts against Saab to ensure that the maximum term of imprisonment is consistent with Cabo Verde law.
The case of Daisy Teresa Rafoi Bleuler—a Swiss citizen and wealth manager charged with FCPA and money laundering offenses arising from the transfer of allegedly corrupt proceeds associated with a PDVSA-related bribery scheme covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update—turned out very differently under Fifth Circuit law. Rafoi was arrested by Italian authorities, again on a U.S.-initiated INTERPOL red notice request, as she vacationed with family in Lake Como. As she underwent extradition proceedings, first in Italy and then in Switzerland, Rafoi filed a motion to dismiss the indictment on jurisdictional grounds.
In an opinion dated November 10, 2021, the Honorable Kenneth M. Hoyt of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas made short work of the government’s argument that Rafoi’s motion should not be heard under the fugitive disentitlement doctrine. The Court held that fugitive disentitlement is a discretionary doctrine, and found that where a foreign national challenges the applicability of U.S. law to their actions, without having affirmatively fled the United States, they should be permitted to do so from abroad. Moving to the merits of the motion to dismiss, Judge Hoyt fond that as a matter of law the indictment was deficient in alleging any action by Rafoi in the territory of the United States such as to bring her within the scope of 15 U.S.C. § 78dd-3, that she acted as an agent of U.S. persons under 15 U.S.C. § 78dd-2, or that she engaged in any financial transactions subject to U.S. jurisdiction under the money laundering statutes. Fundamentally, the Court found that neither the FCPA nor the money laundering statutes should be read so broadly as to apply to foreign nationals acting completely outside the United States, and that any other interpretation would lead to serious constitutional due process concerns under the “void for vagueness” doctrine.
On December 7, 2021, DOJ noticed an appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit. We expect this appeal could lead to an important appellate court ruling on the breadth of the FCPA and money laundering statutes as applied to foreign nationals in 2022, likely to be joined by the heavily-anticipated revisitation of the Hoskins case by the Second Circuit Court of Appeals, covered in our 2020 Mid-Year FCPA Update and still pending after an August 17, 2021 argument.
Roger Ng Motion to Dismiss Denied
We reported in our 2018 Year-End FCPA Update on the indictment of former Goldman Sachs banker “Roger” Ng Chong Hwa on FCPA bribery and money laundering conspiracy charges arising from the 1Malaysia Development Berhad (“1MDB”) scandal in Malaysia. In October 2020, after being extradited to the United States to face these charges, Ng filed a comprehensive motion to dismiss, arguing: (1) the superseding indictment returned after his extradition from Malaysia violated the “rule of specialty,” which prohibits material changes to charges post-extradition; (2) venue in the Eastern District of New York was insufficiently alleged in the indictment; (3) the indictment did not meet the requirement of alleging that he was an “agent of an issuer” because the “U.S. Financial Institution #1” described in the indictment—meant to refer to Goldman Sachs—was in fact an “artificial combination” between various Goldman Sachs entities; (4) he could not have circumvented Goldman Sachs’s internal accounting controls because the alleged bribes were paid with 1MDB funds, rather than money from Goldman Sachs; (5) the money laundering count was deficient because it did not specify the particular Malaysia bribery statute alleged to have been violated as the requisite specified unlawful activity; (6) the so-called “silence provision” in Goldman Sachs’s deferred prosecution agreement—a standard term that prohibits companies from contracting the admitted statement of facts—violated his constitutional right to call witnesses in his defense; and (7) he was entitled to Brady disclosures from Goldman Sachs because the bank’s cooperation with DOJ made it a part of the “prosecution team.”
In September 2021, the Honorable Margo Brodie of the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York denied Ng’s motion to dismiss in its entirety in an equally comprehensive, 160-page memorandum opinion. Trial is currently scheduled to commence in February 2022.
SEC Imposes $35,000 Civil Penalty—In a Case from 2016
We reported in our 2016 Year-End FCPA Update on the SEC’s enforcement action against former Och-Ziff CFO Joel M. Frank in which, without admitting or denying the SEC’s findings, Frank agreed to cease and desist from future violations of the FCPA’s books-and-records and internal controls provisions. The parties further agreed that Frank would pay a civil penalty, but in an unusual move left for another day the determination of the penalty amount. That other day came four-and-a-half years later, on March 16, 2021, when the SEC published a new cease-and-desist order imposing a $35,000 civil penalty. The new order also softened some of the allegations against Frank, acknowledging that he “expressed objections” regarding certain of the payments in question, while still taking the position that because Frank allegedly “had final signing authority” for all expenditures he was responsible for causing the company’s accounting violations.
Baptiste and Boncy FCPA Convictions Reversed for Ineffective Assistance of Counsel
We reported in our 2019 Year-End and then 2020 Mid-Year FCPA updates on the jury trial convictions of retired U.S. Army colonel Joseph Baptiste and businessperson Roger Richard Boncy on conspiracy to violate the FCPA and the Travel Act arising from an FBI sting simulating a bribery scheme involving Haitian port project investments, followed by the post-trial grant of a new trial to both defendants based on the ineffective assistance of Baptiste’s counsel infecting the fundamental fairness of the joint trial. DOJ appealed the new trial grants but, on August 9, 2021, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the First Circuit affirmed the district court’s ruling.
On appeal DOJ did not contest the lower court’s deficient-performance findings—which included that Baptiste’s counsel did not open discovery files or share them with his client, did not obtain independent translations of Haitian-Creole audio recordings even after learning of deficiencies in the government’s translations, and did not subpoena any defense witnesses, including experts who could have testified about Haitian law or business practices. Instead, DOJ argued that the “overwhelming” evidence against both defendants was so strong that there was no prejudice based on the deficient performance of Baptiste’s counsel, and even if there was that prejudice did not extend to Boncy, whose counsel was competent. Writing for the First Circuit panel, the Honorable O. Rogeriee Thompson disagreed and held that the focus of Fifth and Sixth Amendment rights to due process and counsel is on the fundamental fairness of the proceeding, which clearly was undermined for both defendants based on the deficient performance of one defendant’s counsel. Both cases have been remanded to the district court and a joint retrial is currently set for July 2022.
2021 FCPA-RELATED LEGISLATIVE AND POLICY DEVELOPMENTS
In addition to the enforcement developments covered above, 2021 saw numerous important developments in FCPA-related legislative and policy areas.
Congress Strengthens SEC Disgorgement Authority
On January 1, 2021, Congress passed the National Defense Authorization Act (“NDAA”) for the 60th consecutive year, overriding a presidential veto from then-President Trump. Included within the nearly 1,500 pages of omnibus legislation, at Section 6501, is an expansion of the SEC’s statutory authority to seek disgorgement. These revisions are clearly a response to recent Supreme Court decisions in Kokesh v. SEC and Liu v. SEC, both of which narrowed the scope of the SEC’s disgorgement power, which (as our readership knows) is a critical driver of the SEC’s ability to penalize corporate and individual misconduct, including in FCPA cases. The Section 6501 changes explicitly authorize the SEC to seek disgorgement in cases filed in federal court, eliminating any residual doubt after Liu. They also extend the statute of limitations from five years to ten years for SEC enforcement actions based on scienter-based claims, a change which applies to both pending cases and enforcement actions initiated after the passage of the NDAA. For further details regarding the impact of Section 6501, please consult our separate Client Alert “Congress Buries Expansion of SEC Disgorgement Authority in Annual Defense Budget.”
Congress Passes Comprehensive Anti-Money Laundering Legislation
The NDAA also included the Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2020 (“AMLA”), which enacted the most consequential set of anti-money laundering reforms since the passage of the USA PATRIOT Act in 2001. As our readership knows, U.S. enforcers increasingly use the money laundering laws to prosecute and pursue proceeds of corruption passed through the U.S. financial system. The AMLA strengthens the government’s ability to investigate and prosecute corruption-related money laundering. Specifically, to limit the practice of using shell companies to launder ill-gotten gains, the AMLA implemented beneficial ownership reporting requirements for certain U.S. entities and foreign entities registered to do business in the United States and tasked the Department of Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (“FinCEN”) with maintaining a beneficial ownership registry of such reported information, which will be available for use by law enforcement agencies. Other changes made by the AMLA include enhancing the government’s ability to investigate money laundering, including by expanding DOJ’s authority to subpoena foreign banks with U.S.-based correspondent banking accounts. For a detailed summary of the most significant changes enacted by the AMLA, please see our separate Client Alert, “The Top 10 Takeaways for Financial Institutions from the Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2020.”
FinCEN Identifies Corruption as a Key National Priority
On June 30, 2021, FinCEN announced its first set of government-wide anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism priorities, which will be updated every four years pursuant to the AMLA. FinCEN developed these priorities in consultation with federal and state regulators, law enforcement, and national security agencies. In its announcement, FinCEN explained that these priorities were meant to identify and describe the most significant money laundering and terrorist financing threats currently facing the United States to both signal FinCEN’s upcoming regulatory priorities and to provide guidance to covered institutions in developing and updating their compliance programs. Although FinCEN’s announcement stated that the priorities were listed in no particular order, it bears noting that corruption was the first priority listed. Consistent with other statements by the U.S. government in 2021, as reported herein, FinCEN identified anti-corruption as “a core national security interest of the United States,” in which anti-money laundering regulation and enforcement plays a crucial role.
New IRS Treatment of FCPA Disgorgement Payments
The U.S. Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) has long prohibited tax deductions for fines or penalties paid to the government for unlawful conduct, including violations of the FCPA. But a question has arisen over the years as to whether disgorgement and forfeiture constitute a fine or penalty such that it is non-deductible. As covered in our 2017 Year-End FCPA Update, the IRS answered that question in the affirmative, issuing an advice memorandum opining that consistent with the Supreme Court’s decision in Kokesh v. SEC, disgorgement is equivalent to a penalty. The December 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, however, revised the Internal Revenue Code to make an exception for amounts paid to the government for restitution, remediation, or to come into compliance with the law. In January 2021, the IRS issued a finalized rule in response to this law, which sets out a multi-factored inquiry to determine whether an amount paid in disgorgement or forfeiture is deductible as restitution or remediation. The requirements are quite stringent and generally inconsistent with DOJ / SEC practice in FCPA resolutions, including a requirement that the payments must be made directly to victims rather than to the U.S. Treasury, potentially continuing to limit the ability of companies to deduct amounts paid as disgorgement or forfeiture in an FCPA enforcement action.
2021 FCPA-RELATED PRIVATE CIVIL LITIGATION
Although the FCPA does not provide for a private right of action, civil litigants have pursued a variety of causes of action in connection with FCPA-related conduct, with varying degrees of success. A selection of matters with material developments in 2021 follows.
Shareholder Lawsuits / Class Actions
- MTS – As covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, Russian telecommunications company and U.S. issuer Mobile TeleSystems PJSC (“MTS”) reached an $850 million joint FCPA resolution with the SEC and DOJ to resolve allegations of corrupt payments to the daughter of the late Uzbek president, to facilitate access to the telecommunications market in Uzbekistan. Shortly after the announcement of this settlement, a class action suit was filed against MTS and several individual defendants in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York, alleging that MTS issued false and misleading statements about the company’s inability to predict the outcome of the U.S. government’s investigations into its Uzbekistan operations, the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls and compliance systems, and its level of cooperation with U.S. regulatory agencies. On March 1, 2021, the Honorable Ann M. Donnelly dismissed the lawsuit, finding that the plaintiffs did not demonstrate that the challenged statements were false or misleading, that MTS could not have predicted the outcome of the investigation, and that its disclosures about the existence of the investigation were not insufficient. Plaintiffs have appealed the dismissal to the Second Circuit Court of Appeals, and the case is currently set for argument in March 2022.
- VEON – We covered in our 2016 Mid-Year FCPA Update an FCPA resolution by then-VimpelCom Ltd. (now VEON Ltd.) in connection with the same Uzbek fact pattern described above for MTS. VEON also found itself faced with a putative class action arising from alleged material omissions in securities filings relating to the adequacy of its internal controls, which also was dismissed in 2021. Specifically, on March 11, the Honorable Andrew L. Carter of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York granted VEON’s motion to dismiss finding that the plaintiffs failed to establish that the company omitted material facts that it had a duty to disclose. This mooted the case as to lead plaintiffs, but the Court reopened the lead plaintiff appointment process, which remains ongoing.
- IFF – In 2018, following an acquisition of Israel-based Frutarom Industries Ltd, International Flavors & Fragrances, Inc. (“IFF”) disclosed that during the integration process it learned that pre-acquisition Frutarom executives had made improper payments in Russia and Ukraine, and that IFF had disclosed the matter to DOJ. Shareholders brought suit against IFF, Frutarom, and certain executives, claiming they lost millions of dollars when the news became public and IFF’s share price dropped. On March 30, 2021, the Honorable Naomi Reice Buchwald of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York dismissed the lawsuit, explaining that the investors failed to show how they were misled by IFF, failed to allege improper conduct during the putative class period, and failed even to adequately allege how the payments by the Israeli company Frutarom violated U.S. law. The plaintiff shareholders have appealed aspects of the decision to the Second Circuit, with oral arguments scheduled for February 2022.
- 500.com – In 2020, shareholders brought suit against Chinese online gaming company and U.S. issuer 500.com Ltd., alleging that company executives made improper payments to Japanese government officials to secure a lucrative gaming license, and then made misrepresentations concerning the same in the company’s public filings, including filings containing the text of its code of conduct. On September 20, 2021, the Honorable Gary R. Brown of the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York granted 500.com’s motion to dismiss, adopting the report and recommendation of Magistrate Judge A. Kathleen Tomlinson. The two decisions together note that only in rare circumstances have courts permitted statements in a code of conduct to survive motions to dismiss and in those rare cases, the statements were made in response to inquiries or challenges to the company’s conduct rather than general, aspirational statements about how the company expects its employees to act. Regarding the alleged misstatements or omissions unrelated to the code of conduct, Judge Tomlinson found that the plaintiff failed to allege scienter adequately and that 500.com was not obligated to disclose uncharged wrongdoing.
- OSI – As reported in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, OSI Systems, Inc. succeeded in dismissing a putative class action lawsuit that arose from a short-seller’s report relating to alleged corruption in connection with an Albanian scanning contract (the underlying conduct of which was declined for prosecution by DOJ and the SEC), but plaintiffs were given leave to amend. Amend they did, and on October 22, 2021, OSI agreed to a $12.5 million settlement to resolve the matter. The October 2021 settlement agreement has received preliminary approval from the Honorable Fernando M. Olguin of the U.S. District Court for the Central District of California, and a final fairness hearing is scheduled for May 2022.
- Cognizant – Another FCPA enforcement case we covered in our 2019 Year End FCPA Update that wound its way towards a private civil resolution in 2021 concerns Cognizant Technology Solutions Corporation. Following an SEC FCPA resolution and DOJ declination with disgorgement arising from an alleged bribery scheme in India, a putative class of investors sued Cognizant in the U.S. District Court for the District of New Jersey. On September 7, 2021, Cognizant reached an agreement-in-principle to a $95 million settlement of the matter, which was approved by the Honorable Esther Salas on December 20, 2021.
Civil Fraud / RICO Actions
- Samsung – We covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update a DOJ FCPA resolution reached by Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. arising from alleged corruption of Petrobras officials in the “Operation Car Wash” investigation. Also in 2019, Petrobras’s U.S. subsidiary filed a RICO / common-law fraud complaint against Samsung in Texas state court, which Samsung removed to federal district court and moved to dismiss. In June 2020, the district court dismissed the complaint on statute-of-limitation grounds, but on August 11, 2021 the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit revived the case, finding that when Petrobras learned (or should have learned) of the corruption allegations such as to begin the clock was a dispute of fact and that Samsung had not conclusively established that Petrobras’s claims accrued before Petrobras filed its complaint. Following the Fifth Circuit’s remand, the case is now back before the Honorable Lee H. Rosenthal of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas.
- Ericsson – In an unfiled (but still quite noteworthy) action, on May 12, 2021 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson announced that it had reach an agreement to pay competitor Nokia Corporation $97 million to settle potential damages claims arising from the events that were the subject of Ericsson’s FCPA 2019 resolution with DOJ and the SEC. That resolution, covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, resulted in more than $1 billion in fines for alleged FCPA violations in China, Djibouti, Indonesia, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Vietnam. There are no public details about Nokia’s claims, but it would seem that the case was predicated on Nokia losing out on competitive bids due to Ericsson’s alleged corruption.
Whistleblower Actions
- Western Digital – On June 25, 2021, Chief Judge Richard Seeborg of the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California granted Western Digital Corp.’s motion to dismiss a bribery-related whistleblower lawsuit for lack of jurisdiction and failure to state a claim. The lawsuit was brought by a Brazilian citizen formerly employed by Western Digital’s Brazilian subsidiary, who alleged that he was terminated in retaliation for raising bribery and tax fraud concerns in violation of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 (“Dodd-Frank”). In dismissing the case, the Court held that Dodd-Frank’s anti-retaliation provision does not apply to overseas conduct. Moreover, the Court held that, even if the claim alleged domestic wrongdoing, the former employee “failed to allege sufficient facts to give rise to a plausible inference that he suffered adverse employment actions in retaliation for whistleblowing” given the length of time between his report and his termination and the fact that he caused the company to be victimized by a phishing scam close in time to his firing.
2021 INTERNATIONAL ANTI-CORRUPTION DEVELOPMENTS
Multilateral Development Banks
U.S. Federal Court Reinforces World Bank Sovereign Immunity
In our 2016 Year-End FCPA Update, we discussed the landmark Canadian Supreme Court decision in World Bank Group v. Wallace, which concluded that the Bank had not waived its privileges and immunities by providing evidence gathered in a Bank investigation to national law enforcement authorities. On April 5, 2021, Chief Judge Beryl A. Howell of the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia reached a similar conclusion in a lawsuit filed by businessmen Noah J. Rosenkrantz and Christopher Thibedeau against the Inter-American Development Bank (“IDB”) asserting that the internal sanctions proceedings against their company failed to comply with the sanctions procedures governing such procedures, in violation of its contractual obligations. In dismissing the lawsuit, the Court held that the IDB is immune from suit in U.S. federal court as a sovereign entity and emphasized, like the Canadian court in Wallace, that a contrary ruling would undermine the Bank’s ability to carry out its mission. The plaintiffs have appealed the dismissal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit.
Europe
United Kingdom
WGPSN (Holdings)
On March 16, 2021, Scotland’s Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service announced that WGPSN, a subsidiary of John Wood Group PLC, agreed to pay £6.46 million to Scotland’s Civil Recovery Unit to resolve allegations that PSNA Limited, a company WGPSN had acquired, benefitted from improper payments to secure contracts in Kazakhstan. These payments were allegedly made between 2012 and 2015, all prior to WGPSN’s acquisition, and when discovered by WGPSN were voluntarily reported to Scottish authorities.
GPT Special Project Management Ltd.
On April 28, 2021, the UK Serious Fraud Office (“SFO”) announced that Airbus subsidiary GPT Special Project Management pleaded guilty to corruption in violation of section 1 of the Prevention of Corruption Act 1906 and was ordered to pay a confiscation order of £20,603,000, a fine of £7,521,920, and costs of £2,200,000. The charges arise from alleged improper payments involving the Saudi Arabian National Guard. In setting the penalty, Justice Bryan at Southwark Crown Court considered GPT’s guilty plea, the fact that it no longer is in operation, the company’s cooperation with the SFO’s investigation, and the UK government’s role in facilitating the conduct. Also relevant was the fact that parent company Airbus entered into a $3.9 billion deferred prosecution agreement in January 2020 (as covered in our 2020 Mid-Year FCPA Update).
Amec Foster Wheeler Energy Ltd.
As covered above, on June 25, 2021 Amec Foster Wheeler reached a coordinated anti-corruption resolution with UK, U.S., and Brazilian authorities. The U.S. and Brazilian cases related to only to Brazil, while the UK case brought by the SFO is broader and covers alleged corrupt payments between 1996 and 2014 in India, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, and Malaysia, as well as Brazil. Pursuant to a three-year deferred prosecution agreement approved by Lord Justice Edis, sitting at the Royal Courts of Justice, Amec Foster Wheeler agreed to pay £103 million in connection with a 10-count indictment, including nine counts of violating Section 1 of the Criminal Law Act 1977 and Section 1 of the Prevention of Corruption Act 1906 and one count of failure to prevent bribery under Section 7 of the Bribery Act 2010.
Petrofac Ltd.
On October 1, 2021, the SFO secured the conviction of Petrofac for seven separate counts of failure to prevent bribery between 2011 and 2017. Petrofac admitted to failing to prevent former senior executives of the group’s subsidiaries from using agents to pay bribes of £32 million to win oil contracts in Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates worth approximately £2.6 billion. Petrofac will pay a confiscation order of £22.8 million; a fine of approximately £47.2 million; and the SFO’s investigation costs of £7 million. On the same day, Petrofac’s former Global Head of Sales David Lufkin was sentenced to a two-year custodial sentence, suspended for 18 months, as a result of his January 14, 2021, guilty plea admitting to three individual counts of bribery related to corrupt offers and payments made between 2012 and 2018 to influence the award of contracts to Petrofac in the United Arab Emirates. Lufkin had previously pleaded guilty in February 2019 to 11 counts of bribery already brought by the SFO (as discussed in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update).
Unaoil Individual Prosecutions
On February 24, 2021, the SFO secured the conviction of former SBM Offshore executive Paul Bond arising out of his role in allegedly conspiring to bribe public officials to secure oil contracts from Iraq’s South Oil Company in the years following the overthrow of Saddam Hussain in 2003. A jury found the former senior sales manager guilty on two counts of conspiracy to give corrupt payments following a retrial of his case. On March 1, 2021, Bond was sentenced to three-and-a-half years in prison, making him the fourth individual to be sentenced in the case involving Iraq’s South Oil Company, which forms part of the SFO’s broader investigation into bribery at Unaoil. As covered in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update, Bond’s three co-defendants have been sentenced to a collective total of 11 years and four months in prison.
On June 17, 2021, the SFO secured an approximately £402,000 confiscation order by consent against former Unaoil executive Basil Al Jarah. And on November 3, 2021, Stephen Whiteley, former Vice President at SBM Offshore and Unaoil’s territory manager for Iraq, was ordered to repay criminal gains of £100,000.
In a judgement handed down on December 10, 2021, the UK Court of Appeal quashed the conviction of Ziad Akle, another Unaoil executive who was convicted in 2020 of conspiracy to give corrupt payments as covered in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update. The Court criticized the SFO for its contact with a U.S.-based “fixer” who had offered to assist in obtaining the convictions of related parties. The Court also found that the SFO had failed to disclose material relating to that contact, which was necessary for the defense to properly bring its case. The Court refused an application for a retrial on the grounds of the SFO’s misconduct. The UK Attorney General has since announced an independent review into the matter. Bond has appealed his conviction on the same grounds as Akle.
SFO Deferred Prosecution Agreements with Two Unidentified Companies
On July 19, 2021, the SFO entered into separate deferred prosecution agreements with two UK-based companies for bribery offenses. The SFO did not identify the companies because the investigations are ongoing, but confirmed that the criminal conduct saw bribes paid in relation to multi-million pound UK contracts. The two companies will pay more than £2.5 million between them, representing disgorgement of profits along with a financial penalty, and the SFO acknowledged that both companies fully cooperated. We will report back on these agreements when the companies names are made public.
France
A bill to strengthen the fight against corruption in France was registered at the French National Assembly on October 19, 2021. The bill outlines several proposals concerning the French Anti-Corruption Agency (“AFA”), the extension of anti-corruption obligations of public and private actors, the regulation of lobbying, and negotiated justice. Among other things, the bill would extend anti-corruption obligations to subsidiaries of large foreign organizations. The text also would make companies and public entities (other than the French State) criminally liable if a lack of supervision led to the commission of one or more offenses by an employee.
Italy
After more than three years of proceedings, in March 2021 an Italian court acquitted oil companies Royal Dutch Shell and Eni SpA, as well as a number of individuals, including the Eni CEO, of charges that they paid more than $1 billion to acquire the license to an offshore block in Nigeria. Prosecutors alleged that the money was intended as bribes, while the companies successfully defended with evidence that the payment was legitimate and intended to resolve long-running disputes as to the block’s ownership.
Kyrgyzstan
On May 31, 2021, Kyrgyzstan’s State Committee for National Security announced the arrest of former Prime Minister Omurbek Babanov as part of an investigation into corruption involving a gold mine project in Kumtor. The project was operated by Canadian company Centerra Gold until the Kyrgyz government took it over, citing a new law allowing it to take control of a project for up to three months due to environmental or safety violations. The Kumtor mine accounts for more than 12% of the national economy, according to Centerra, which has denounced the Kyrgyz government’s seizure.
Norway
In our 2015 Year-End FCPA Update, we reported that several senior level officers of Norwegian fertilizer manufacturer Yara International ASA were sentenced to prison in Norway for their role in an alleged scheme to pay bribes to government officials in India, Libya, and Russia. The former chief legal officer in particular, U.S. citizen Kendrick Wallace, received a two-and-a-half year prison sentence for his role. In 2017 the Norwegian appeals court upheld Wallace’s conviction and revised his sentence to seven years, finding that his conduct had been “very central” to the alleged scheme.
Norway subsequently submitted a request for extradition of Wallace. On June 11, 2021, the Honorable Sean P. Flynn, Magistrate Judge of the U.S. District Court for the Middle District of Florida, denied the request. The Court found that “Wallace cannot be extradited because the prosecution for the offense of which extradition is sought has become barred by lapse of time according to the laws of the United States.” Specifically, the Court found that while Wallace’s crimes were committed in 2007, he was indicted in 2014, exceeding the applicable five-year statute of limitations in the United States. The DOJ provided evidence that Norway sought evidence pursuant to Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty requests—which would toll the statute of limitations in the United States pursuant to 18 U.S.C. § 3292—but the Court found the specific evidentiary showing lacking, and ordered Wallace’s release from custody.
Russia
The Russian Federation Prosecutor General’s office reported nearly 30,000 corruption-related crimes in the first nine months of 2021, a 12.7% increase as compared to the same period a year ago, with bribery accounting for more than half of all corruption-related offenses. The reported damage caused by corruption-related crimes also increased from 45 billion rubles (approximately $612 million) to 53 billion rubles (approximately $719 million). In 2020, the number of corruption-related convictions of Russian officials was at an eight-year low of just under 7,000, continuous decline from a high of approximately 11,500 in 2015, but the number of convictions stemming from large-scale bribes, defined as greater than one million rubles (approximately $13,700), has increased 12-fold since 2012.
On the legislative front, on October 1, 2021, the Russian Duma approved the National Plan For Countering Corruption through 2024. This plan prioritizes prohibiting anyone who has been fined for corrupt activities from holding government positions, improving the procedures for the submission and auditing of government employees’ asset declarations, implementing technology to combat corruption, instituting anti-corruption regulations involving the purchase of goods and services for government/municipal use, monitoring international agreements for cooperation in fighting corruption, and employing Duma deputies to participate in an inter-parliamentary organization aimed at preventing corruption.
And on the judicial front, on June 9, 2021, a Moscow court issued a decision classifying activist Alexei Navalny’s political organization, the Anti-Corruption Foundation (“ACF”), as an “extremist” movement. Under the applicable “anti-extremism” law, authorities can jail ACF members and freeze their assets, and those associated with the group cannot run for public office. On August 10, 2021, Russia’s financial watchdog—the Federal Financial Monitoring Service—also added ACF to its blacklist of groups accused of extremist activities or terrorism, which freezes the organization’s bank account and prevents ACF from opening new accounts.
Sweden
In our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, we covered the trial acquittal in Sweden of three former Telia executives—former CEO Lars Nyberg, former deputy CEO and head of Eurasia unit Tero Kivisaari, and former general counsel for the Eurasia unit Olli Tuohimaa—on charges of bribing Uzbek’s then-first daughter Gulnara Karimova in exchange for telecommunications contracts in Uzbekistan. In February 2021, a Swedish appeals court upheld the acquittals, agreeing that Karimova, the daughter of Uzbekistan’s former president, was not a government official under Swedish law.
Switzerland
In January 2021, a Swiss court convicted Beny Steinmetz of 2019 charges (discussed in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update) of paying bribes to the wife of former-Guinean President Lansana Conté and of related forgery to obtain a mining concession. He was sentenced to five years in prison and ordered to pay a CHF 50 million fine (~ $56.5 million).
In November 2021, three Swiss subsidiaries of Netherlands-based SBM Offshore were ordered to pay more than CHF 7 million (~ $7.6 million) for failing to prevent the bribery of public officials in Angola, Equatorial Guinea, and Nigeria between 2006 and 2012. The Office of the Attorney General of Switzerland found that these companies had entered into sham contracts with shell companies to pay more than $22 million in bribes. The Office of the Attorney General alleged that in light of the “extent and duration of the acts of corruption,” the companies’ risk assessment measures and anti-corruption controls were allegedly “either non-existent, or wholly inadequate.” This order is in addition to the more than $800 million that SBM Offshore has already paid to resolve corruption probes dating back to its 2017 FCPA resolutions reported in our 2017 Year-End FCPA Update.
Ukraine
Ukrainian President Zelensky’s focus in the first half of 2021 was on securing the release of the remainder of a $5-billion IMF loan to bolster Ukraine’s economy. After a six-week virtual mission to Ukraine in the beginning of 2021, the IMF refused to release the funds in what some viewed as an indication that Ukraine had not met the IMF’s expectations for tackling corruption. Following this refusal, in June 2021, Ukraine’s parliament, the Verkhovna Rada, passed two bills: the first reestablished the High Judicial Council, a special commission on appointing judges that will be majority-comprised of international experts; and pursuant to the second bill, public officials who fail to submit or submit false income or asset declarations could face prison sentences. Additionally, on November 8, 2021, President Zelensky signed into law amendments to legislation that provide for the independence of the anti-corruption bureau (“NABU”). Subsequently, on November 22, 2021, following a review by its Executive Board, the IMF announced that Ukrainian authorities would be allowed to draw on an additional $699 million.
The Americas
Brazil
In February 2021, President Bolsonaro disbanded Operation Car Wash, one of the most prolific anti-corruption investigations of all time and a staple of these updates for years. Operation Car Wash led to dozens of convictions, many prominent enforcement actions, and hundreds of millions of dollars in penalties within Brazil and billions of dollars globally. Still, the ripples of Operation Car Wash continued throughout the year. For example, on February 22, 2021, Korean engineering company Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. entered into a leniency agreement in Brazil to resolve allegations concerning contracts with Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. (Petrobras). Samsung Heavy Industries, as covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, previously in November 2019 entered into a deferred prosecution agreement with DOJ and agreed to pay a $75.5 million criminal fine to resolve FCPA anti-bribery conspiracy charges arising from the company’s alleged provision of $20 million to an intermediary, while knowing that some or all of that amount would be paid to officials at Petrobras. Half of the U.S. criminal fine was to be credited to a parallel resolution with Brazilian authorities. In connection with the Brazilian leniency agreement, Samsung Heavy Industries agreed to pay approximately R$ 706 million in damages to Petrobras together with R$ 106 million in fines. And on April 15, 2021, Brazil’s Supreme Court upheld a ruling annulling one of the most notable convictions resulting from Operation Car Wash—that of former President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, on grounds that the lower court in which Lula was tried did not have jurisdiction. The case was transferred to a federal court for retrial and, should no conviction follow, Lula will be able to run for presidential office in the upcoming 2022 election.
In August 2021, Brazil’s Federal Prosecution Service (“MPF”) filed a criminal complaint against two executives at French engineering company Doris Group over allegedly corrupt activity concerning platform vessel contracts totaling more than $200 million. The MPF also charged a former treasurer of Brazil’s Workers’ Party and two associates for active and passive money laundering. The executives allegedly paid bribes via a financial operator to a former manager of Petrobras and the former treasurer. The financial operator and Petrobras manager both signed collaboration agreements with the MPF in which they confessed to their roles in the scheme and cooperated by providing relevant documents and information.
In September 2021, a review body within the São Paulo prosecutor’s office vacated a resolution prosecutors reached with EcoRodovias in 2020. The now-nullified agreement was the culmination of a two-year bribery investigation into EcoRodovias and its subsidiaries concerning allegations that the companies engaged in a cartel that bribed public officials to obtain road concessions contracts between 1998 and 2015. In signing the 2020 agreement, EcoRodovias admitted to paying bribes and agreed to pay a fine of $113.72 million. The review body threw out the agreement due to a lack of evidence of illegal conduct.
And on October 27, 2021, Rolls Royce signed an agreement with Brazil’s Office of the Comptroller and Attorney General’s Office to pay $27.8 million to settle allegations that it bribed Brazilian public officials in connection with its contracts with Petrobras. As covered in our 2017 Mid-Year FCPA Update, the company in 2017 previously agreed to pay more than $800 million through a global resolution with the SFO, DOJ, and MPF. Under the new agreement, Brazilian officials will credit the $25.6 million that Rolls Royce paid to the MPF, leaving the company to pay another $2.2 million.
Canada
As reported in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, in September 2018 Canada passed legislation allowing deferred prosecution agreements for corporate offenders. In 2019, following a long-running investigation into alleged bribery of Libyan officials, engineering and construction giant SNC-Lavalin became one of the first major companies to seek such an agreement. Canadian prosecutors, however, reportedly were unwilling to negotiate with the company, and in 2021, prosecutors charged the company with several offenses, including fraud against the government. The Royal Canadian Mounted Police also arrested two former executives and charged them with fraud and forgery offenses tied to the investigation. The company has publicly stated that it is cooperating with the investigation and that prosecutors have invited it to negotiate a settlement. According to SNC-Lavalin, it is the first company to receive such an offer.
In August 2021, the Court of Appeal for Ontario threw out the bribery convictions of two former employees of Cryptometrics. As discussed in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update, following trial in 2018, U.S. citizen Robert Barra and UK citizen Shailesh Govindia were sentenced to two-and-a-half years in prison for agreeing to bribe Indian aviation officials, including employees of Air India. But the appellate court found a “reasonable possibility” that prosecutors delayed disclosing emails they exchanged with a principal witness—the former Cryptometrics COO—and that such delay unduly impacted the trial’s fairness. The appellate court further found that the prosecution’s slow production of potentially exculpatory information, only after repeated requests from the defense, deprived the defense of the opportunity to conduct further lines of inquiry or obtain additional evidence.
Costa Rica
Costa Rican officials have been investigating an alleged scheme known as “Cochinilla,” involving allegations that certain construction companies bribed government officials to secure contracts to build public roads, resulting in approximately $125 million in misappropriated funds. On June 14, 2021, the Costa Rican Judicial Investigation Police executed 57 search warrants and made 28 arrests in connection with the investigation, including at the Casa Presidencial, the National Highway Council, the Ministry of Public Works and Transport, and the Public Transport Council, as well as at private homes and at the offices of several construction companies. In August 2021, the Judicial Investigation Police unearthed a trove of invoices apparently related to the investigation buried in a municipal cemetery.
Additionally, on November 16, 2021, six mayors—including the current mayors of San José, Escazú, Alajuela, Osa, and San Carlos—were arrested in connection with the “Diamante” investigation into public works corruption. The Diamante investigators conducted more than 80 raids across the country in connection with the probe.
Ecuador
In April 2021, Ecuador’s Comptroller General Pablo Celi, former Oil Minister José Augusto Briones, and several others were arrested as part of the long-running investigation concerning Ecuador’s state-owned oil company Empresa Pública de Hidrocarburos del Ecuador (“PetroEcuador”). The alleged scheme, covered previously in these pages, allegedly allowed contracting companies to charge PetroEcuador artificially inflated prices to supply fuel, with a percentage of the profits then kicked back to PetroEcuador executives. Augusto died in his jail cell by apparent suicide while awaiting trial.
El Salvador
In July 2021, prosecutors in El Salvador issued an arrest warrant for former president Salvador Sánchez Cerén in connection to the “Public Looting” scam that allegedly occurred while Sánchez Cerén was serving as Vice President from 2009 to 2014. The scandal allegedly involved $351 million in government funds illegally used to pay bonuses to government employees and their associates. Two weeks after the warrant was issued, Sánchez Cerén and his family fled to Nicaragua.
Peru
In an offshoot of the Odebrecht investigation (covered in our 2019 Year-End FCPA Update), in May 2021 Peru’s Attorney General and National Public Prosecution Office announced a plea agreement with Peruvian real estate and construction company Aenza (formerly Graña y Montero), to resolve allegations that the company, two subsidiaries, and certain former employees were involved in corruption in connection with several public infrastructure projects in the country. Under the agreement, Aenza will pay approximately $126 million to the state over several years.
Earlier, in March 2021, prosecutors charged former presidential candidate Keiko Fujimori with money laundering following a multi-year investigation into allegations that she received more than $1 million in bribes from Odebrecht during a prior presidential run. Prosecutors are seeking a sentence of 30 years in prison, while Fujimori denies any wrongdoing. In June 2021, Fujimori’s opponent in the presidential race claimed victory, which Fujimori disputed before conceding in August 2021. The first hearing related to Fujimori’s trial began in late August 2021.
Finally, on September 28, 2021, Magistrate Judge Thomas Hixson of the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California granted Peru’s request to extradite former Peruvian President Alejandro Toledo. Peru had been seeking Toledo’s extradition since May 2018, and Toledo was arrested in 2019, in connection with alleged corruption and money laundering in an Odebrecht project for the construction of the Peru-Brazil Southern Interoceanic Highway. In his ruling, Judge Hixson found that there was enough evidence to “establish probable cause to believe that Toledo committed collusion and money laundering.” The Court said that this included testimony from Odebrecht’s former executive director in Peru, and Mr. Toledo’s admission during the extradition proceeding that he had received approximately $500,000 in Odebrecht bribes.
Asia
China
In 2020, China’s Supreme People’s Procuratorate (“SPP”) launched the first phase of a pilot program focusing on corporate criminal compliance. Although China does not have a mechanism equivalent to a U.S.-style deferred prosecution agreement, the pilot program encourages local procuratorates to decline prosecutions or arrests for corporate criminal cases, or to propose lighter or suspended sentences, where companies are committed to making compliance enhancements and implementing remediation plans. In April 2021, the SPP published the Work Plan on Launching the Pilot Program for Corporate Compliance Reform, which signals the launch of the second phase of the pilot program and its expansion to 10 provinces and cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong. In June 2021, the SPP, along with eight other national authorities, issued the Guiding Opinions on Establishing a Third-Party Supervision and Evaluation Mechanism for the Compliance of Enterprises Involved in Criminal Cases (for Trial Implementation). Under these guiding opinions, the SPP can refer a company that qualifies for the pilot program to a yet-unspecified third-party organization to investigate, evaluate, supervise, and inspect compliance commitments made by the company. The SPP confirmed in a press release in June 2021 that bribery-related cases may qualify for leniency under the pilot program, citing an example concerning Shenzhen Y Technology Co., Ltd, an audio equipment supplier whose employee was suspected of bribing customers to secure advantages in the procurement process, but which the SPP decided not to prosecute in lieu of a compliance supervision agreement.
On September 20, 2021, the Supervision Law of the People’s Republic of China came into effect, with implementing regulations issued by the National Supervision Commission. The National Supervision Commission was established in 2018 and is primarily responsible for supervising China’s anti-corruption efforts. The Supervision Law seeks to standardize the National Supervision Commission’s work by setting forth the scope, jurisdiction, procedures, and oversight of China’s anti-corruption agencies. In the same month, the National Supervision Commission, the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection (“CCDI”), and the SPP, among other government agencies, jointly issued a document titled “Opinions on Further Promoting the Investigation of Bribery and Acceptance of Bribes.” These opinions emphasize the importance of investigating those offering bribes, which marks a turn for an enforcement regime that historically has focused predominately on those who accept improper payments. These opinions also suggest that enforcement authorities should explore the implementation of a “blacklist” that would impose market restrictions on those that make improper payments, although implementing guidance on this “blacklist” proposal has yet to be issued.
Last but not least, 2021 saw a seismic shift in China’s data and privacy protection laws, with the developments likely to have far-reaching implications for cross-border investigations and litigation. The Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress first passed the Data Security Law, which took effect on September 1, 2021. Among other things, Article 36 of the Data Security Law prohibits “provid[ing] data stored within the People’s Republic of China to foreign judicial or law enforcement bodies without the approval of the competent authority of the People’s Republic of China.” In August 2021, the Standing Committee of China’s National People’s Congress passed the Personal Information Protection Law (“PIPL”), which came into effect on November 1, 2021. The PIPL is China’s first comprehensive legislation regulating personal data processing activities, and it shares many similarities with the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation, including, among other things, its extraterritorial reach, restrictions on data transfer, compliance obligations, and sanctions for non-compliance. In October 2021, the Cyberspace Administration of China (“CAC”) published the “Draft Measures for Data Export Security Assessment” to regulate the export of data in accordance with the Cybersecurity Law, the Data Security Law, and the PIPL. Under the Draft Measures, data processors must apply to the CAC for a “security assessment” of the outbound data in certain circumstances. For a detailed analysis of these new legislative developments, please see our separate Client Alerts, “China Constricts Sharing of In-Country Corporate and Personal Data Through New Legislation“ and “China Passes the Personal Information Protection Law, to Take Effect on November 1.”
Hong Kong
In May 2019, the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) charged Catherine Leung Kar-cheung, a former senior banker at JPMorgan Chase & Co., in connection with the long-running “Sons and Daughters” investigation. The ICAC accused Leung of offering a job to the son of a logistics company chairperson in an effort to win a mandate for an initial public offering. In January 2021, the district court acquitted Leung of the charges, finding that there was insufficient evidence that she corruptly sought to secure the IPO mandate by making the job offer.
India
The Indian Government has issued standard operating procedures that must be followed by Indian police before commencing any investigation against Indian public officials for alleged violations of India’s Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988. One of these standards is to require additional approvals to open an investigation, which have been criticized as erecting barriers to bringing enforcement actions against public officials.
In November 2021, India’s Enforcement Directorate arrested a former cabinet minister of the State of Maharashtra, Anil Deshmukh, on allegations involving money laundering and extortion. Deshmukh, who stepped down from his post earlier this year, is accused of using police officials to extort various hotels, restaurants, and bars in Mumbai, and of using shell companies to siphon the funds received for personal use. He is accused of extorting up to INR 100 crore (~ $13.4 million) per month while in office.
Indonesia
In August 2021, former Indonesian social affairs minister Juliari Batubara was sentenced to 12 years in prison by the Jakarta Corruption Court over a multi-million dollar COVID-19 graft scandal. A judge found the former politician “convincingly guilty of corruption” for receiving IDR 32.4 billion (~ $2.25 million) in kickbacks related to procurement intended for COVID-19 social assistance packages. The Court also fined Batubara IDR 500 million (~ $350,000) and ordered him to return IDR 14.5 billion (~ $1 million) in funds. As a result of his sentence, Batubara also will be banned from public office for four years after serving his prison term.
In 2021, Indonesia’s Corruption Eradication Commission (Komisi Pemberantasan Korupsi Republik Indonesia) (“KPK”) removed 57 of its graft investigators and personnel, while subjecting two dozen more to re-training, after 75 of its personnel failed a tailor-made civil service exam implemented as part of an effort to fold the body into the civil service. Controversy has surrounded the composition of the test: the National Commission on Human Rights has said that the test was plagued with “baseless stigmatization” and “illegal conduct,” while the Indonesian Ombudsman found that the document that set forth the legal basis for organizing the test was signed by officials who did not attend the meeting to discuss it. The KPK has defended the exam, which was taken by 1,300 staff. Dozens of the employees plan to appeal their dismissals.
Japan
In May 2021, the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (“METI”) revised the Guidelines for the Prevention of Bribery of Foreign Public Officials. These revised Guidelines include a new subsection on mergers and acquisitions and provide additional guidance on third-party due diligence, facilitation payments, and applicability of the “agreement system” under the Japanese Criminal Procedure Code to bribery offenses. The due diligence provisions closely track the recommendations made by DOJ and the SEC in the FCPA Resource Guide. In addition, the revised Guidelines urge Japanese companies to prohibit small facilitation payments, noting that such payments could be made “in order to obtain a wrongful gain in business” in violation of the Unfair Competition Prevention Act.
Malaysia
The Malaysian government reached two corporate resolutions in 2021 in connection with the 1Malaysia Development Berhad (“1MDB”) scandal. First, in February 2021, the Malaysian banking group AMMB Holdings Berhad agreed to pay MYR 2.83 billion (~ $682.3 million) to settle outstanding claims and actions related to AMMB’s involvement in the 1MDB scandal, although the specifics of that involvement were not reported. Second, in March 2021, Deloitte PLT agreed to pay $80 million to the Malaysian government to settle claims related to its auditing of reports issued by 1MDB and a former 1MDB subsidiary. Also related to 1MDB, on August 5, 2021, DOJ announced that it had repatriated to Malaysia an additional $452 million in funds in connection with the scandal, bringing the total repatriated to more than $1.2 billion.
In other enforcement developments, we reported in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update on amendments to the Malaysia Anti-Corruption Commission Act 2009 that took effect in June 2020, allowing for corporate liability. Under Section 17A, a commercial organization commits a criminal offense if a person associated with the organization corruptly gives any gratification with intent to obtain or retain any business or advantage for the commercial organization. In March 2021, Pristine Offshore Sdn Bhd became the first organization charged by the Malaysia Anti-Corruption Commission (“MACC”) under Section 17A, for allegedly having paid MYR 321,350 (~ $78,000) to the chief operating officer of Deleum Primera Sdn Bhd to secure a subcontract for the supply of workboats Both Pristine Offshore and its former director have pleaded not guilty.
Singapore
In February 2021, Singapore’s Corrupt Practices Investigation Bureau charged three former employees of a Singaporean subsidiary of Royal Dutch Shell with bribing shipping inspectors in exchange for assistance in stealing millions of metric tons of fuel from the company. In May 2021, Daewoo Engineering and Construction executives Ro Sung-Young and Kim Young-Gyu pleaded guilty to conspiring to bribe a Singapore Land Transport Authority official in exchange for contracts with the authority. Prosecutors also charged the official, alleging that he received bribes totaling SGD 1.2 million (~ $893,300) between 2014 and 2019. Also in May, a Singapore court sentenced Chang Peng Hong Clarence, a former Regional Director for Marine Fuels at BP plc’s Singapore subsidiary, to 4.5 years in prison for receiving bribes of almost $4 million from Koh Seng Lee, the executive director of a Singaporean petroleum and petroleum products wholesaler, in exchange for promoting that company’s business within BP. The court also ordered Chang to pay a SGD 6.2 million (~ $4.7 million) penalty.
South Korea
In January 2021, the Korean government launched the Corruption Investigation Office for High-Ranking Officials (“CIO”), an independent investigative agency with jurisdiction to prosecute corruption cases involving high-ranking public officials. The creation of the CIO, which has exclusive prosecution authority over financial crimes involving certain categories of senior officials (as well as private parties involved in the investigations), fulfills a key campaign promise of President Moon Jae-In, who came to power in 2017 following a corruption scandal that resulted in the impeachment of his predecessor (as discussed in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update). The CIO was active throughout 2021, conducting multiple investigations that even extended to searches of the Supreme Prosecutor’s Office and offices of National Assembly members. Perhaps predictably, these measures have led to claims that the CIO is acting too aggressively.
On the legislative front, in November and December 2021 the Korean National Assembly passed a series of amendments to the Improper Solicitation and Graft Act (“Anti-Graft Act”) and the Act on the Prevention of Corruption and the Establishment and Management of the Anti-Corruption and Civil Rights Commission. These amendments expand the law and its proscriptions to include additional improper advantages such as employment and internship opportunities, selection of scholarship recipients, positive reviews of dissertations and granting of degrees, and activities of prison guards. The amendments also increase the threshold for permissible agricultural gifts given to public officials during public holidays, and allow for anonymous reporting of Anti-Graft Act violations through attorneys.
The Middle East and Africa
Israel
Months after the corruption trial of Benjamin Netanyahu restarted following delays due to COVID-19, Netanyahu’s election loss ended his 12 years as Israeli Prime Minister. As covered most recently in our 2020 Year-End FCPA Update, the Israeli Attorney General announced indictments in February 2019 stemming from three separate allegations of wrongdoing. On February 8, 2021, Netanyahu pleaded not guilty, and the trial then was postponed again due to a disagreement over certain documents. One former media adviser to Netanyahu and his family recently testified regarding regulatory favors Netanyahu allegedly awarded to media tycoons in return for positive press coverage and gifts. The witness, who previously was charged and signed a cooperation deal with the government, also provided investigators with recordings of conversations with Netanyahu and his family.
Namibia
In 2021, state-owned National Fishing Corporation of Namibia (“Fishcor”), and several executives including former CEO Mike Nghipunya, were charged with racketeering, conspiracy, fraud, money laundering, tax evasion, and obstruction of justice. The investigation began in 2019, after Wikileaks published more than 30,000 documents from a former managing director of Icelandic seafood company Samherji’s Namibian operations. According to prosecutors, Fishcor illegally sold quotas to Samherji for $11.1 million, with funds then being provided to others, including a former Namibian fisheries minister. Pretrial hearings are scheduled for January 2022.
South Africa
The trial of former South African President Jacob Zuma for allegedly accepting bribes related to a 1994 arms purchase spent most of 2021 plagued with delays. The National Prosecuting Authority accuses Zuma of accepting bribes on hundreds of occasions. Zuma was first charged in 2005, but the charges have been dropped and reinstated many times over the years amid allegations of political interference, and recent delays have been caused by the unexplained simultaneous resignation of Zuma’s entire legal team and Zuma’s application to remove the chief prosecutor on alleged bias grounds. Zuma’s trial is currently set to begin in April 2022.
The following Gibson Dunn lawyers and alumnae participated in preparing this client update: F. Joseph Warin, John Chesley, Richard Grime, Patrick Stokes, Kelly Austin, Patrick Doris, Matthew Nunan, Oleh Vretsona, Oliver Welch, Christopher Sullivan, Anna Aguillard, Claire Aristide, Anthony Balzofiore, Junghyun Baek, Sean Brennan, Alexandra Buettner, Lizzy Brilliant, Ella Alves Capone, Josiah Clarke, Priya Datta, Bobby DeNault, Nathan Eagan, Amanda Kenner, Derek Kraft, Michael Kutz, Caroline Leahy, Nicole Lee, Allison Lewis, Jenny Lotova, Andrei Malikov, Megan Meagher, Katie Mills, Erin Morgan, Sandy Moss, Monica Murphy, Jaclyn Neely, Ning Ning, Kareen Ramadan, Hayley Smith, Jason Smith, Pedro Soto, Laura Sturges, Karthik Ashwin Thiagarajan, Katie Tomsett, Dillon Westfall, Sophie White, Terry Wong, and Caroline Ziser Smith.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding these issues. We have more than 110 attorneys with FCPA experience, including a number of former federal prosecutors and SEC officials, spread throughout the firm’s domestic and international offices. Please contact the Gibson Dunn attorney with whom you work, or any of the following:
Washington, D.C.
F. Joseph Warin (+1 202-887-3609, fwarin@gibsondunn.com)
Richard W. Grime (+1 202-955-8219, rgrime@gibsondunn.com)
Patrick F. Stokes (+1 202-955-8504, pstokes@gibsondunn.com)
Judith A. Lee (+1 202-887-3591, jalee@gibsondunn.com)
David P. Burns (+1 202-887-3786, dburns@gibsondunn.com)
David Debold (+1 202-955-8551, ddebold@gibsondunn.com)
Michael S. Diamant (+1 202-887-3604, mdiamant@gibsondunn.com)
John W.F. Chesley (+1 202-887-3788, jchesley@gibsondunn.com)
Daniel P. Chung (+1 202-887-3729, dchung@gibsondunn.com)
Stephanie Brooker (+1 202-887-3502, sbrooker@gibsondunn.com)
M. Kendall Day (+1 202-955-8220, kday@gibsondunn.com)
Robert K. Hur (+1 202-887-3674, rhur@gibsondunn.com)
Adam M. Smith (+1 202-887-3547, asmith@gibsondunn.com)
Oleh Vretsona (+1 202-887-3779, ovretsona@gibsondunn.com)
Courtney M. Brown (+1 202-955-8685, cmbrown@gibsondunn.com)
Jason H. Smith (+1 202-887-3576, jsmith@gibsondunn.com)
Ella Alves Capone (+1 202-887-3511, ecapone@gibsondunn.com)
Pedro G. Soto (+1 202-955-8661, psoto@gibsondunn.com)
New York
Zainab N. Ahmad (+1 212-351-2609, zahmad@gibsondunn.com)
Matthew L. Biben (+1 212-351-6300, mbiben@gibsondunn.com)
Reed Brodsky (+1 212-351-5334, rbrodsky@gibsondunn.com)
Joel M. Cohen (+1 212-351-2664, jcohen@gibsondunn.com)
Lee G. Dunst (+1 212-351-3824, ldunst@gibsondunn.com)
Mark A. Kirsch (+1 212-351-2662, mkirsch@gibsondunn.com)
Alexander H. Southwell (+1 212-351-3981, asouthwell@gibsondunn.com)
Lawrence J. Zweifach (+1 212-351-2625, lzweifach@gibsondunn.com)
Karin Portlock (+1 212-351-2666, kportlock@gibsondunn.com)
Denver
Robert C. Blume (+1 303-298-5758, rblume@gibsondunn.com)
John D.W. Partridge (+1 303-298-5931, jpartridge@gibsondunn.com)
Ryan T. Bergsieker (+1 303-298-5774, rbergsieker@gibsondunn.com)
Laura M. Sturges (+1 303-298-5929, lsturges@gibsondunn.com)
Los Angeles
Nicola T. Hanna (+1 213-229-7269, nhanna@gibsondunn.com)
Debra Wong Yang (+1 213-229-7472, dwongyang@gibsondunn.com)
Marcellus McRae (+1 213-229-7675, mmcrae@gibsondunn.com)
Michael M. Farhang (+1 213-229-7005, mfarhang@gibsondunn.com)
Douglas Fuchs (+1 213-229-7605, dfuchs@gibsondunn.com)
San Francisco
Winston Y. Chan (+1 415-393-8362, wchan@gibsondunn.com)
Thad A. Davis (+1 415-393-8251, tadavis@gibsondunn.com)
Charles J. Stevens (+1 415-393-8391, cstevens@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Li-Ming Wong (+1 415-393-8333, mwong@gibsondunn.com)
Palo Alto
Benjamin Wagner (+1 650-849-5395, bwagner@gibsondunn.com)
London
Patrick Doris (+44 20 7071 4276, pdoris@gibsondunn.com)
Charlie Falconer (+44 20 7071 4270, cfalconer@gibsondunn.com)
Sacha Harber-Kelly (+44 20 7071 4205, sharber-kelly@gibsondunn.com)
Michelle Kirschner (+44 20 7071 4212, mkirschner@gibsondunn.com)
Matthew Nunan (+44 20 7071 4201, mnunan@gibsondunn.com)
Philip Rocher (+44 20 7071 4202, procher@gibsondunn.com)
Steve Melrose (+44 20 7071 4219, smelrose@gibsondunn.com)
Paris
Benoît Fleury (+33 1 56 43 13 00, bfleury@gibsondunn.com)
Bernard Grinspan (+33 1 56 43 13 00, bgrinspan@gibsondunn.com)
Munich
Benno Schwarz (+49 89 189 33-110, bschwarz@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Walther (+49 89 189 33-180, mwalther@gibsondunn.com)
Mark Zimmer (+49 89 189 33-130, mzimmer@gibsondunn.com)
Hong Kong
Kelly Austin (+852 2214 3788, kaustin@gibsondunn.com)
Oliver D. Welch (+852 2214 3716, owelch@gibsondunn.com)
São Paulo
Lisa A. Alfaro (+5511 3521-7160, lalfaro@gibsondunn.com)
Fernando Almeida (+5511 3521-7093, falmeida@gibsondunn.com)
Singapore
Joerg Bartz (+65 6507 3635, jbartz@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
On January 24, 2022, the Federal Trade Commission announced its annual update of thresholds for pre-merger notifications of certain M&A transactions under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976 (“HSR Act”). Pursuant to the statute, the HSR Act’s jurisdictional thresholds are updated annually to account for changes in the gross national product. The new thresholds will take effect on February 23, 2022, applying to transactions that close on or after that date.
The size of transaction threshold for reporting proposed mergers and acquisitions under Section 7A of the Clayton Act will increase by $9.0 million, from $92 million in 2021 to $101 million for 2022.
|
Original Threshold |
2021 Threshold |
2022 Threshold |
|
$10 million |
$18.4 million |
$20.2 million |
|
$50 million |
$92.0 million |
$101 million |
|
$100 million |
$184.0 million |
$202 million |
|
$110 million |
$202.4 million |
$222.2 million |
|
$200 million |
$368.0 million |
$403.9 million |
|
$500 million |
$919.9 million |
$1.0098 billion |
|
$1 billion |
$1,839.8 million |
$2.0196 billion |
The maximum fine for violations of the HSR Act has increased from $43,792 per day to $46,517.
The amounts of the filing fees have not changed, but the thresholds that trigger each fee have increased:
|
Fee |
Size of Transaction |
|
$45,000 |
Valued at more than $101 million but less than $202 million |
|
$125,000 |
Valued at $202 million or more but less than $1.0098 billion |
|
$280,000 |
Valued at $1.0098 billion or more |
The 2022 thresholds triggering prohibitions on certain interlocking directorates on corporate boards of directors are $41,034,000 for Section 8(a)(l) (size of corporation) and $4,103,400 for Section 8(a)(2)(A) (competitive sales). The Section 8 thresholds took effect on January 21, 2022.
If you have any questions about the new HSR size of transaction thresholds, or HSR and antitrust/competition regulations and rulemaking more generally, please contact any of the partners or counsel listed below.
The following Gibson Dunn lawyers prepared this client alert: Adam Di Vincenzo, Andrew Cline, and Chris Wilson.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist clients in addressing any questions they may have regarding the HSR Act or antitrust issues raised by business transactions. Please feel free to contact the Gibson Dunn attorney with whom you usually work in the firm’s Antitrust and Competition Practice Group, or the following:
Adam Di Vincenzo – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3704, adivincenzo@gibsondunn.com)
Andrew Cline – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3698, acline@gibsondunn.com)
Chris Wilson – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8520, cwilson@gibsondunn.com)
Rachel S. Brass – Co-Chair, Antitrust & Competition Group, San Francisco
(+1 415-393-8293, rbrass@gibsondunn.com)
Stephen Weissman – Co-Chair, Antitrust & Competition Group, Washington, D.C.
(+1 202-955-8678, sweissman@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
BlackRock, Vanguard and State Street Global Advisors (“State Street”) recently issued their voting policy updates for 2022, as well as guidance about their 2022 priorities for their portfolio companies. On January 18, 2022, BlackRock’s CEO issued his annual “Letter to CEOs” (available here), following closely on the heels of State Street’s CEO, who issued his annual letter to public company directors (available here) on January 12.
These pronouncements from the “Big Three” asset managers reflect a number of common themes, including an emphasis on climate and the transition to a Net Zero economy, diversity at the board level and throughout the workforce, and effective human capital management. Links to the BlackRock and Vanguard voting policies for 2022 are below. State Street’s voting policy updates span several documents that provide guidance on areas that State Street views as focal points for the coming year. Links to these documents are also below.
BlackRock Proxy Voting Guidelines for U.S. Securities (effective as of January 2022)
Vanguard Proxy Voting Policy for U.S. Companies (effective as of March 1, 2022)
State Street
1. BlackRock
2022 Letter to CEOs
In his 2022 letter titled “The Power of Capitalism,” BlackRock CEO Larry Fink encourages companies to focus on their purpose and put that purpose at the foundation of their relationships with stakeholders, in order to be valued by their stakeholders and deliver long-term value for their shareholders. The letter urges companies to think about whether they are creating an environment that helps their employee-stakeholders navigate the new world of work that has emerged from the pandemic. The letter observes that most stakeholders now expect companies to play a role in moving toward a Net Zero global economy and discusses BlackRock’s approach to climate and sustainability. This is a priority area for BlackRock because of its need, as a capitalist and fiduciary to its clients, to understand how companies are adjusting their business to massive changes in the economy. Mr. Fink also emphasizes that divesting from entire sectors, or simply passing carbon-intensive assets from public to private markets, will not move the world to Net Zero. BlackRock does not pursue divestment from oil and gas companies as a policy, but believes that action by “foresighted companies” in a variety of carbon-intensive industries is a critical part of the transition to a greener economy. Government participation on the policy, regulatory and disclosure fronts is also critical because, Mr. Fink notes, “businesses can’t do this alone, and they cannot be the climate police.”
The letter concludes with a reminder that BlackRock has built a stewardship team so it can understand companies’ progress throughout the year, and not just during proxy season. BlackRock previously announced an initiative to give more of its clients the option to vote their own holdings, rather than BlackRock casting votes on their behalf. The letter notes that this option is now available to certain institutional clients, including pension funds that support 60 million people. The letter also commits to expanding that universe as BlackRock is committed to a future where every investor, including individual investors, have the option to participate in the proxy voting process.
2022 BlackRock Voting Policy Updates
30% Target on Board Diversity
BlackRock believes boards should aspire to 30% diversity, and encourages companies to have at least two directors who identify as female and at least one who identifies as being from an “underrepresented group.” The definition of “underrepresented group” is broad and includes individuals who identify as racial or ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+, underrepresented based on national, Indigenous, religious or cultural identity, individuals with disabilities and veterans. Although the wording of the policy is aspirational, insufficient board diversity was a top reason BlackRock opposed the election of directors in 2021.
Board Diversity Disclosure
BlackRock updated its expectations for disclosure about board diversity. It asks that companies disclose how the diversity characteristics of the board, in aggregate, are aligned with a company’s long-term strategy and business model, and whether a diverse slate of nominees is considered for all available board seats.
Votes on Compensation Committee Members
BlackRock appears to be strengthening its position on votes for compensation committee members where there is a lack of alignment between pay and performance. In that situation, BlackRock will vote “against” the say-on-pay proposal and relevant compensation committee members (rather than simply “considering” negative votes for committee members).
Sustainability Reporting
BlackRock will continue to ask that companies report in accordance with the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (“TCFD”) framework. In recognition of continuing advances in sustainability reporting standards, the 2022 voting guidelines recognize that in addition to TCFD, many companies report using industry-specific metrics other than those developed by the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (“SASB”). For those companies, BlackRock asks that they highlight metrics that are industry- or company- specific. It also recommends that companies disclose any multinational standards they have adopted, any industry initiatives in which they participate, any peer group benchmarking undertaken, and any assurance processes to help investors understand their approach to sustainable and responsible business conduct.
Climate Risk
BlackRock continues to ask companies to disclose Net Zero-aligned business plans that are consistent with their business model and sector. For 2022, it is encouraging companies to: (1) demonstrate that their plans are resilient under likely decarbonization pathways and the global aspiration to limit warming to 1.5°C; and (2) disclose how considerations related to having a reliable energy supply and a “just transition” (that protects the most vulnerable from energy price shocks and economic dislocation) affect their plans. BlackRock also updated its voting policies to reflect its existing approach of signaling concerns about a company’s plans or disclosures in its votes on directors, particularly at companies facing material climate risks. In determining how to vote, it will continue to assess whether a company’s disclosures are aligned with the TCFD and provide short-, medium-, and long-term reduction targets for Scope 1 and 2 emissions.
ESG Performance Metrics
BlackRock does not have a position on the use of ESG performance metrics, but it believes that where companies choose to use them, they should be relevant to the company’s business and strategy, clearly articulated, and appropriately rigorous, like other financial and non-financial performance metrics.
Votes on Committee Members at Controlled Companies
BlackRock may vote “against,” or “withhold” votes from, directors serving on “key” committees (audit, compensation, nominating/governance), that it does not consider to be independent, including at controlled companies. Previously, this policy was limited to votes on insiders or affiliates serving on the audit committee, and did not extend to other committees.
2. Vanguard
Vanguard’s voting policy updates address several of the same areas as BlackRock’s, including oversight of climate risk, and board diversity and related disclosures. The introduction to the voting policies also contains more explicit language emphasizing that proposals often require fact-intensive analyses based on an expansive set of factors, and that proposals are voted case-by-case at the direction of the boards of individual Vanguard funds.
Climate Risk Oversight “Failures”
Vanguard’s voting policies outline certain situations in which funds will oppose the re-election of directors on “accountability” grounds—that is, “because of governance failings or as a means to escalate other issues that remain unaddressed by a company.” Under Vanguard’s current policies, funds will consider votes “against,” or “withhold” votes from, directors or a committee for governance or material risk oversight failures.
For 2022, Vanguard has updated this policy to clarify that in cases where there is a risk oversight “failure,” funds will generally vote “against,” or “withhold” votes from, the chair of the committee responsible for overseeing a particular material risk (or the lead independent director and board chair, if a risk does not fall under the purview of a specific committee). The policy has also been updated to reflect that it covers material social and environmental risks, including climate change. On the subject of climate change, the updated policy lists factors that funds will consider in evaluating whether board oversight of climate risk is appropriate, including: (1) the materiality of the risk; (2) the effectiveness of disclosures to enable the market to understand and price the risk; (3) whether a company has disclosed business strategies, including reasonable risk mitigation plans in the context of anticipated regulatory requirements and changes in market activity, in line with the Paris Agreement or subsequent agreements; and (4) company specific-context, regulations and expectations. Funds will also consider the board’s overall governance of climate risk and the effectiveness of its independent oversight of this area.
Board Diversity and Qualifications
For 2022, Vanguard has clarified its expectations on disclosure about board diversity and qualifications. The policy states that boards can inform shareholders about the board’s current composition and related strategy by disclosing at least: (1) statements about the board’s intended composition strategy, including expectations for year-over-year progress, from the nominating/governance committee or other relevant directors; (2) policies for promoting progress toward greater board diversity; and (3) current attributes of the board’s composition. The policy states that board diversity disclosure should cover, at a minimum, the genders, races, ethnicities, tenures, skills and experience that are represented on the board. While disclosure about self-identified personal characteristics such as race and ethnicity can be presented at the aggregate or individual level, Vanguard expects to see disclosure about tenure, skills and experience at the individual level.
Under its policy on board “accountability” votes, a lack of progress on board diversity and/or disclosures about board diversity may lead to votes “against,” or “withhold” votes from, the chair of the nominating/governance committee. Vanguard has updated this policy for 2022 to reflect its expectations about the various dimensions of diversity (gender, race, etc.) that should be represented on boards and about companies’ disclosures. The policy includes a reminder that “many boards still have an opportunity to increase diversity across different dimensions,” and that these boards “should demonstrate how they intend to continue making progress.”
Director Overboarding
Vanguard has clarified how its overboarding policy applies to directors who are named executive officers (NEOs). Although Vanguard’s limit of two public company boards remains in place, the policy updates clarify that the two boards could consist of either the NEO’s own board and one outside board, or two outside boards if an NEO does not sit on the board at their own company. Vanguard funds will generally oppose the election of directors who exceed this limit at their outside board(s), but not at the company where they are an NEO.
For other directors, Vanguard’s existing limit of four public company boards is unchanged.
Vanguard funds will also look for companies to have good governance practices on director commitments, including adopting a policy on outside board service and disclosure about how the board oversees the policy.
Unilateral Board Adoption of Exclusive Forum Provisions
Vanguard has updated its voting policy on board “accountability” votes where a company adopts policies limiting shareholder rights. Under this policy, Vanguard funds will generally oppose the election of the independent board chair or lead director, and the members of the nominating/governance committee, in response to unilateral board actions that “meaningfully limit” shareholder rights. For 2022, this policy has been updated to specify that these board actions may include the adoption of an exclusive forum provision without shareholder approval.
Proposals on Virtual and Hybrid Shareholder Meetings
According to Vanguard, data show that virtual meetings can increase shareholder participation and reduce costs. Vanguard funds will consider supporting proposals on virtual meetings if meeting procedures and requirements are disclosed ahead of time, there is a formal process for shareholders to submit questions, real-time video footage is available, shareholders can call into the meeting or send recorded messages, and shareholder rights are not unreasonably curtailed.
3. State Street
In his letter, State Street CEO Cyrus Taraporevala announces that in 2022, State Street’s main focus “will be to support the acceleration of the systemic transformations underway in climate change and the diversity of boards and workforces.” To that end, the letter attaches three guidance documents outlining State Street’s expectations and voting policies for the 2022 proxy season in the areas of climate change and diversity, equity and inclusion. State Street has also published other guidance documents on director overboarding/time commitments and human capital for the 2022 proxy season.
The guidance documents are worth reading in their entirety because they provide detailed information about the practices and disclosures State Street expects to see from its portfolio companies in both 2022 and 2023, and about State Street’s related voting policies. A summary of the key highlights is below.
Corporate Climate Disclosures
General
State Street expects all companies in its portfolio to provide disclosures in accordance with the four pillars of the TCFD framework: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets. In approaching its disclosure expectations, State Street will begin by engaging with companies. The guidance document includes a list of questions (organized by the four TCFD pillars) that State Street may ask companies as part of its engagement efforts.
For companies that it believes are not making sufficient progress after engagement, State Street will consider taking action through its votes on directors and/or shareholder proposals. Starting in 2022, at S&P 500 companies, State Street may vote against the independent board leader if a company fails to provide sufficient disclosure in accordance with the TCFD framework, including about board oversight of climate-related risks and opportunities, total Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas (“GHG”) emissions, and targets for reducing GHG emissions.
Companies in “Carbon-Intensive Sectors”
For several years, State Street has had specific disclosure expectations for companies in “carbon-intensive sectors” (oil and gas, utilities and mining), and the guidance document outlines what State Street expects to see beginning in 2022. Disclosures are expected to address: (1) interim GHG emissions reductions targets to accompany long-term climate ambitions; (2) discussion of the impacts of scenario-planning on strategy and financial planning; (3) use of carbon pricing in capital allocation decisions; and (4) Scope 1, Scope 2 and material categories of Scope 3 emissions.
Climate Change Shareholder Proposals
State Street will evaluate climate-related shareholder proposals on a case-by-case basis, taking into account factors that include the reasonableness of a proposal, alignment with the TCFD framework and SASB standards where relevant, emergent market and industry trends, peer performance, and dialogue with the board, management and other stakeholders. For companies in carbon-intensive sectors, State Street will consider alignment with its disclosure expectations specific to these companies. The guidance also addresses specific factors State Street will consider in assessing climate-related lobbying proposals.
Climate Transition Plan Disclosures
Related to the broader subject of climate disclosures, State Street has also issued guidance specific to disclosures about companies’ climate transition plans. In the guidance, State Street notes that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to reaching Net Zero, and that climate-related risks and opportunities are highly nuanced across and within industries. It plans to continue developing its disclosure expectations over time, including taking into account any disclosures mandated by regulators. In his letter, State Street CEO Cyrus Taraporevala emphasizes that what State Street is seeking from climate transition plans, as a long-term investor, “is not purity but pragmatic clarity around how and why a particular transition plan helps a company make meaningful progress.” Mr. Taraporevala also emphasizes the need to take a big-picture look at whether the climate commitments individual companies make have the effect of reducing climate impacts at the aggregate level. In this regard, he observes that so-called “brown-spinning” (public companies selling off their highest-emitting assets to private equity or other market participants), “reduces disclosure, shields polluters, and allows the publicly-traded company to appear more ‘green,’ without any overall reduction in the level of emissions on the planet.” State Street recognizes that in the near term, additional investments in light fossil fuels may be necessary to propel the transition to Net Zero.
In light of these considerations, State Street intends its guidance document on climate transition plans as a “first step” to provide transparency about the core criteria State Street expects companies to address in developing their plans. These criteria are organized into ten categories that generally align with those found in two external frameworks: the Institutional Investors Group on Climate Change (IIGCC) Net Zero Investment Framework and Climate Action 100+ Net-Zero Company Benchmark. The criteria include decarbonization strategy, capital allocation, climate governance, climate policy and stakeholder engagement.
As a companion to its 2022 policy on holding independent board leaders accountable for climate disclosures (discussed above), this year, State Street plans to launch an engagement campaign on climate transition plan disclosure targeted at “significant emitters in carbon-intensive sectors.” Starting in 2023, it will hold directors at these companies accountable if their company fails to show adequate progress in meeting its climate transition disclosure expectations.
Diversity Disclosures
State Street’s guidance document lists five topics it expects all of its portfolio companies to address in their diversity disclosures:
- Board oversight—How the board oversees the company’s diversity, equity and inclusion efforts, including the potential impacts of products and services on diverse communities;
- Strategy—The company’s timebound and specific diversity goals (related to gender, race and ethnicity at a minimum), the policies and programs in place to meet these goals, and how they are measured, managed and progressing;
- Goals—Same as Strategy.
- Metrics—Measures of the diversity of the company’s global workforce and board. For employees, this should include diversity by gender, race and ethnicity (at a minimum) where permitted by law, broken down by industry-relevant employment categories or seniority levels, for all full-time employees. In the U.S., companies are expected to use the disclosure framework from the EEO-1 at a minimum. For the board, disclosures should be provided by gender, race and ethnicity (at a minimum), and can be on an aggregate or individual level; and
- Board diversity—Efforts to achieve diversity at the board level, including how the nominating/governance committee ensures diverse candidates are considered as part of the recruitment process.
State Street also encourages companies to consider providing disclosures about other dimensions of diversity (LGBTQ+, disabilities, etc.), as it views these attributes as furthering the overarching goal of contributing to the diversity of thought on boards and in the workforce.
Diversity and Proxy Voting
State Street will consider disclosures about board diversity in deciding how to vote on directors, as follows:
Racial/Ethnic Diversity – S&P 500 Companies
In 2022, State Street will vote “against,” or “withhold” votes from:
- The chair of the nominating/ governance committee if the company does not disclose the racial and ethnic composition of its board, either at the aggregate or individual level;
- The chair of the nominating/ governance committee if the company does not have at least one director from “an underrepresented racial or ethnic community”; and
- The chair of the compensation committee, if the company does not disclose its EEO-1 report, with acceptable disclosure including the original report, or the exact content of the report translated into custom graphics.
Gender Diversity
State Street may vote “against,” or “withhold” votes from, the chair of the nominating/governance committee:
- Beginning in 2022, for companies in all markets, if there is not at least one female director on the board; and
- Beginning in 2023, at Russell 3000 companies, if the board does not have at least 30% female directors. State Street may waive this policy if a company engages with it and provides a specific, timebound plan for reaching 30%.
If a company fails to meet the gender diversity expectations for three consecutive years, State Street may vote against all incumbent nominating/governance committee members.
The guidance also outlines State Street’s approach to voting on diversity-related shareholder proposals, including specific criteria relating to proposals seeking reporting on diversity, “pay gap” proposals, and proposals seeking racial equity audits.
State Street notes that its voting policies currently focus on increasing board diversity, but that in coming years it intends to shift its focus to the workforce and executive levels. Related to the subject of workforce diversity, the guidance previews ten recommended areas of focus for boards in overseeing racial and ethnic diversity. These are addressed in more detail in a publication issued by State Street in partnership with Russell Reynolds and the Ford Foundation.
Director Overboarding
For 2022, State Street is moving toward an approach that relies more heavily on nominating/governance committee oversight (and enhanced disclosures) about whether directors have enough time to fulfill their commitments. The updated approach is designed to ensure that nominating/governance committees are evaluating directors’ time commitments, regularly assessing director effectiveness, and providing disclosure about their policies and efforts. State Street cites two factors as the key drivers of these updates: its own research showing that boards with overcommitted directors have been slower to adopt leading governance practices and provide robust shareholder rights, and concerns about “tokenism” (nominating already-overcommitted diverse directors) and the need to broaden the candidate pools of diverse directors. The policy updates also address service on SPAC boards.
As a result of the policy updates, beginning in March 2022, State Street will apply the following overboarding limits to directors:
- For board chairs or lead directors, three public company boards; and
- Other director nominees who are not public company NEOs, four public company boards.
State Street may consider waiving these limits and support a director’s election if the company discloses its policy on outside board seats. This policy (or the related disclosure) must include:
- A numerical limit on public company board seats that does not exceed State Street policies by more than one;
- Consideration of public company board leadership positions;
- An affirmation that all directors are currently in compliance with the policy; and
- A description of the nominating/governance committee’s annual process for review outside board commitments.
This waiver policy will not apply to public company NEOs, who remain subject to State Street’s existing limit of two public company boards.
In calculating outside boards, State Street will not count mutual fund boards or SPAC boards, but it expects the nominating/governance committee to consider these boards in evaluating directors’ time commitments.
Human Capital Management (HCM) Disclosures and Practices
State Street’s guidance document lists the five topics it expects companies to address in their HCM disclosures: (1) board oversight; (2) strategy (specifically, how a company’s approach to HCM advances its overall long-term business strategy); (3) compensation, and how it helps to attract and retain employees and incentivize contributions to an effective HCM strategy; (4) “voice” (how companies solicit and act on employee feedback, and how the workforce is engaged in the organization); and (5) how the company advances diversity, equity and inclusion.
State Street emphasizes that it expects companies to provide specificity on these subjects. For example, rather than disclosing that employees are surveyed regularly, State Street suggests that companies disclose survey frequency, examples of questions asked, and relevant examples of actions taken in response to employee feedback. State Street also encourages companies to consider emerging disclosure frameworks, such as the framework outlined by the Human Capital Management Coalition, which includes 35 institutional investors representing over $6.6 trillion in assets.
State Street will approach HCM issues by starting with engagement, focusing on the companies and industries with the greatest HCM risks and opportunities. For companies that it believes are not making sufficient progress after engagement, State Street will consider taking action through its votes on directors and/or shareholder proposals. It will consider supporting shareholder proposals at companies whose HCM disclosures are not sufficiently aligned with State Street’s disclosure expectations.
The following Gibson Dunn lawyers assisted in the preparation of this client update: Elizabeth Ising and Lori Zyskowski.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist with any questions you may have regarding these issues. To learn more about these issues, please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work in the Securities Regulation and Corporate Governance and Executive Compensation and Employee Benefits practice groups, or any of the following practice leaders and members:
Securities Regulation and Corporate Governance Group:
Elizabeth Ising – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8287, eising@gibsondunn.com)
Lori Zyskowski – New York, NY (+1 212-351-2309, lzyskowski@gibsondunn.com)
Ron Mueller – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8671, rmueller@gibsondunn.com)
Thomas J. Kim – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3550, tkim@gibsondunn.com)
Mike Titera – Orange County, CA (+1 949-451-4365, mtitera@gibsondunn.com)
Aaron Briggs – San Francisco, CA (+1 415-393-8297, abriggs@gibsondunn.com)
Julia Lapitskaya – New York, NY (+1 212-351-2354, jlapitskaya@gibsondunn.com)
Cassandra Tillinghast – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3524, ctillinghast@gibsondunn.com)
Executive Compensation and Employee Benefits Group:
Stephen W. Fackler – Palo Alto/New York (+1 650-849-5385/+1 212-351-2392, sfackler@gibsondunn.com)
Sean C. Feller – Los Angeles (+1 310-551-8746, sfeller@gibsondunn.com)
Krista Hanvey – Dallas (+ 214-698-3425, khanvey@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
As we do each year, we offer our observations on new developments and recommended practices for calendar-year filers to consider in preparing their Form 10-K. This alert reviews the recent amendments to Regulation S-K adopted by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and discusses how public companies are reacting to these new requirements. In addition, it discusses other disclosure topics, including Environmental, Social, and Governance (“ESG”) issues such as human capital management, climate change, and cybersecurity, that, in light of increasing investor focus and forthcoming rulemaking, continue to be a top priority for public companies.
The following Gibson Dunn attorneys assisted in preparing this client update: Mike Titera, Justine Robinson, Andrew Fabens, Hillary Holmes, Elizabeth Ising, Thomas Kim, David Korvin, Ron Mueller, Jim Moloney, and Victor Twu.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist with any questions you may have regarding these issues. To learn more about these issues, please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work in the Securities Regulation and Corporate Governance and Capital Markets practice groups, or any of the following practice leaders and members:
Securities Regulation and Corporate Governance Group:
Elizabeth Ising – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8287, eising@gibsondunn.com)
James J. Moloney – Orange County, CA (+1 949-451-4343, jmoloney@gibsondunn.com)
Lori Zyskowski – New York (+1 212-351-2309, lzyskowski@gibsondunn.com)
Brian J. Lane – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3646, blane@gibsondunn.com)
Ronald O. Mueller – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8671, rmueller@gibsondunn.com)
Thomas J. Kim – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3550, tkim@gibsondunn.com)
Mike Titera – Orange County, CA (+1 949-451-4365, mtitera@gibsondunn.com)
Aaron Briggs – San Francisco, CA (+1 415-393-8297, abriggs@gibsondunn.com)
Julia Lapitskaya – New York, NY (+1 212-351-2354, jlapitskaya@gibsondunn.com)
Capital Markets Group:
Andrew L. Fabens – New York (+1 212-351-4034, afabens@gibsondunn.com)
Hillary H. Holmes – Houston (+1 346-718-6602, hholmes@gibsondunn.com)
Stewart L. McDowell – San Francisco (+1 415-393-8322, smcdowell@gibsondunn.com)
Peter W. Wardle – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7242, pwardle@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
Adding to the growing list of jurisdictions that have passed pay transparency laws, effective May 15, 2022, employers in New York City will be required to include salary ranges in job postings.
Brief Summary
The new pay transparency law makes it an “unlawful discriminatory practice” under the New York City Human Rights Law (“NYCHRL”) for an employer to advertise a job, promotion, or transfer opportunity without stating the position’s minimum and maximum salary in the advertisement.
The salary range may include the lowest and highest salaries that the employer believes in “good faith” that it would pay for the job, promotion, or transfer at the time of the posting.
Notably, the law does not define “advertise” and it does not differentiate between jobs that are posted externally versus internally. The law also does not define a “salary,” nor does it clarify the requirements for non-salaried positions.
Covered Employers
The law applies to all employers with at least four employees in New York City, and independent contractors are counted towards that threshold. Significantly, however, the law does not apply to temporary positions advertised by temporary staffing agencies.
Enforcement and Penalties
The New York City Commission on Human Rights is authorized to take action to implement the law, including, among other things, through the promulgation of rules and/or imposition of civil penalties under the NYCHRL.
Growing Trend of Pay Transparency Laws
New York City’s pay transparency law is part of a growing trend in the United States.
In 2021, Colorado enacted a law that requires employers to disclose, among other things, the compensation or range of possible compensation in job postings. Of note, Colorado’s law is more expansive than New York City’s in that it requires employers with even one employee based in Colorado to post such salary information in any job postings for remote work (i.e., work that is performable anywhere, including Colorado).
Last year, Connecticut and Nevada enacted similar pay transparency laws, and Rhode Island passed a law (effective January 1, 2023) which will require employers to provide wage or salary range information to applicants and employees under certain conditions.
California, Maryland, and Washington also have laws requiring salary disclosure, but only upon the request of an applicant or employee, and each law’s disclosure requirements vary slightly. Maryland, for example, requires disclosure of a position’s wage range upon request of any applicant. In comparison, California requires disclosure upon request from applicants who have completed an initial interview and Washington requires disclosure upon request from applicants who have received an offer.
This trend appears poised to continue as other state legislatures, including Massachusetts and South Carolina, are considering pay transparency bills.
Similar to laws banning questions related to an applicant’s salary history during the hiring process, these pay transparency laws are aimed at promoting equal pay. Where state or local law provide for a private right of action, employers may face “tag-along” claims alleging pay disclosure non-compliance in addition to claims of workplace discrimination and/or retaliation.
Takeaway
All covered employers in New York City should take steps to ensure compliance with these new pay transparency requirements effective May 2022. And, employers operating in multiple jurisdictions should carefully monitor the ever-growing patchwork of pay transparency laws in order to ensure compliance wherever located.
The following Gibson Dunn attorneys assisted in preparing this client update: Danielle Moss, Harris Mufson, Gabby Levin, and Meika Freeman.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding these developments. To learn more about these issues, please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work, any member of the firm’s Labor and Employment practice group, or the following:
Danielle J. Moss – New York (+1 212-351-6338, dmoss@gibsondunn.com)
Harris M. Mufson – New York (+1 212-351-3805, hmufson@gibsondunn.com)
Gabrielle Levin – New York (+1 212-351-3901, glevin@gibsondunn.com)
Jason C. Schwartz – Co-Chair, Labor & Employment Group, Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8242, jschwartz@gibsondunn.com)
Katherine V.A. Smith – Co-Chair, Labor & Employment Group, Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7107, ksmith@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
California has seen a flurry of legislative activity over the last couple of years focused on protecting the rights of employees entering separation or settlement agreements with employers. Employers who have not updated their separation or severance agreement templates in the last few years should consider whether updates to their agreements are needed. This is especially true in light of SB 331 which Governor Gavin Newsom signed into law on October 7, 2021. SB 331, or the “Silenced No More Act,” introduces additional restrictions on settlement agreements, non-disparagement agreements and separation agreements executed with employees in California after January 1, 2022.
Background – Recent Legal Developments
California has made a number of changes to requirements for separation and settlement agreements over the past few years, including but not limited to:
- SB 1431, effective January 1, 2019, which amended the language of Section 1542 of the California Civil Code, often cited in settlement agreements, to read as follows: “A general release does not extend to claims that the creditor or releasing party does not know or suspect to exist in his or her favor at the time of executing the release and that, if known by him or her, would have materially affected his or her settlement with the debtor or released party.”
- SB 820 which prohibits provisions in settlement agreements entered into after January 1, 2019 that prevent the disclosure of facts related to sexual assault, harassment, and discrimination claims “filed in a civil action” or in “a complaint filed in an administrative action.” SB 820 did not prohibit provisions requiring confidentiality of a settlement payment amount, and the law included an exception for provisions protecting the identity of the claimant where requested by the claimant.
- SB 1300, effective January 1, 2019, amended California’s Fair Employment and Housing Act to prohibit employers from requiring employees to agree to a non-disparagement agreement or other document limiting the disclosure of information about unlawful workplace acts in exchange for a raise or bonus, or as a condition of employment or continued employment. SB 1300 further prohibited employers from requiring, in exchange for a raise or bonus or as a condition of employment or continued employment, that an individual “execute a statement that he or she does not possess any claim or injury against the employer” or release “a right to file and pursue a civil action or complaint with, or otherwise notify, a state agency, other public prosecutor, law enforcement agency, or any court or other governmental entity.” Under the law, any such agreement is contrary to public policy and unenforceable. That said, negotiated settlement agreements of civil claims supported by valuable consideration were exempted from these prohibitions.
- AB 749 went into effect on January 1, 2020 and further impacted settlement agreements by limiting the inclusion of “no-rehire” provisions in agreements that settle employment disputes. AB 749 created Code of Civil Procedure Section 1002.5, which prohibits an agreement to settle an employment dispute from containing “a provision prohibiting, preventing, or otherwise restricting a settling party that is an aggrieved person from obtaining future employment with the employer against which the aggrieved person has filed a claim, or any parent company, subsidiary, division, affiliate, or contractor of the employer.” AB 749 defined an “aggrieved person” as “a person who has filed a claim against the person’s employer in court, before an administrative agency, in an alternative dispute resolution forum, or through the employer’s internal complaint process.” Notably, AB 749 continued to allow a “no-rehire” provision in a settlement agreement with an employee whom the employer, in good faith, determined engaged in sexual harassment or sexual assault. AB 749 did not restrict the execution of a severance agreement that is unrelated to a claim filed by the employee against the employer.
- AB 2143, which took effect January 1, 2021, modified the provisions enacted by AB 749 to further clarify and expand when employers can include a “no-rehire” provision in separation or settlement agreements. Specifically, AB 2143 amended Code of Civil Procedure Section 1002.5 to also allow a “no-rehire” provision if the aggrieved party has engaged in “any criminal conduct.” AB 2143 also clarified that in order to include a “no-rehire” provision in a separation or settlement agreement, an employer must have made and documented a good-faith determination that such individual engaged in sexual harassment, sexual assault, or any criminal conduct before the aggrieved employee raised his or her claim. Finally, AB 2143 also made clear that the restriction on “no-rehire” provisions set forth in Code of Civil Procedure Section 1002.5 applies only to employees whose claims were filed in “good faith.”
SB 331 – Key Changes
Against this legal backdrop, SB 331 has introduced additional restrictions that employers should keep in mind when entering into settlement or separation agreements with employees in California.
Settlement Agreements
Building on the protections included in SB 820, SB 331 expanded SB 820’s prohibition on provisions that prevent the disclosure of facts to include all facts related to all forms of harassment, discrimination, and retaliation—not just those related to sexual assault, sexual harassment, or sex discrimination. Just as with SB 820, parties can agree to prevent the disclosure of the settlement payment amount, and the identity of the claimant can be protected where requested by the claimant.
Non-Disparagement Covenants and Separation Agreements
Consistent with SB 1300, SB 331 prohibits an employer from requiring an employee to agree to a non-disparagement agreement or other document limiting the disclosure of “information about unlawful acts in the workplace” in exchange for a raise or bonus, or as a condition of employment or continued employment. SB 331 also prohibits an employer from including in any separation agreement with an employee or former employee any provision that prevents the disclosure of “information about unlawful acts in the workplace” which includes, but is not limited to, information pertaining to harassment or discrimination or any other conduct that the employee has reasonable cause to believe is unlawful.
Effective January 1, 2022, any non-disparagement or other contractual provision that restricts an employee’s ability to disclose information related to conditions in the workplace must include, in substantial form, the following language: “Nothing in this agreement prevents you from discussing or disclosing information about unlawful acts in the workplace, such as harassment or discrimination or any other conduct that you have reason to believe is unlawful.”
Finally, SB 331 also provides that any separation agreement with an employee or former employee related to an employee’s separation from employment that includes a release of claims must provide: (i) notice that the employee has the right to consult an attorney regarding the agreement and (ii) a reasonable time period of at least five (5) business days in which to consult with an attorney. An employee may sign the agreement before the end of such reasonable time period so long as such employee’s decision is “knowing and voluntary” and is not induced by the employer through fraud, misrepresentation or a threat to withdraw or alter the offer prior to the expiration of such reasonable period of time or by providing different terms to the employees who sign such an agreement before the expiration of such time period. The SB 331 requirements do not apply to a negotiated agreement to resolve an underlying claim filed by an employee in court, before an administrative agency, in arbitration, or through an employer’s internal complaint process.
Conclusion and Next Steps
SB 331 represents the latest step taken by California intended to protect employees’ rights by restraining employers from preventing the disclosure of information regarding certain workplace conditions.
When evaluating separation or severance agreement templates, employers should consider whether the agreements:
- Include language requiring that a settlement or severance amount be held in the strictest confidence by the employee or former employee.
- Have the latest amended Section 1542 language.
- Have the appropriate disclosures for any non-disparagement provisions.
- Provide employees with sufficient disclosures and time to consider the separation agreement.
- Include limitations on individuals which are now prohibited.
Employers should navigate these requirements with care. Compliance with California’s multifaceted legal protections for employees and former employees will require careful drafting. Employers should consider seeking the assistance of legal counsel to refresh templates prior to entering into settlement or separation agreements in California.
The following Gibson Dunn attorneys assisted in preparing this client update: Tiffany Phan, Florentino Salazar, Sean Feller, Jason Schwartz, and Katherine V.A. Smith.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding these developments. To learn more about these issues, please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work, any member of the firm’s Labor and Employment practice group, or the following:
Tiffany Phan – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7522, tphan@gibsondunn.com)
Sean C. Feller – Co-Chair, Executive Compensation & Employee Benefits Group, Los Angeles
(+1 310-551-8746, sfeller@gibsondunn.com)
Jason C. Schwartz – Co-Chair, Labor & Employment Group, Washington, D.C.
(+1 202-955-8242, jschwartz@gibsondunn.com)
Katherine V.A. Smith – Co-Chair, Labor & Employment Group, Los Angeles
(+1 213-229-7107, ksmith@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
Introduction
On 12 January 2022, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) released a Discussion Paper on the expansion of the Hong Kong regulatory framework to stablecoins (e.g. crypto-assets pegged to fiat currencies). The Paper considers the adequacy of the existing regulatory framework in light of the growing use of stablecoins and other types of crypto-assets in financial markets, and the challenges posed by this increase in their prevalence. It further poses eight questions for consideration by the industry, including the scope of a proposed new regulatory regime to cover what the HKMA describes as “payment-related stablecoins”.
This client alert provides an overview of the HKMA’s views on crypto-assets and stablecoins as outlined in the Paper, discusses the implications for players in the stablecoin ecosystem if the proposed changes are implemented, and suggested next steps for interested parties.
The HKMA has requested responses to the Paper by 31 March 2022, and has indicated that it intends to introduce this new stablecoin regulatory regime by 2023-2024.
HKMA’s views on crypto-assets and financial stability
The Paper provides a valuable insight into the HKMA’s views on crypto-assets in general, and stablecoins in particular, including their linkages to the traditional financial system and ramifications on financial stability.
In introducing its proposal to regulate payment related stablecoins, the HKMA has made it clear that while the current size and trading activity of crypto-assets globally may not pose an immediate threat to the stability of the global financial system from a systemic point of view, it does consider the increasing prevalence of crypto-assets to have the potential to impact financial stability. In particular, the HKMA has flagged that it considers the growing exposure of institutional investors, as well as certain segments of the retail public, to such assets as an alternative to, or to complement traditional asset classes, indicates growing interconnectedness with the mainstream financial system.
Further, as noted by the HKMA, it understands that while Hong Kong authorised banks (Authorised Institutions or AIs) currently undertake only limited activities in relation to crypto-assets, AIs are interested in pursuing these activities further, given that they face increasing demand from customers for crypto-related products and services. This is consistent with what we understand is a steady increase in high net wealth investors hungry for yield demanding access to crypto-assets through their private wealth managers, as well as an uptick in demand from retail investors in Hong Kong eager for the same exposure to upside. To this end, the HKMA has flagged that it will soon provide AIs with more detailed regulatory guidance in relation to their interface with and provision of services to customers in relation to crypto-assets.
Finally, the HKMA has also noted its concerns that the ease of anonymous transfer of crypto-assets may make them susceptible to the risk of illicit and money laundering / terrorist financing activities.
The HKMA’s views on stablecoins
The Paper also flags the HKMA’s view that stablecoins are increasingly viewed as a ‘widely acceptable means of payment’ and that this, alongside the actual increase in their use, has increased the potential for their incorporation into the mainstream financial system. In the HKMA’s opinion, this in turn raises broader monetary and financial stability implications and has resulted in the regulation of stablecoins becoming a key priority for the HKMA, which has stated in the Paper that it wishes to ensure that such coins “are appropriately regulated before they operate in Hong Kong or are marketed to the public of Hong Kong”.
The Paper goes on to identify a number of potential risks that may arise in relation to the use of stablecoins, including, in summary:
- Payment integrity risks where stablecoins are commonly accepted as a means of payment and operational disruptions or failures occur in relation to the stablecoins;
- Banking stability risks if banks were to increase their exposure to stablecoins, particularly if stablecoins were viewed as a substitute for bank deposits;
- Monetary policy risks in relation to the issue and redemption of HKD-backed stablecoins, which could affect interbank HKD demand and supply; and
- User protection risks where a user may have no or limited recourse in relation to operational disruptions or failures of a stablecoin.
Given these potential risks, the HKMA has stated in the Paper that it considers it appropriate to expand the regulatory perimeter to cover payment-related stablecoins in the first instance, although it has not ruled out the possibility of regulating other forms of stablecoins as well.
The HKMA’s discussion questions for industry consideration
The HKMA has noted in the Paper that it considers ‘the need to regulate [stablecoins] is well justified and the tool to regulate…[can] be decided at a later stage’. However, it has indicated that it wishes for feedback from the industry and the public on the scope of the regulatory regime applicable to stablecoins, and to this end has set out eight discussion questions for industry consideration. A summary of the key questions posed by the HKMA, as well as the HKMA’s views on those questions, is set out below.
| Question 1: Should we regulate activities relating to all types of stablecoins or give priority to those payment-related stablecoins that pose higher risks to the monetary and financial systems while providing flexibility in the regime to make adjustments to the scope of stablecoins that may be subject to regulation as needed in the future? |
In posing this question, the HKMA has noted that it intends to take a risk-based approach focused initially on payment-related stablecoins at this stage given their predominance in the market and higher potential to be incorporated into the mainstream financial market (as discussed above). However, the HKMA has noted that it intends to ensure that whatever regime is introduced is sufficiently flexible that it could extend to other types of stablecoins in the future. As such, issuers and traders of other types of stablecoins should not expect to avoid regulatory scrutiny forever.
| Question 2: What types of stablecoin-related activities should fall under the regulatory ambit, e.g. issuance and redemption, custody and administration, reserves management? |
The HKMA has proposed regulating a broad range of stablecoin-related activities, including:
- Issuing, creating or destroying stablecoins;
- Managing reserve assets to ensure stabilisation of stablecoin value;
- Validating transactions and records;
- Storing private keys used to provide access to stablecoins;
- Facilitating the redemption of stablecoins;
- Transmission of funds to settle transactions; and
- Executing transactions in stablecoins.
This broad list is based on a list of activities in relation to stablecoins published by the Financial Stability Board[1] and as such may be viewed as in keeping with international standards. However, as discussed below in relation to Question 5, the breadth of this regime may raise concerns regarding the degree of overlap between this regime and others proposed by Hong Kong regulators, including the proposed VASP regime to be administered by the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) (see our alert here).
| Question 3: What kind of authorisation and regulatory requirements would be envisaged for those entities subject to the new licensing regime? |
The HMKA has suggested that it considers that entities subject to the new stablecoin licensing regime would be subject to the following requirements:
- authorisation and prudential requirements, including adequate financial resources and liquidity requirements;
- fit and proper requirements in relation to both management and ownership;
- requirements relating to the maintenance and management of reserves of backing assets; and systems; and
- controls, governance and risk management requirements.
Further, given that it is common for multiple entities to be involved in different parts of a stablecoin arrangement, the HKMA has noted that such entities could be subject to part or all of the requirements, depending on the services they offer.
If requirements in relation to these matters are ultimately implemented by the HKMA, the stablecoin regime would cover some of the requirements of the proposed VASP regime, with the exception of requirements of reserves of backing assets, which will presumably only be applied to stablecoins given their nature.
| Question 4: What is the intended coverage as to who needs a licence under the intended regulatory regime? |
The HKMA has signalled that it believes that only entities incorporated in Hong Kong and holding a relevant licence granted by HKMA should carry out regulated activities, to enable the HKMA to exercise effective regulation on the relevant entities. As such, it has stated in the Paper that it expects that foreign companies / groups which intend to provide regulated activities in Hong Kong or actively market those activities in Hong Kong to incorporate a company in Hong Kong and apply for a licence to the HKMA under this regime.
If implemented, this would have significant ramifications for those global crypto-exchanges currently offering trading in stablecoins to Hong Kong users from offshore. These businesses would be faced with a choice between either incorporating in Hong Kong and seeking a licence, or discontinuing their trading for Hong Kong users.
| Question 5: When will this new, risk-based regime on stablecoins be established, and would there be regulatory overlap with other financial regulatory regimes in Hong Kong, including but not limited to the SFC’s VASP regime, and the SVF licensing regime of the PSSVFO? |
The HKMA has stated that it will collaborate and coordinate with other financial regulators when defining the scope of its oversight and will seek to avoid regulatory arbitrage, including in relation to areas which ‘may be subject to regulation by more than one local financial authority’.
However, an HKMA-administered regime of the breadth proposed above would create a situation in which an exchange undertaking transactions in non-stablecoin crypto-assets would be regulated by the SFC under its proposed new VASP regime while being regulated by both the SFC and the HKMA under its stablecoin regime. In this respect, we note that the proposed definition of ‘virtual asset’ under the proposed new VASP regime ‘applies equally to virtual coins that are stable (i.e. the so-called “stablecoins”)’.[2] While the HKMA and SFC share regulatory responsibility for Registered Institutions (i.e. Authorised Institutions which are separately licensed by the SFC to undertake securities and futures business), that shared regulatory responsibility concerns distinctly different types of activities. In contrast, we consider that from an exchange’s perspective, the act of executing transactions in stablecoins is substantially similar to executing transactions in non-stablecoin crypto-assets. As such, this approach may lead to unnecessary and undesirable regulatory inefficiencies if exchanges are required to be licensed under both the SFC and HKMA regimes to undertake transactions in crypto-assets.
| Question 6: Stablecoins could be subject to run and become potential substitutes of bank deposits. Should the HKMA require stablecoin issuers to be AIs under the Banking Ordinance, similar to the recommendations in the Report on Stablecoins issued by the US President’s Working Group on Financial Markets? |
While not expressly stating that it will not require stablecoin issuers to be regulated as AIs under the Banking Ordinance, the HKMA has indicated that it expects that the requirements applicable to stablecoin issuers will instead borrow from Hong Kong’s current regulatory framework for stored value facilities (SVF). However, the HKMA has signalled that certain stablecoin issuers may be subject to higher prudential requirements than SVF issuers where they issue stablecoins of systemic importance.
| Question 7: [Does] the HKMA also have plan[s] to regulate unbacked crypto-assets given their growing linkage with the mainstream financial system and risk to financial stability? |
The HKMA has not expressly ruled out regulating unbacked crypto-assets, and has stated that it is necessary to continue monitoring the risks posed by this asset class. In stating this, the HKMA has also pointed to the VASP regime, suggesting that the HKMA’s approach to this area is likely to depend on the success of that regime once implemented.
| Question 8: For current or prospective parties and entities in the stablecoins ecosystem, what should they do before the HKMA’s regulatory regime is introduced? |
The HKMA has advised current and prospective players in the stablecoin ecosystem to provide feedback on the proposals set out in the Discussion Paper, and has noted that in the interim, it will continue to supervise AIs’ activities in relation to crypto-assets and implement the SVF licensing regime pending implementation of this new regime.
Conclusion
The Discussion Paper provides a valuable insight into the HKMA’s plans for the future of stablecoin regulation in Hong Kong. While some concerns exist as to the potential overlap between the HKMA’s new proposed regime and the SFC’s VASP regime, it is clear that the HKMA intends to ensure that it is regarded as the primary regulator of stablecoins going forward, and that it sees the regulation of this asset class as closely linked to its key objective of ensuring financial stability.
____________________________
[1] See Financial Stability Board, Regulation, Supervision and Oversight of “Global Stablecoin” Arrangements: Final Report and High-Level Recommendations, https://www.fsb.org/wp-content/uploads/P131020-3.pdf, page 10.
[2] See Financial Services and the Treasury Bureau, Public Consultation on Legislative Proposals to Enhance Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Regulation in Hong Kong (Consultation Conclusions), https://www.fstb.gov.hk/fsb/en/publication/consult/doc/consult_conclu_amlo_e.pdf, paragraph 2.8.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding these developments. If you wish to discuss any of the matters set out above, please contact any member of Gibson Dunn’s Crypto Taskforce (cryptotaskforce@gibsondunn.com) or the Global Financial Regulatory team, including the following authors in Hong Kong:
William R. Hallatt (+852 2214 3836, whallatt@gibsondunn.com)
Emily Rumble (+852 2214 3839, erumble@gibsondunn.com)
Arnold Pun (+852 2214 3838, apun@gibsondunn.com)
Becky Chung (+852 2214 3837, bchung@gibsondunn.com)
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
Decided January 13, 2022
National Federation of Independent Business v. Occupational Safety and Health Administration, No. 21A244; and
Ohio v. Occupational Safety and Health Administration, No. 21A247
On Thursday, January 13, 2022, by a 6–3 vote, the Supreme Court prevented the implementation of an OSHA rule that would have imposed a vaccine-or-testing regime on employers with 100 or more employees.
Background:
On November 5, 2021, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (“OSHA”) issued an emergency temporary standard (“ETS”) governing employers with 100 or more employees. The ETS mandated covered employers to “develop, implement, and enforce a mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policy, with an exception for employers” that require unvaccinated employees to undergo weekly COVID-19 testing and to wear a mask during the workday.
Business groups and States filed petitions for review of the ETS in each regional Court of Appeals, contending that OSHA exceeded its statutory authority under the Occupational Safety and Health Act. The Fifth Circuit stayed the ETS and later held that the OSHA mandate was overly broad, not justified by a “grave” danger from COVID-19, and constitutionally dubious. After all petitions for review were consolidated in the Sixth Circuit, that court dissolved the Fifth Circuit’s stay. The panel majority held that COVID-19 was an emergency warranting an ETS and that OSHA had likely acted within its statutory authority.
Issue:
Whether to stay implementation of the vaccine-or-testing mandate pending the outcome of litigation challenging OSHA’s statutory authority to require employers with 100 or more employees to develop, adopt, and enforce a vaccine-and-testing regime for their employees.
Court’s Holding:
The vaccine-or-testing mandate should be stayed because OSHA likely lacks the statutory authority to adopt the vaccine-or-test mandate in the absence of an unmistakable delegation from Congress.
“It is telling that OSHA, in its half century of existence, has never before adopted a broad public health regulation of this kind—addressing a threat that is untethered, in any causal sense, from the workplace.”
Per Curiam Opinion of the Court
What It Means:
- The Court’s decision prevents the implementation of the OSHA mandate, which applies to 84 million Americans. Echoing its recent decision in Alabama Ass’n of Realtors v. Dep’t of Health & Human Services, the Court emphasized that agency action with such “vast economic and political significance” requires a clear delegation from Congress. It is doubtful that the stay will be lifted to allow OSHA to enforce the mandate before the ETS expires in May, meaning that it is unlikely employers will ever actually be subject to the ETS’s vaccine-or-testing mandate.
- The challengers had argued that covered employers would incur unrecoverable compliance costs and that employees would quit rather than comply. The federal government, for its part, had argued that the OSHA mandate would save over 6,500 lives and prevent hundreds of thousands of hospitalizations. The Court stayed the mandate without resolving this dispute on the ground that only Congress could properly weigh such tradeoffs.
- The Court’s decision to hear oral argument on the stay applications may signal the beginning of a trend, as this is the second time this Term that the Court moved an application to vacate a stay from the emergency docket to the argument calendar.
- Other Mandates: The Court stayed lower court injunctions against the vaccine mandate issued by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (“CMS”). See Biden v. Missouri, 21A240; Becerra v. Louisiana, 21A241. By a 5–4 vote, the Court ruled that the Secretary of Health and Human Services likely has the statutory authority to require vaccination for healthcare workers at facilities that participate in Medicare and Medicaid. Today’s decisions do not address the federal contractor vaccine mandate that is presently enjoined on a nationwide basis by a federal district court in Georgia. Four other federal district courts also have enjoined the government from enforcing that mandate. So far, the Sixth and Eleventh Circuits have refused to stay the injunctions against the federal contractor mandate pending appeal.
The Court’s opinions are available here and here.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding developments at the Supreme Court. Please feel free to contact the following practice leaders:
Appellate and Constitutional Law Practice
| Allyson N. Ho +1 214.698.3233 aho@gibsondunn.com |
Mark A. Perry +1 202.887.3667 mperry@gibsondunn.com |
Lucas C. Townsend +1 202.887.3731 ltownsend@gibsondunn.com |
| Bradley J. Hamburger +1 213.229.7658 bhamburger@gibsondunn.com |
Related Practice: Labor and Employment:
| Eugene Scalia +1 202.955.8543 escalia@gibsondunn.com |
Jessica Brown +1 303.298.5944 jbrown@gibsondunn.com |
Jason C. Schwartz +1 202.955.8242 jschwartz@gibsondunn.com |
| Katherine V.A. Smith +1 213.229.7107 ksmith@gibsondunn.com |
The tense political battles between former President Donald J. Trump and the United States House of Representatives under Democratic leadership renewed debates over the nature and extent of Congress’s authority to investigate and conduct oversight and have wide-ranging implications for congressional investigation of not just the Executive Branch but also of private parties.
In furtherance of the House of Representatives’ vigorous efforts to investigate President Trump, three House committees issued a series of subpoenas to banks and an accounting firm seeking the personal financial records of the President relating to periods both before and after he took office. The President and his business entities resisted, challenging the congressional subpoenas in court, thus drawing the judiciary into the fray. The President’s challenges culminated in the issuance of the Supreme Court’s historic decision in Trump v. Mazars and Trump v. Deutsche Bank AG, which announced groundbreaking new principles of law that will have profound implications for congressional oversight and investigations. In addition, the D.C. Circuit recently encountered related questions of congressional authority over the Executive Branch in connection with separate information requests to former White House Counsel Donald McGahn, leading to a series of hotly debated rulings (and an eventual settlement) in Committee on the Judiciary v. McGahn.
These cases arose against a seemingly well-established backdrop. It has long been understood that Congress possesses inherent constitutional authority to inquire into matters that could become the subject of legislation, such as through the use of compulsory process directed to both government officials and private citizens. As the Supreme Court recognized nearly a century ago, Congress “cannot legislate wisely or effectively in the absence of information respecting the conditions which the legislation is intended to affect or change.” Thus, “the power of inquiry—with process to enforce it—is an essential and appropriate auxiliary to the legislative function.” The Executive and Legislative Branches often resolve disputes about congressional requests for information through the “hurly-burly, the give-and-take of the political process between the legislative and the executive.” Only recently has Congress resorted repeatedly to the courts in an effort to enforce subpoenas against Executive Branch officials.
Washington, D.C. partners Michael Bopp and Thomas Hungar, with Chantalle Carles Schropp, prepared this article, originally published by the University of Virginia’s Journal of Law & Politics, Vol. 37, No. 1, in 2021.
© 2022 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
On December 15, 2021, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC” or “Commission”) held a virtual open meeting where it considered four rule proposals, including two that are particularly pertinent to all public companies: (i) amendments regarding Rule 10b5-1 insider trading plans and related disclosures and (ii) new share repurchase disclosures rules.
Both proposals passed, though only the proposed amendments regarding Rule 10b5-1 insider trading plans and related disclosures passed unanimously; the proposed new share repurchase disclosures rules passed on party lines. Notably, these proposals only have a 45-day comment period, which is shorter than the more customary 60- or 90-day comment periods. Commissioner Roisman, in particular, raised concerns about the 45-day comment periods being too short, noting that the comment periods run “not only over several holidays,” but “also concurrent with five other rule proposals that have open comment periods.”
Below, please find summary descriptions of the these two rule proposals, as well as certain Commissioners’ concerns related to these proposals.
The following Gibson Dunn attorneys assisted in preparing this update: Ronald Mueller, Andrew Fabens, James Moloney, Lori Zyskowski, Thomas Kim, Brian Lane, and Elizabeth Ising.
The current Supreme Court term promises to be one of the most eventful and impactful in recent memory. In this episode of “The Two Teds,” Ted Boutrous and Ted Olson discuss some of the key cases that will be heard during this session, covering topics that include abortion rights and the First Amendment.
Previous Episode | Next Episode
All episodes of The Two Teds are available on GibsonDunn.com and wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also subscribe to be notified of new episodes via e-mail.
HOSTS:
Ted Boutrous – Theodore J. Boutrous, Jr., a partner in the Los Angeles office of Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP, is global Co-Chair of the firm’s Litigation Group and previously led the firm’s Appellate, Crisis Management, Transnational Litigation and Media groups. He also is a member of the firm’s Executive and Management Committees. Recognized for a decade of excellence in the legal profession, the Daily Journal in 2021 named Mr. Boutrous as a Top Lawyer of the Decade for his victories. As a tireless advocate and leader for high-stakes and high-profile cases, Mr. Boutrous was also named the 2019 “Litigator of the Year, Grand Prize Winner” by The American Lawyer.
Ted Olson – Theodore B. Olson is a Partner in Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher’s Washington, D.C. office; a founder of the Firm’s Crisis Management, Sports Law, and Appellate and Constitutional Law Practice Groups. Mr. Olson was Solicitor General of the United States during the period 2001-2004. From 1981-1984, he was Assistant Attorney General in charge of the Office of Legal Counsel in the U.S. Department of Justice. Except for those two intervals, he has been a lawyer with Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher in Los Angeles and Washington, D.C. since 1965.
This year marks an important turning point for the seven-member Court, as new judges will soon comprise nearly half its bench. In June, the New York Senate confirmed the appointment of Anthony Cannataro and Madeline Singas. Judge Cannataro, who was formerly the Administrative Judge of the Civil Court of the City of New York, filled the vacancy left by Judge Paul Feinman, who passed away. Judge Singas, who was formerly the Nassau County District Attorney, filled the vacancy left by the retired Judge Leslie Stein. As Judges Feinman and Stein often voted with Chief Judge DiFiore and Judge Garcia to form a majority in the Court’s decisions, it remains to be seen if that pattern continues.
The Court will also change in 2022 because Judge Eugene Fahey, a swing vote, reaches his mandatory retirement age at the end of this year. To fill his seat, Governor Kathy Hochul nominated Shirley Troutman, a justice in the Appellate Division, Third Department. If confirmed, she would be the second African American woman to sit on the Court. Justice Troutman has extensive experience as a prosecutor and a judge. She also has spent her career upstate, providing geographic balance. On the other hand, analysts have expressed concern that the Court lacks “professional diversity,” as it would include four former prosecutors and only one judge (Fahey, or Troutman) with judicial experience in the Appellate Division.
Despite this turnover, the Court continued previous trends, with the pace of decisions reduced and a high number of fractured opinions. After Judge Feinman’s passing, the Court ordered several cases to be reargued in a “future court session,” which may suggest that his was a potential swing vote in those cases. Nevertheless, the Court continued to resolve significant issues in a wide array of areas, from territorial jurisdiction and agency deference to consumer protection and insurance contracts.
The New York Court of Appeals Round-Up & Preview summarizes key opinions primarily in civil cases issued by the Court over the past year and highlights a number of cases of potentially broad significance that the Court will hear during the coming year. The cases are organized by subject.
To view the Round-Up, click here.
Gibson Dunn’s New York office is home to a team of top appellate specialists and litigators who regularly represent clients in appellate matters involving an array of constitutional, statutory, regulatory, and common-law issues, including securities, antitrust, commercial, intellectual property, insurance, First Amendment, class action, and complex contract disputes. In addition to our expertise in New York’s appellate courts, we regularly brief and argue some of the firm’s most important appeals, file amicus briefs, participate in motion practice, develop policy arguments, and preserve critical arguments for appeal. That is nowhere more critical than in New York—the epicenter of domestic and global commerce—where appellate procedure is complex, the state political system is arcane, and interlocutory appeals are permitted from the vast majority of trial-court rulings.
Our lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have regarding developments at the New York Court of Appeals, or any other state or federal appellate courts in New York. Please feel free to contact any member of the firm’s Appellate and Constitutional Law practice group, or the following lawyers in New York:
Mylan L. Denerstein (+1 212-351-3850, mdenerstein@gibsondunn.com)
Akiva Shapiro (+1 212-351-3830, ashapiro@gibsondunn.com)
Seth M. Rokosky (+1 212-351-6389, srokosky@gibsondunn.com)
Please also feel free to contact the following practice group leaders:
Allyson N. Ho – Dallas (+1 214.698.3233, aho@gibsondunn.com)
Mark A. Perry – Washington, D.C. (+1 202.887.3667, mperry@gibsondunn.com)
© 2021 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
Virginia and Colorado, which earlier this year enacted comprehensive state privacy laws following California’s 2018 lead, are now poised to follow California in another way in 2022: writing implementing regulations and weighing changes to the laws themselves. Companies should account for these regulations and changes as they develop programs to comply with the laws, which take effect in 2023.
In Virginia, lawmakers are exploring possible updates to the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (“VCDPA”), which passed in March 2021, such as giving a state agency rulemaking authority. Unlike the California and Colorado laws, the VCDPA itself does not give a state agency the power to issue regulations to implement the new law. But a recent report mandated by the VCDPA recommended that the legislature give the Virginia Attorney General’s Office (“Virginia AG”) or another agency such rulemaking authority.
The report was issued in response to a provision in the VCDPA, which required the creation of a working group made up of government, business, and community representatives to study potential changes to the VCDPA before it goes into effect. The group met six times before issuing its final report in November. In addition to rulemaking authority, the report also suggested other significant changes, including increasing the Virginia AG’s enforcement budget, allowing the Virginia AG to collect actual damages from violations that cause consumer harm, giving companies a right to cure violations that would sunset in the future, requiring companies to honor an automated global opt-out signal, changing the “right to delete” to a “right to opt out of sale,” and considering amending statutory definitions such as “sale,” “personal data,” “publicly available information,” and “sensitive data,” among others. The final report is available here.
In Colorado, meanwhile, the Colorado Attorney General’s Office (“Colorado AG”), which already has rulemaking authority, has begun the rulemaking process for the Colorado Privacy Act (“CPA”), which passed in July 2021. In its regulatory agenda for 2022, the Colorado AG stated that it expects to propose and finalize rules for universal opt-out tools, which are mechanisms that allow users to automatically inform websites that they want to opt out of the processing of their personal data.
As we have reported in prior updates, California is tackling these issues in its own privacy laws, particularly as California is transitioning from the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”) to the California Privacy Rights Act (“CPRA”), which will take effect in 2023. In the meantime, the California Attorney General’s Office (“California AG”) promulgation of CCPA regulations that were last revised in March 2021, remain in force. Now, the new CPRA-created California Privacy Protection Agency has embarked in earnest on its own rulemaking to consider amending the California AG’s CCPA rules and to enact its own rules for the CPRA. In response to a request for comments on its proposed rulemaking, the agency received scores of comments from individuals, organizations, and government officials, which are available here.
There is no sign of a slowdown in the development of state privacy laws. In fact, more than two dozen other states have floated their own proposals for comprehensive privacy laws.
Although the precise contours of these laws remain in flux, the laws will almost certainly usher in notable regulatory changes affecting how companies collect and manage data while imposing a host of new obligations and potential liability. Companies would be well-served to focus their compliance programs accordingly.
We will continue to monitor developments, and are available to discuss these issues as applied to your particular business.
This alert was prepared by Ryan T. Bergsieker, Cassandra L. Gaedt-Sheckter, and Eric M. Hornbeck.
Gibson Dunn lawyers are available to assist in addressing any questions you may have about these developments. Please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work, the authors, or any member of the firm’s Privacy, Cybersecurity and Data Innovation practice group.
Privacy, Cybersecurity and Data Innovation Group:
United States
Alexander H. Southwell – Co-Chair, PCDI Practice, New York (+1 212-351-3981, asouthwell@gibsondunn.com)
S. Ashlie Beringer – Co-Chair, PCDI Practice, Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5327, aberinger@gibsondunn.com)
Debra Wong Yang – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7472, dwongyang@gibsondunn.com)
Matthew Benjamin – New York (+1 212-351-4079, mbenjamin@gibsondunn.com)
Ryan T. Bergsieker – Denver (+1 303-298-5774, rbergsieker@gibsondunn.com)
David P. Burns – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3786, dburns@gibsondunn.com)
Nicola T. Hanna – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7269, nhanna@gibsondunn.com)
Howard S. Hogan – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3640, hhogan@gibsondunn.com)
Robert K. Hur – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3674, rhur@gibsondunn.com)
Joshua A. Jessen – Orange County/Palo Alto (+1 949-451-4114/+1 650-849-5375, jjessen@gibsondunn.com)
Kristin A. Linsley – San Francisco (+1 415-393-8395, klinsley@gibsondunn.com)
H. Mark Lyon – Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5307, mlyon@gibsondunn.com)
Karl G. Nelson – Dallas (+1 214-698-3203, knelson@gibsondunn.com)
Ashley Rogers – Dallas (+1 214-698-3316, arogers@gibsondunn.com)
Deborah L. Stein – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7164, dstein@gibsondunn.com)
Eric D. Vandevelde – Los Angeles (+1 213-229-7186, evandevelde@gibsondunn.com)
Benjamin B. Wagner – Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5395, bwagner@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Li-Ming Wong – San Francisco/Palo Alto (+1 415-393-8333/+1 650-849-5393, mwong@gibsondunn.com)
Cassandra L. Gaedt-Sheckter – Palo Alto (+1 650-849-5203, cgaedt-sheckter@gibsondunn.com)
Europe
Ahmed Baladi – Co-Chair, PCDI Practice, Paris (+33 (0)1 56 43 13 00, abaladi@gibsondunn.com)
James A. Cox – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4250, jacox@gibsondunn.com)
Patrick Doris – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4276, pdoris@gibsondunn.com)
Kai Gesing – Munich (+49 89 189 33-180, kgesing@gibsondunn.com)
Bernard Grinspan – Paris (+33 (0)1 56 43 13 00, bgrinspan@gibsondunn.com)
Penny Madden – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4226, pmadden@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Walther – Munich (+49 89 189 33-180, mwalther@gibsondunn.com)
Alejandro Guerrero – Brussels (+32 2 554 7218, aguerrero@gibsondunn.com)
Vera Lukic – Paris (+33 (0)1 56 43 13 00, vlukic@gibsondunn.com)
Sarah Wazen – London (+44 (0) 20 7071 4203, swazen@gibsondunn.com)
Asia
Kelly Austin – Hong Kong (+852 2214 3788, kaustin@gibsondunn.com)
Connell O’Neill – Hong Kong (+852 2214 3812, coneill@gibsondunn.com)
Jai S. Pathak – Singapore (+65 6507 3683, jpathak@gibsondunn.com)
© 2021 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.
Institutional Shareholder Services (“ISS”) and Glass, Lewis & Co. (“Glass Lewis”), the two major proxy advisory firms, recently released updates to their proxy voting policies for the 2022 proxy season. The ISS U.S. policy updates are available here. The ISS updates will apply for shareholder meetings on or after February 1, 2022, except for those policies subject to a transition period. ISS plans to release an updated Frequently Asked Questions document that will include more information about its policy changes in the coming weeks.[1]
The Glass Lewis updates are included in its 2022 U.S. Policy Guidelines and the 2022 ESG Initiatives Policy Guidelines, which cover shareholder proposals. Both documents are available here. The Glass Lewis 2022 voting guidelines will apply for shareholder meetings held on or after January 1, 2022.
This alert reviews the ISS and Glass Lewis updates. Both firms have announced policy updates on the topics of board diversity, multi-class stock structures, and climate-related management and shareholder proposals. Glass Lewis also issued several policy updates that focus on nominating/governance committee chairs, as well new policies specific to special purpose acquisition companies (“SPACs”).
A. Board Diversity
- ISS – Racial/Ethnic Diversity. At S&P 1500 and Russell 3000 companies, beginning in 2022, ISS will generally recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the chair of the nominating/governance committee (or other directors, on a case-by-case basis) if the board “has no apparent racially or ethnically diverse members.” This policy was announced last year, with a one-year transition. There is an exception for companies where there was at least one racially or ethnically diverse director at the prior annual meeting and the board makes a firm commitment to appoint at least one such director within a year.
- ISS – Gender Diversity. ISS announced that, beginning in 2023, it will expand its policy on gender diversity, which since 2020 has applied to S&P 1500 and Russell 3000 companies, to all other companies. Under this policy, ISS generally recommends “against” or “withhold” votes for the chair of the nominating/governance committee (or other directors, on a case-by-case basis) where there are no women on the board. The policy includes an exception analogous to the one in the voting policy on racial/ethnic diversity.
- Glass Lewis – Gender Diversity. Beginning in 2022, Glass Lewis will generally recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the chair of the nominating/governance committee at Russell 3000 companies that do not have at least two gender diverse directors (as announced in connection with its 2021 policy updates), or the entire committee if there is no gender diversity on the board. In 2023, Glass Lewis will move to a percentage-based approach and issue negative voting recommendations for the nominating/governance committee chair if the board is not at least 30% gender diverse. Glass Lewis is using the term “gender diverse” in order to include individuals who identify as non-binary. Glass Lewis also updated its policies to reflect that it will recommend in accordance with mandatory board composition requirements in applicable state laws, whether they relate to gender or other forms of diversity. It will not issue negative voting recommendations for directors where applicable state laws do not mandate board composition requirements, are non-binding, or only impose reporting requirements.
- Glass Lewis – Diversity Disclosures. With respect to disclosure about director diversity and skills, for 2021, Glass Lewis had announced that it would begin tracking companies’ diversity disclosures in four categories: (1) the percentage of racial/ethnic diversity represented on the board; (2) whether the board’s definition of diversity explicitly includes gender and/or race/ethnicity; (3) whether the board has a policy requiring women and other diverse individuals to be part of the director candidate pool; and (4) board skills disclosure. For S&P 500 companies, beginning in 2022, Glass Lewis may recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the chair of the nominating/governance committee if a company fails to provide any disclosure in each of these four categories. Beginning in 2023, it will generally oppose election of the committee chair at S&P 500 companies that have not provided any aggregate or individual disclosure about the racial/ethnic demographics of the board.
B. Companies with Multi-Class Stock or Other Unequal Voting Rights
- ISS. ISS announced that, after a one-year transition period, in 2023, it will begin issuing adverse voting recommendations with respect to directors at all U.S. companies with unequal voting rights. Stock with “unequal voting rights” includes multi-class stock structures, as well as less common practices such as maintaining classes of stock that are not entitled to vote on the same ballot items or nominees, and loyalty shares (stock with time-phased voting rights). ISS’s policy since 2015 has been to recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for directors of newly-public companies that have multiple classes of stock with unequal voting rights or certain other “poor” governance provisions that are not subject to a reasonable sunset, including classified boards and supermajority voting requirements to amend the governing documents. Companies that were publicly traded before the 2015 policy change, however, were grandfathered and so were not subject to this policy. ISS had sought public comment about whether, in connection with the potential expansion of this policy to all U.S. companies, the policy should apply to all or only some nominees. The final policy does not specify, saying that the adverse voting recommendations may apply to “directors individually, committee members, or the entire board” (except new nominees, who will be evaluated case-by-case). For 2022, the current policy would continue to apply to newly-public companies. ISS tweaked the policy language to reflect that a “newly added reasonable sunset” would prevent negative voting recommendations in subsequent years. ISS considers a sunset period reasonable if it is no more than seven years.
- Glass Lewis. Beginning in 2022, Glass Lewis will recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the chair of the nominating/governance committee at companies that have multi-class share structures with unequal voting rights if they are not subject to a “reasonable” sunset (generally seven years or less).
C. Climate-Related Proposals and Board Accountability at “High-Impact” Companies
- ISS – Say on Climate. In 2021, both shareholders and management submitted Say on Climate proposals. For 2022, ISS is adopting voting policies that document the frameworks it has developed for analyzing these proposals, as supplemented by feedback from ISS’s 2021 policy development process. Under the new policies, ISS will recommend votes case-by-case on both management and shareholder proposals, taking into consideration a list of factors set forth in each policy. For management proposals asking shareholders to approve a company’s climate transition action plan, ISS will focus on “the completeness and rigor of the plan,” including the extent to which a company’s climate-related disclosures align with Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (“TCFD”) recommendations and other market standards, disclosure of the company’s operational and supply chain greenhouse gas (“GHG”) emissions (Scopes 1, 2 and 3), and whether the company has made a commitment to be “net zero” for operational and supply chain emissions (Scopes 1, 2 and 3) by 2050. For shareholder proposals requesting Say on Climate votes or other climate-related actions (such as a report outlining a company’s GHG emissions levels and reduction targets), ISS will recommend votes case-by-case taking into account information such as the completeness and rigor of a company’s climate-related disclosures and the company’s actual GHG emissions performance.
- ISS – Board Accountability on Climate at High-Impact Companies. ISS also adopted a new policy applicable to companies that are “significant GHG emitters” through their operations or value chain. For 2022, these are companies that Climate Action 100+ has identified as disproportionately responsible for GHG emissions. During 2022, ISS will generally recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the responsible committee chair in cases where ISS determines a company is not taking minimum steps needed to understand, assess and mitigate climate change risks to the company and the larger economy. Expectations about the minimum steps that are sufficient “will increase over time.” For 2022, minimum steps are detailed disclosure of climate-related risks (such as according to the TCFD framework”) and “appropriate GHG emissions reduction targets,” which ISS considers “any well-defined GHG reduction targets.” Targets for Scope 3 emissions are not required for 2022, but targets should cover at least a significant portion of the company’s direct emissions. For 2022, ISS plans to provide additional data in its voting analyses on all Climate Action 100+ companies to assist its clients in making voting decisions and in their engagement efforts. As a result of this new policy, companies on the Climate Action 100 + list should be aware that the policy requires both disclosure in accordance with a recognized framework, and quantitative GHG reduction targets, and that ISS plans to address its new climate policies in its updated FAQs, so there may be more specifics about this policy when the FAQs are released.
- Glass Lewis – Say on Climate. Glass Lewis also added a policy on Say on Climate proposals for 2022, but takes a different approach from ISS. Glass Lewis supports robust disclosure about companies’ climate change strategies. However, it has concerns with Say on Climate votes because it views the setting of long-term strategy (which it believes includes climate strategy) as the province of the board and believes shareholders may not have the information necessary to make fully informed voting decisions in this area. In evaluating management proposals asking shareholders to approve a company’s climate transition plans, Glass Lewis will evaluate the “governance of the Say on Climate vote” (the board’s role in setting strategy in light of the Say on Climate vote, how the board intends to interpret the results of the vote, and the company’s engagement efforts with shareholders) and the quality of the plan on a case-by-case basis. Glass Lewis expects companies to clearly identify their climate plans “in a distinct and easily understandable document,” which it believes should align with the TCFD framework. Glass Lewis will generally oppose shareholder proposals seeking to approve climate transition plans or to adopt a Say on Climate vote, but will take into account the request in the proposal and company-specific factors.
D. Additional ISS Updates
ISS adopted the following additional updates of note:
- Shareholder Proposals Seeking Racial Equity Audits. ISS adopted a formal policy reflecting its approach to shareholder proposals asking companies to oversee an independent racial equity or civil rights audit. These proposals, which were new for 2021, are expected to return again in 2022 given the continued public focus on issues related to race and equality. ISS will recommend votes case-by-case on these proposals, taking into account several factors listed in its new policy. These factors focus on a company’s processes or framework for addressing racial inequity and discrimination internally, its public statements and track record on racial justice, and whether the company’s actions are aligned with market norms on civil rights and racial/ethnic diversity.
- Capital Authorizations. ISS adopted what it characterizes as “minor” and “clarifying” changes to its voting policies on common and preferred stock authorizations. For both policies, ISS will apply the same dilution limits to underperforming companies, and will no longer treat companies with total shareholder returns in the bottom 10% of the U.S. market differently. ISS also clarified that problematic uses of capital that would lead to a vote “against” a proposed share increase include long-term poison pills that are not shareholder-approved, rather than just poison pills adopted in the last three years. ISS reorganized the policy on common stock authorizations to distinguish between general and specific uses of capital and to clarify the hierarchy of factors it considers in applying the policy.
- Three-Year Burn Rate Calculation for Equity Plans. Beginning in 2023, ISS will move to a “Value-Adjusted Burn Rate” in analyzing equity plans. ISS believes this will more accurately measure the value of recently granted equity awards, using a methodology that more precisely measures the value of option grants and calculations that are more readily understood by the market (actual stock price for full-value awards, and the Black-Scholes value for stock options). According to ISS, when the current methodology was adopted, resource limitations prevented it from doing the more extensive calculations needed for the Value-Adjusted Burn Rate.
- Updated FAQs on ISS Compensation Policies and COVID-19. ISS also issued an updated set of FAQs (available here) with guidance on how it intends to approach COVID-related pay decisions in conducting its pay-for-performance qualitative evaluation. According to the FAQs, many investors believe that boards are now positioned to return to annual incentive program structures as they existed prior to the pandemic. Accordingly, the FAQs reflect that ISS plans to return to its pre-pandemic approach on mid-year changes to metrics, targets and measurement periods, and on company responsiveness where a say-on-pay proposal gets less than 70% support.
E. Additional Glass Lewis Updates
Glass Lewis adopted several additional updates, as outlined below. Where relevant, for purposes of comparison, the discussion also addresses how ISS approaches the issue.
- Waiver of Retirement or Tenure Policies. Glass Lewis appears to be taking a stronger stance on boards that waive their retirement or tenure policies. Beginning in 2022, if the board waives a retirement age or term limit for two or more years in a row, Glass Lewis will generally recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the nominating/governance committee chair, unless a company provides a “compelling rationale” for the waiver. By way of comparison, ISS does not have an analogous policy.
- Adoption of Exclusive Forum Clauses Without Shareholder Approval. Under its existing policies, Glass Lewis generally recommends “against” or “withhold” votes for the nominating/governance committee chair at companies that adopted an exclusive forum clause during the past year without shareholder approval. With a growing number of companies adopting exclusive forum clauses that apply to claims under the Securities Act of 1933, Glass Lewis updated its policy to reflect that the policy applies to the adoption of state and/or federal exclusive forum clauses. The existing exception will remain in place for clauses that are “narrowly crafted to suit the particular circumstances” facing a company and/or include a reasonable sunset provision. By way of comparison, ISS does not have an analogous policy.
- Board Oversight of E&S Issues. For S&P 500 companies, starting in 2022, Glass Lewis will generally recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for the chair of the nominating/governance committee if a company does not provide “explicit disclosure” about the board’s role in overseeing environmental and social issues. This policy is taking effect after a transition year in which Glass Lewis noted concerns about disclosures it did not view as adequate. For 2022, Glass Lewis also will take the same approach for Russell 1000 companies that it took last year with S&P 500 companies, noting a concern where there is a lack of “clear disclosure” about which committees or directors are charged with oversight of E&S issues. Glass Lewis does not express a preference for a particular oversight structure, stating that boards should select the structure they believe is best for them.
- Independence Standard on Direct Payments for Directors. In evaluating director independence, Glass Lewis treats a director as not independent if the director is paid to perform services for the company (other than serving on the board) and the payments exceed $50,000 or no amount is disclosed. Glass Lewis clarified that this standard also captures payments to firms where a director is the principal or majority owner. By way of comparison, ISS’s independence standards likewise cover situations where a director is a partner or controlling shareholder in an entity that has business relationships with the company in excess of numerical thresholds used by ISS.
- Approach to Committee Chairs at Companies with Classified Boards. A number of Glass Lewis’ voting policies focus on committee chairs because it believes the chair has “primary responsibility” for a committee’s actions. Currently, if Glass Lewis policies would lead to a negative voting recommendation for a committee chair, but the chair is not up for election because the board is classified, Glass Lewis notes a concern with respect to the chair in its proxy voting analysis. Beginning in 2022, this policy will change and if Glass Lewis has identified “multiple concerns,” it will generally issue (on a case-by-case basis) negative voting recommendations for other committee members who are up for election.
- Written Consent Shareholder Proposals. Glass Lewis documented its approach to shareholder proposals asking companies to lower the ownership threshold required for shareholders to act by written consent. It will generally recommend in favor of these proposals if a company has no special meeting right or the special meeting ownership threshold is over 15%. Glass Lewis will continue its existing policy of opposing proposals to adopt written consent if a company has a special meeting threshold of 15% or lower and “reasonable” proxy access provisions. By way of comparison, ISS generally supports proposals to adopt written consent, taking into account a variety of factors including the ownership threshold. It will recommend votes case-by-case only if a company has an “unfettered” special meeting right with a 10% ownership threshold and other “good” governance practices, including majority voting in uncontested director elections and an annually elected board.
- SPAC Governance. Glass Lewis added voting guidelines that are specific to the SPAC context. When evaluating companies that have gone public through a de-SPAC transaction during the past year, it will review their governance practices to assess “whether shareholder rights are being severely restricted indefinitely” and whether restrictive provisions were submitted to an advisory vote at the meeting where shareholders voted on the de-SPAC transaction. If the board adopted certain practices prior to the transaction (such as a multi-class stock structure or a poison pill, classified board or other anti-takeover device), Glass Lewis will generally recommend “against” or “withhold” votes for all directors who served at the time the de-SPAC entity became publicly traded if the board: (a) did not also submit these provisions for a shareholder advisory vote at the meeting where the shareholders voted on the de-SPAC transaction; or (b) did not also commit to submitting the provisions for shareholder approval at the company’s first annual meeting after the de-SPAC transaction; or (c) did not also provide for a reasonable sunset (three to five years for a poison pill or classified board and seven years or less for multi-class stock structures). By way of comparison, as discussed above, for several years, ISS has had voting policies that address “poor” governance provisions at newly-public companies, including multiple classes of stock with unequal voting rights, classified boards and supermajority voting requirements to amend the governing documents. For 2022, ISS has clarified that the definition of “newly-public companies” includes SPACs.
- “Overboarding” and SPAC Board Seats. Under its “overboarding” policies, Glass Lewis generally recommends “against” or “withhold” votes for directors who are public company executives if they serve on a total of more than two public company boards. It applies a higher limit of five public company boards for other directors. The 2022 policy updates clarify that where a director’s only executive role is at a SPAC, the higher limit will apply. By way of comparison, ISS treats SPAC CEOs the same as other public company CEOs, on the grounds that a SPAC CEO “has a time-consuming job: to find a suitable target and consummate a transaction within a limited time period.” Accordingly, SPAC CEOs are subject to the same overboarding limit ISS applies to other public company CEOs (two public company boards besides their own).
_________________________
[1] ISS also issued an updated set of FAQs on COVID-related compensation decisions.
The following Gibson Dunn lawyers assisted in the preparation of this client update: Elizabeth Ising, Ronald Mueller, and Lori Zyskowski.
Gibson Dunn’s lawyers are available to assist with any questions you may have regarding these issues. To learn more about these issues, please contact the Gibson Dunn lawyer with whom you usually work in the Securities Regulation and Corporate Governance and Executive Compensation and Employee Benefits practice groups, or any of the following practice leaders and members:
Securities Regulation and Corporate Governance Group:
Elizabeth Ising – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8287, eising@gibsondunn.com)
Lori Zyskowski – New York, NY (+1 212-351-2309, lzyskowski@gibsondunn.com)
Ron Mueller – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-955-8671, rmueller@gibsondunn.com)
Thomas J. Kim – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3550, tkim@gibsondunn.com)
Michael Titera – Orange County, CA (+1 949-451-4365, mtitera@gibsondunn.com)
Aaron Briggs – San Francisco, CA (+1 415-393-8297, abriggs@gibsondunn.com)
Julia Lapitskaya – New York, NY (+1 212-351-2354, jlapitskaya@gibsondunn.com)
Cassandra Tillinghast – Washington, D.C. (+1 202-887-3524, ctillinghast@gibsondunn.com)
Executive Compensation and Employee Benefits Group:
Stephen W. Fackler – Palo Alto/New York (+1 650-849-5385/+1 212-351-2392, sfackler@gibsondunn.com)
Sean C. Feller – Los Angeles (+1 310-551-8746, sfeller@gibsondunn.com)
Krista Hanvey – Dallas (+ 214-698-3425, khanvey@gibsondunn.com)
© 2021 Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP
Attorney Advertising: The enclosed materials have been prepared for general informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice.